Ezra MacDonald
VistaFormer: Scalable Vision Transformers for Satellite Image Time Series Segmentation
Sep 13, 2024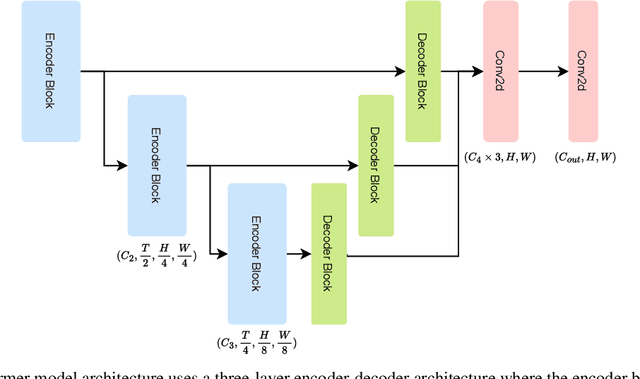
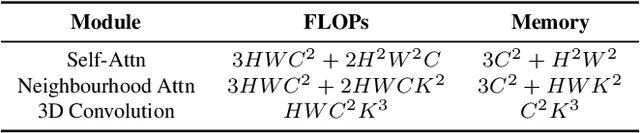
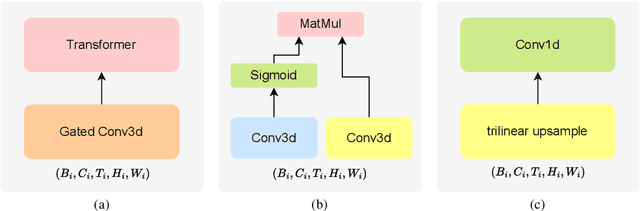
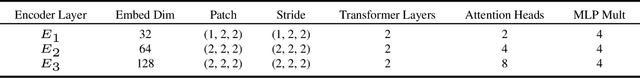
Abstract:We introduce VistaFormer, a lightweight Transformer-based model architecture for the semantic segmentation of remote-sensing images. This model uses a multi-scale Transformer-based encoder with a lightweight decoder that aggregates global and local attention captured in the encoder blocks. VistaFormer uses position-free self-attention layers which simplifies the model architecture and removes the need to interpolate temporal and spatial codes, which can reduce model performance when training and testing image resolutions differ. We investigate simple techniques for filtering noisy input signals like clouds and demonstrate that improved model scalability can be achieved by substituting Multi-Head Self-Attention (MHSA) with Neighbourhood Attention (NA). Experiments on the PASTIS and MTLCC crop-type segmentation benchmarks show that VistaFormer achieves better performance than comparable models and requires only 8% of the floating point operations using MHSA and 11% using NA while also using fewer trainable parameters. VistaFormer with MHSA improves on state-of-the-art mIoU scores by 0.1% on the PASTIS benchmark and 3% on the MTLCC benchmark while VistaFormer with NA improves on the MTLCC benchmark by 3.7%.
MineSegSAT: An automated system to evaluate mining disturbed area extents from Sentinel-2 imagery
Nov 03, 2023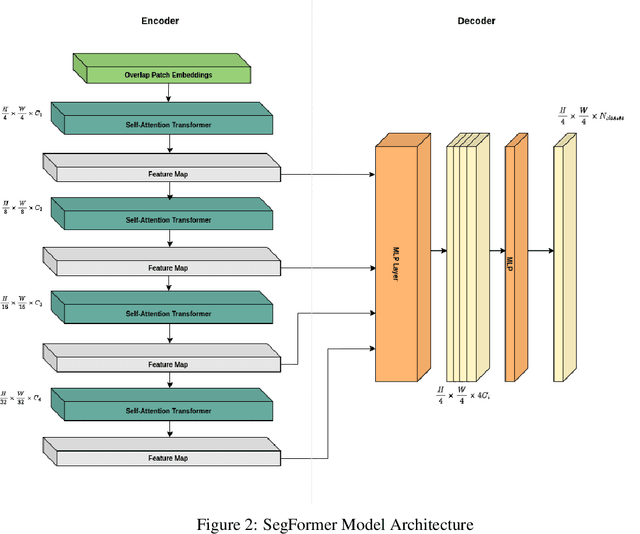
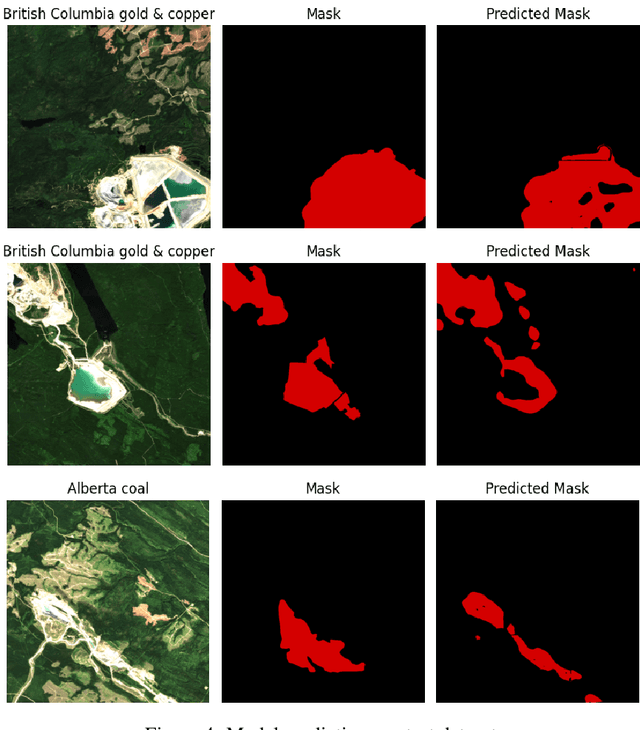
Abstract:Assessing the environmental impact of the mineral extraction industry plays a critical role in understanding and mitigating the ecological consequences of extractive activities. This paper presents MineSegSAT, a model that presents a novel approach to predicting environmentally impacted areas of mineral extraction sites using the SegFormer deep learning segmentation architecture trained on Sentinel-2 data. The data was collected from non-overlapping regions over Western Canada in 2021 containing areas of land that have been environmentally impacted by mining activities that were identified from high-resolution satellite imagery in 2021. The SegFormer architecture, a state-of-the-art semantic segmentation framework, is employed to leverage its advanced spatial understanding capabilities for accurate land cover classification. We investigate the efficacy of loss functions including Dice, Tversky, and Lovasz loss respectively. The trained model was utilized for inference over the test region in the ensuing year to identify potential areas of expansion or contraction over these same periods. The Sentinel-2 data is made available on Amazon Web Services through a collaboration with Earth Daily Analytics which provides corrected and tiled analytics-ready data on the AWS platform. The model and ongoing API to access the data on AWS allow the creation of an automated tool to monitor the extent of disturbed areas surrounding known mining sites to ensure compliance with their environmental impact goals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge