Evanildo Gomes Lacerda Jr
A unified framework for dataset shift diagnostics
May 17, 2022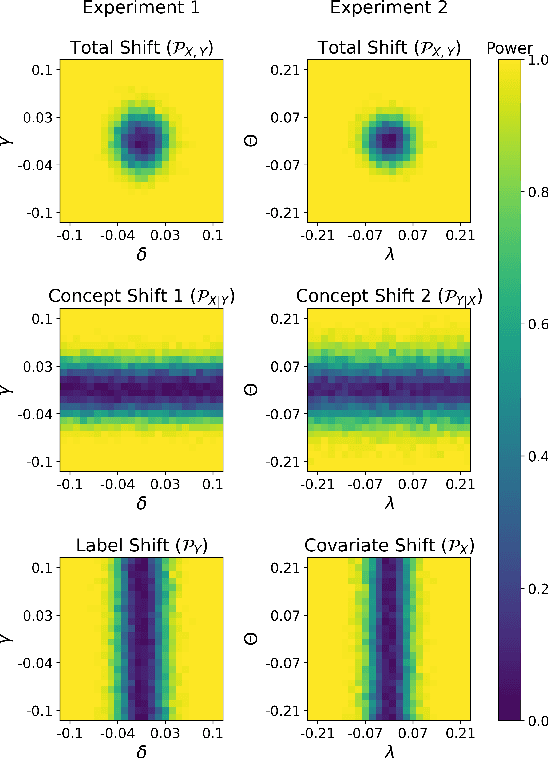
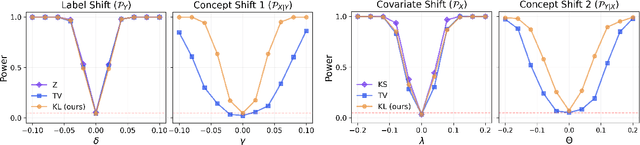
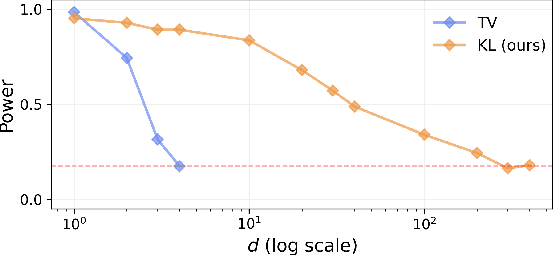
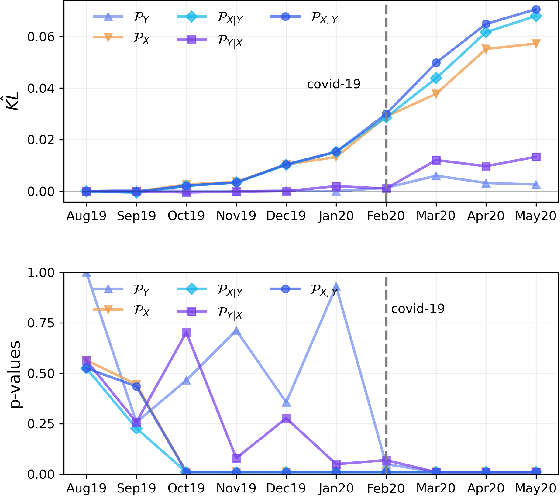
Abstract:Most machine learning (ML) methods assume that the data used in the training phase comes from the distribution of the target population. However, in practice one often faces dataset shift, which, if not properly taken into account, may decrease the predictive performance of the ML models. In general, if the practitioner knows which type of shift is taking place - e.g., covariate shift or label shift - they may apply transfer learning methods to obtain better predictions. Unfortunately, current methods for detecting shift are only designed to detect specific types of shift or cannot formally test their presence. We introduce a general framework that gives insights on how to improve prediction methods by detecting the presence of different types of shift and quantifying how strong they are. Our approach can be used for any data type (tabular/image/text) and both for classification and regression tasks. Moreover, it uses formal hypotheses tests that controls false alarms. We illustrate how our framework is useful in practice using both artificial and real datasets. Our package for dataset shift detection can be found in https://github.com/felipemaiapolo/detectshift.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge