Evangelos Boukas
Robust Uncertainty Estimation for Classification of Maritime Objects
Jul 03, 2023
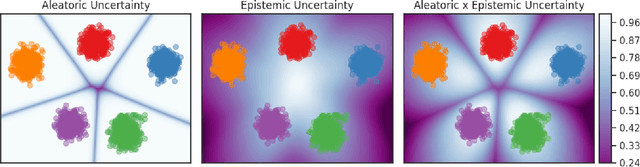
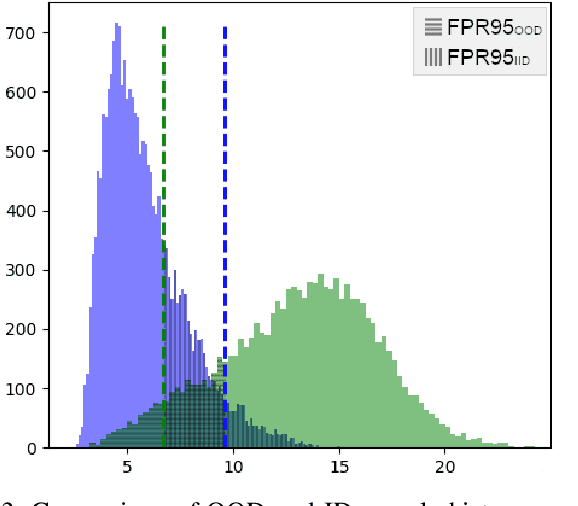
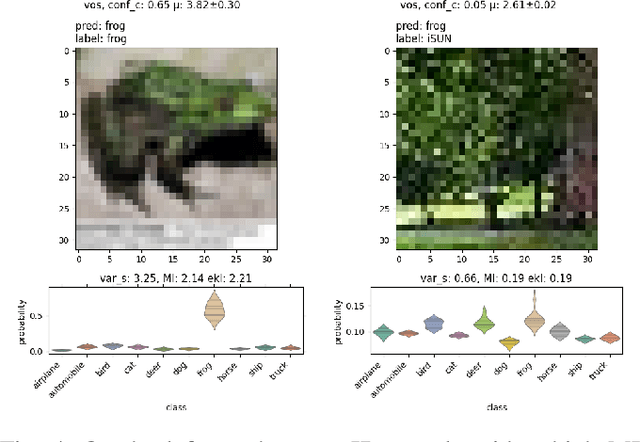
Abstract:We explore the use of uncertainty estimation in the maritime domain, showing the efficacy on toy datasets (CIFAR10) and proving it on an in-house dataset, SHIPS. We present a method joining the intra-class uncertainty achieved using Monte Carlo Dropout, with recent discoveries in the field of outlier detection, to gain more holistic uncertainty measures. We explore the relationship between the introduced uncertainty measures and examine how well they work on CIFAR10 and in a real-life setting. Our work improves the FPR95 by 8% compared to the current highest-performing work when the models are trained without out-of-distribution data. We increase the performance by 77% compared to a vanilla implementation of the Wide ResNet. We release the SHIPS dataset and show the effectiveness of our method by improving the FPR95 by 44.2% with respect to the baseline. Our approach is model agnostic, easy to implement, and often does not require model retraining.
Human-Machine Interface for Remote Training of Robot Tasks
Sep 25, 2018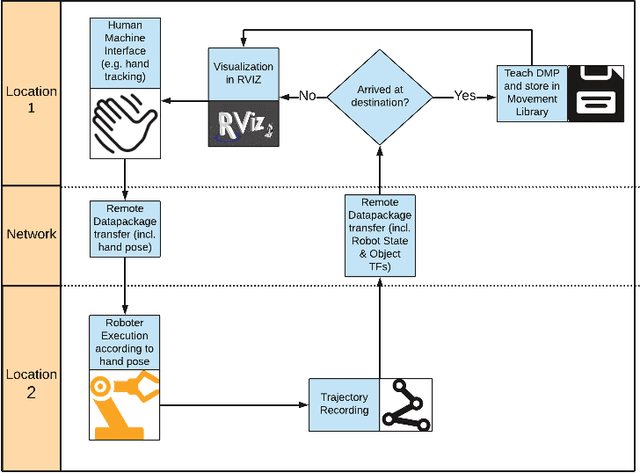
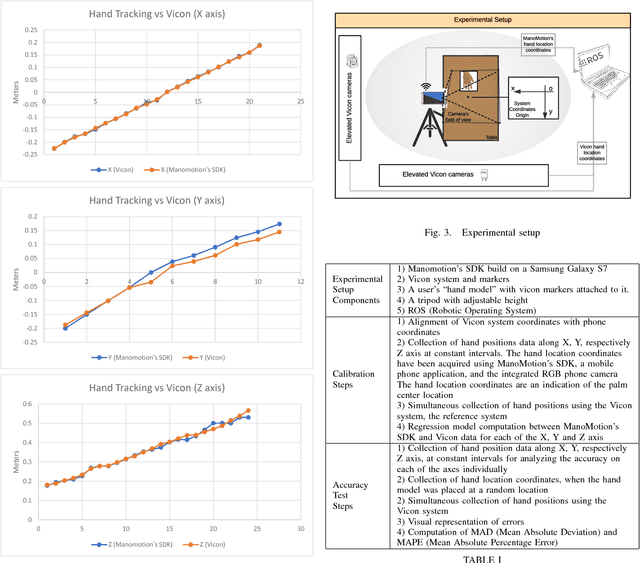
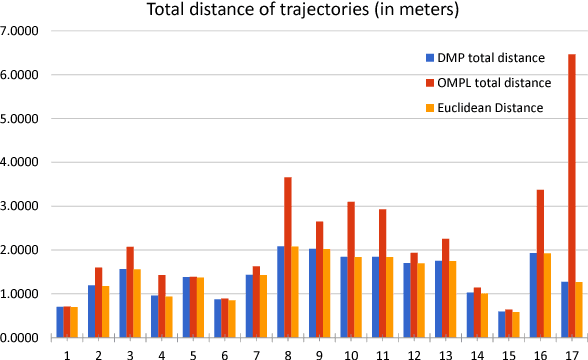
Abstract:Regardless of their industrial or research application, the streamlining of robot operations is limited by the proximity of experienced users to the actual hardware. Be it massive open online robotics courses, crowd-sourcing of robot task training, or remote research on massive robot farms for machine learning, the need to create an apt remote Human-Machine Interface is quite prevalent. The paper at hand proposes a novel solution to the programming/training of remote robots employing an intuitive and accurate user-interface which offers all the benefits of working with real robots without imposing delays and inefficiency. The system includes: a vision-based 3D hand detection and gesture recognition subsystem, a simulated digital twin of a robot as visual feedback, and the "remote" robot learning/executing trajectories using dynamic motion primitives. Our results indicate that the system is a promising solution to the problem of remote training of robot tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge