Eungyeom Ha
New Benchmarks for Asian Facial Recognition Tasks: Face Classification with Large Foundation Models
Oct 15, 2023Abstract:The face classification system is an important tool for recognizing personal identity properly. This paper introduces a new Large-Scale Korean Influencer Dataset named KoIn. Our presented dataset contains many real-world photos of Korean celebrities in various environments that might contain stage lighting, backup dancers, and background objects. These various images can be useful for training classification models classifying K-influencers. Most of the images in our proposed dataset have been collected from social network services (SNS) such as Instagram. Our dataset, KoIn, contains over 100,000 K-influencer photos from over 100 Korean celebrity classes. Moreover, our dataset provides additional hard case samples such as images including human faces with masks and hats. We note that the hard case samples are greatly useful in evaluating the robustness of the classification systems. We have extensively conducted several experiments utilizing various classification models to validate the effectiveness of our proposed dataset. Specifically, we demonstrate that recent state-of-the-art (SOTA) foundation architectures show decent classification performance when trained on our proposed dataset. In this paper, we also analyze the robustness performance against hard case samples of large-scale foundation models when we fine-tune the foundation models on the normal cases of the proposed dataset, KoIn. Our presented dataset and codes will be publicly available at https://github.com/dukong1/KoIn_Benchmark_Dataset.
HOD: A Benchmark Dataset for Harmful Object Detection
Oct 08, 2023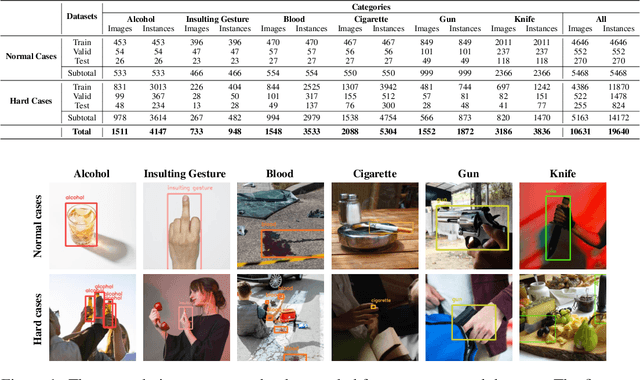
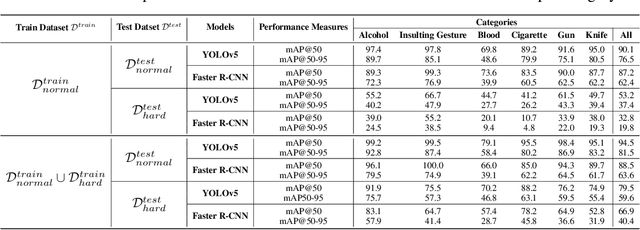
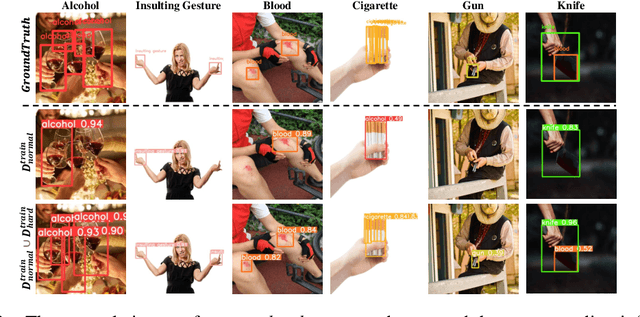
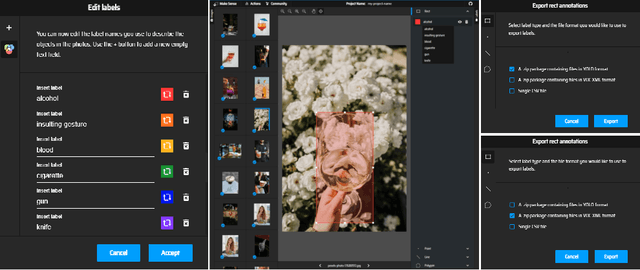
Abstract:Recent multi-media data such as images and videos have been rapidly spread out on various online services such as social network services (SNS). With the explosive growth of online media services, the number of image content that may harm users is also growing exponentially. Thus, most recent online platforms such as Facebook and Instagram have adopted content filtering systems to prevent the prevalence of harmful content and reduce the possible risk of adverse effects on users. Unfortunately, computer vision research on detecting harmful content has not yet attracted attention enough. Users of each platform still manually click the report button to recognize patterns of harmful content they dislike when exposed to harmful content. However, the problem with manual reporting is that users are already exposed to harmful content. To address these issues, our research goal in this work is to develop automatic harmful object detection systems for online services. We present a new benchmark dataset for harmful object detection. Unlike most related studies focusing on a small subset of object categories, our dataset addresses various categories. Specifically, our proposed dataset contains more than 10,000 images across 6 categories that might be harmful, consisting of not only normal cases but also hard cases that are difficult to detect. Moreover, we have conducted extensive experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed dataset. We have utilized the recently proposed state-of-the-art (SOTA) object detection architectures and demonstrated our proposed dataset can be greatly useful for the real-time harmful object detection task. The whole source codes and datasets are publicly accessible at https://github.com/poori-nuna/HOD-Benchmark-Dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge