Erlend Lundby
A novel corrective-source term approach to modeling unknown physics in aluminum extraction process
Sep 22, 2022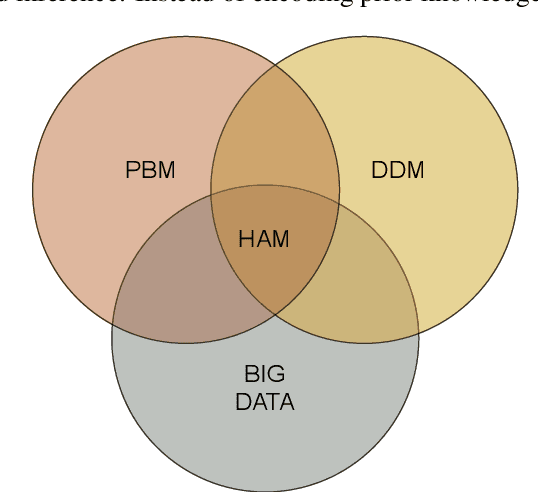
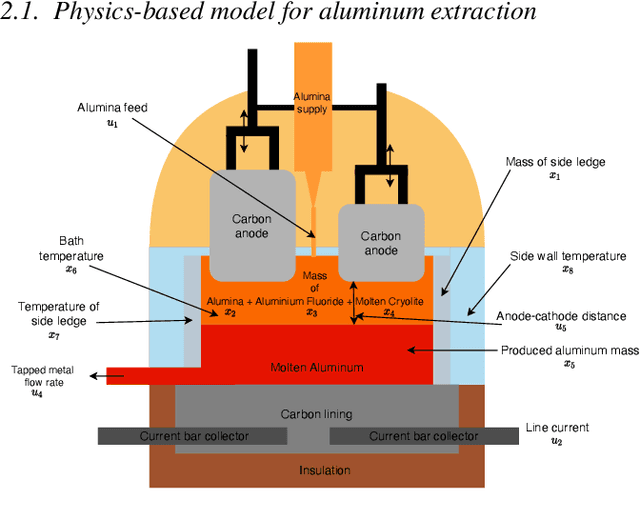

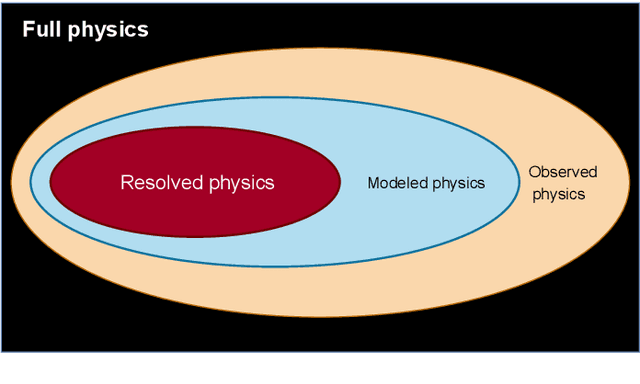
Abstract:With the ever-increasing availability of data, there has been an explosion of interest in applying modern machine learning methods to fields such as modeling and control. However, despite the flexibility and surprising accuracy of such black-box models, it remains difficult to trust them. Recent efforts to combine the two approaches aim to develop flexible models that nonetheless generalize well; a paradigm we call Hybrid Analysis and modeling (HAM). In this work we investigate the Corrective Source Term Approach (CoSTA), which uses a data-driven model to correct a misspecified physics-based model. This enables us to develop models that make accurate predictions even when the underlying physics of the problem is not well understood. We apply CoSTA to model the Hall-H\'eroult process in an aluminum electrolysis cell. We demonstrate that the method improves both accuracy and predictive stability, yielding an overall more trustworthy model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge