Erin Winter
WebRED: Effective Pretraining And Finetuning For Relation Extraction On The Web
Feb 18, 2021

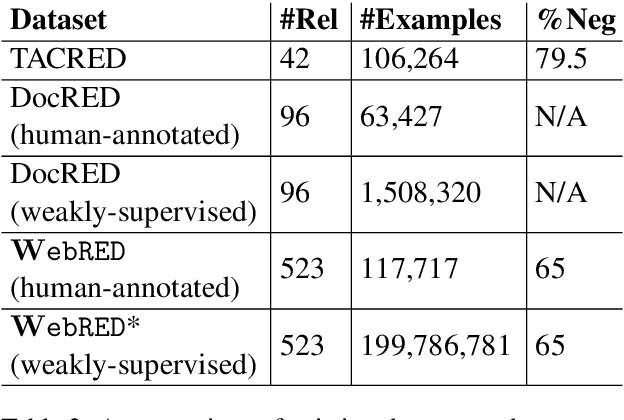
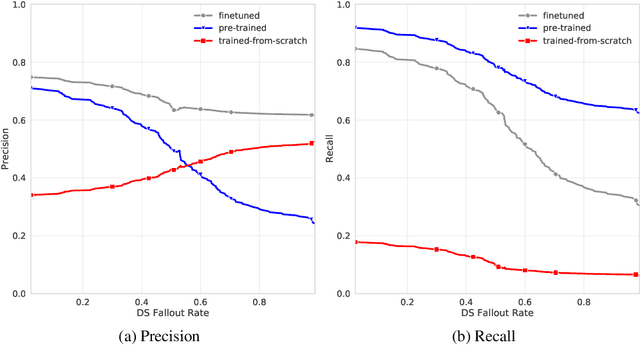
Abstract:Relation extraction is used to populate knowledge bases that are important to many applications. Prior datasets used to train relation extraction models either suffer from noisy labels due to distant supervision, are limited to certain domains or are too small to train high-capacity models. This constrains downstream applications of relation extraction. We therefore introduce: WebRED (Web Relation Extraction Dataset), a strongly-supervised human annotated dataset for extracting relationships from a variety of text found on the World Wide Web, consisting of ~110K examples. We also describe the methods we used to collect ~200M examples as pre-training data for this task. We show that combining pre-training on a large weakly supervised dataset with fine-tuning on a small strongly-supervised dataset leads to better relation extraction performance. We provide baselines for this new dataset and present a case for the importance of human annotation in improving the performance of relation extraction from text found on the web.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge