Elise F. Palzer
mvlearnR and Shiny App for multiview learning
Nov 25, 2023Abstract:The package mvlearnR and accompanying Shiny App is intended for integrating data from multiple sources or views or modalities (e.g. genomics, proteomics, clinical and demographic data). Most existing software packages for multiview learning are decentralized and offer limited capabilities, making it difficult for users to perform comprehensive integrative analysis. The new package wraps statistical and machine learning methods and graphical tools, providing a convenient and easy data integration workflow. For users with limited programming language, we provide a Shiny Application to facilitate data integration anywhere and on any device. The methods have potential to offer deeper insights into complex disease mechanisms. Availability and Implementation: mvlearnR is available from the following GitHub repository: https://github.com/lasandrall/mvlearnR. The web application is hosted on shinyapps.io and available at: https://multi-viewlearn.shinyapps.io/MultiView_Modeling/
sJIVE: Supervised Joint and Individual Variation Explained
Feb 26, 2021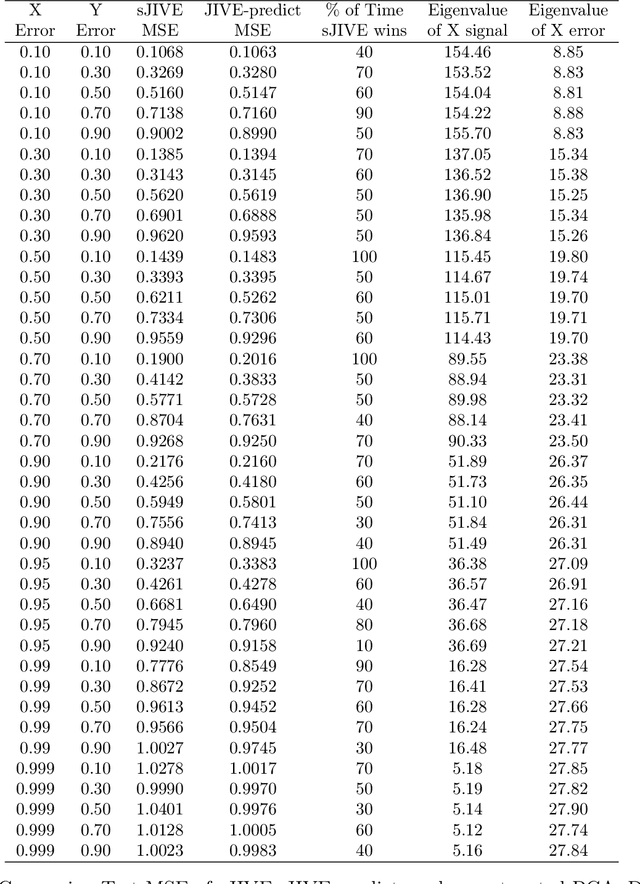


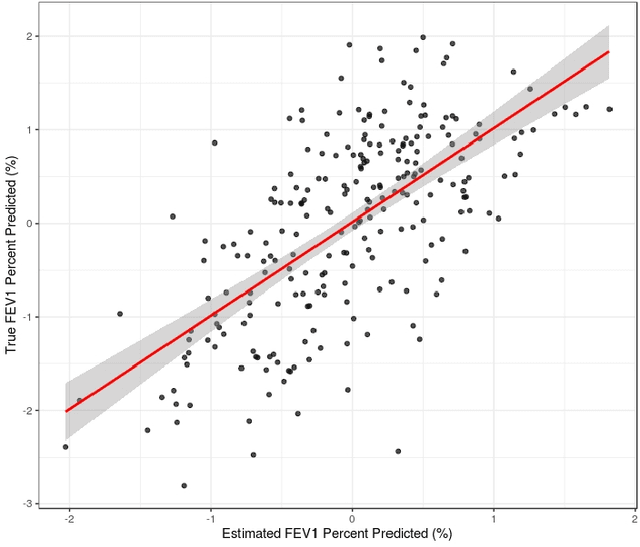
Abstract:Analyzing multi-source data, which are multiple views of data on the same subjects, has become increasingly common in molecular biomedical research. Recent methods have sought to uncover underlying structure and relationships within and/or between the data sources, and other methods have sought to build a predictive model for an outcome using all sources. However, existing methods that do both are presently limited because they either (1) only consider data structure shared by all datasets while ignoring structures unique to each source, or (2) they extract underlying structures first without consideration to the outcome. We propose a method called supervised joint and individual variation explained (sJIVE) that can simultaneously (1) identify shared (joint) and source-specific (individual) underlying structure and (2) build a linear prediction model for an outcome using these structures. These two components are weighted to compromise between explaining variation in the multi-source data and in the outcome. Simulations show sJIVE to outperform existing methods when large amounts of noise are present in the multi-source data. An application to data from the COPDGene study reveals gene expression and proteomic patterns that are predictive of lung function. Functions to perform sJIVE are included in the R.JIVE package, available online at http://github.com/lockEF/r.jive .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge