Egide Ndamuzi
Modelling and characterization of fine Particulate Matter dynamics in Bujumbura using low cost sensors
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:Air pollution is a result of multiple sources including both natural and anthropogenic activities. The rapid urbanization of the cities such as Bujumbura economic capital of Burundi, is one of these factors. The very first characterization of the spatio-temporal variability of PM2.5 in Bujumbura and the forecasting of PM2.5 concentration have been conducted in this paper using data collected during a year, from august 2022 to august 2023, by low cost sensors installed in Bujumbura city. For each commune, an hourly, daily and seasonal analysis were carried out and the results showed that the mass concentrations of PM2.5 in the three municipalities differ from one commune to another. The average hourly and annual PM2.5 concentrations exceed the World Health Organization standards. The range is between 28.3 and 35.0 microgram/m3 . In order to make prediction of PM2.5 concentration, an investigation of RNN with Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) has been undertaken.
Modelling spatio-temporal trends of air pollution in Africa
Aug 21, 2022
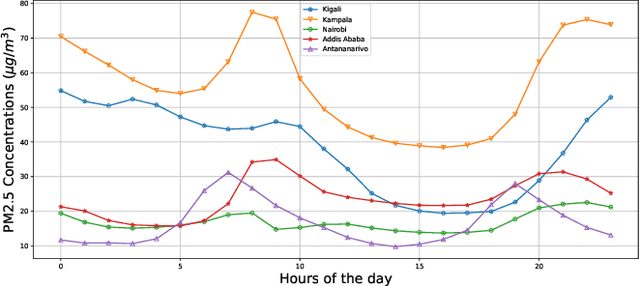
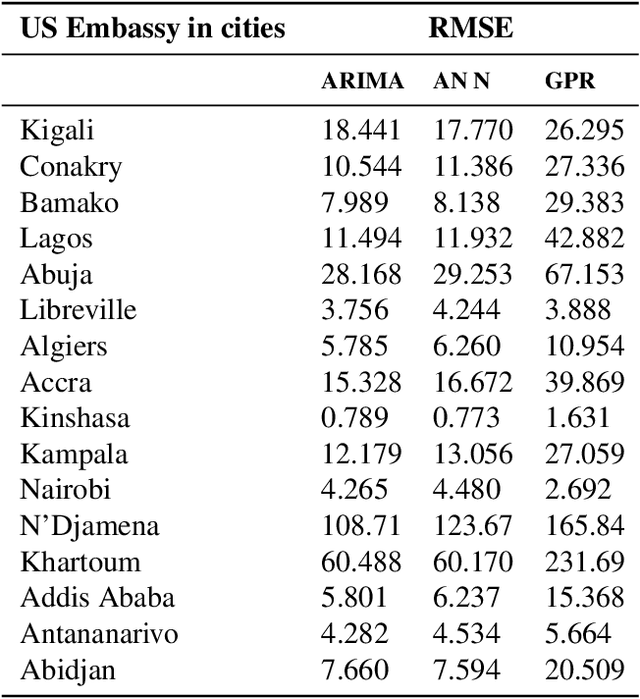
Abstract:Atmospheric pollution remains one of the major public health threat worldwide with an estimated 7 millions deaths annually. In Africa, rapid urbanization and poor transport infrastructure are worsening the problem. In this paper, we have analysed spatio-temporal variations of PM2.5 across different geographical regions in Africa. The West African region remains the most affected by the high levels of pollution with a daily average of 40.856 $\mu g/m^3$ in some cities like Lagos, Abuja and Bamako. In East Africa, Uganda is reporting the highest pollution level with a daily average concentration of 56.14 $\mu g/m^3$ and 38.65 $\mu g/m^3$ for Kigali. In countries located in the central region of Africa, the highest daily average concentration of PM2.5 of 90.075 $\mu g/m^3$ was recorded in N'Djamena. We compare three data driven models in predicting future trends of pollution levels. Neural network is outperforming Gaussian processes and ARIMA models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge