Edward J. Wang
Multi-agent Self-triage System with Medical Flowcharts
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Online health resources and large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as a first point of contact for medical decision-making, yet their reliability in healthcare remains limited by low accuracy, lack of transparency, and susceptibility to unverified information. We introduce a proof-of-concept conversational self-triage system that guides LLMs with 100 clinically validated flowcharts from the American Medical Association, providing a structured and auditable framework for patient decision support. The system leverages a multi-agent framework consisting of a retrieval agent, a decision agent, and a chat agent to identify the most relevant flowchart, interpret patient responses, and deliver personalized, patient-friendly recommendations, respectively. Performance was evaluated at scale using synthetic datasets of simulated conversations. The system achieved 95.29% top-3 accuracy in flowchart retrieval (N=2,000) and 99.10% accuracy in flowchart navigation across varied conversational styles and conditions (N=37,200). By combining the flexibility of free-text interaction with the rigor of standardized clinical protocols, this approach demonstrates the feasibility of transparent, accurate, and generalizable AI-assisted self-triage, with potential to support informed patient decision-making while improving healthcare resource utilization.
Development of a One Dollar Blood Pressure Monitor
Aug 11, 2023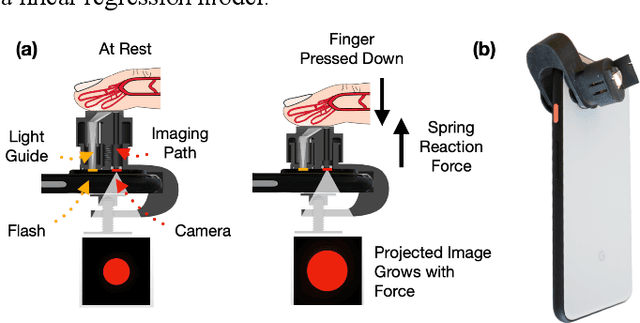
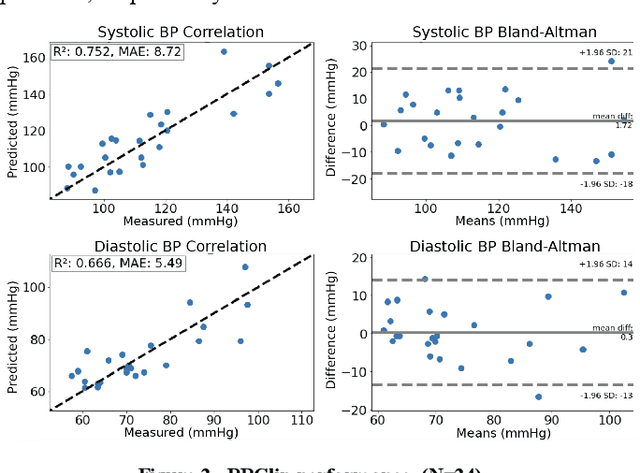
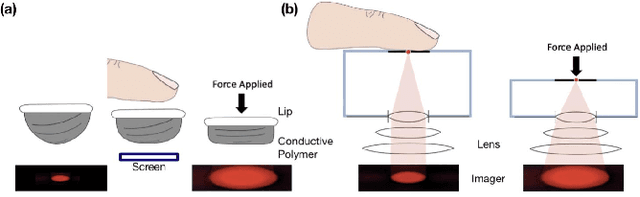
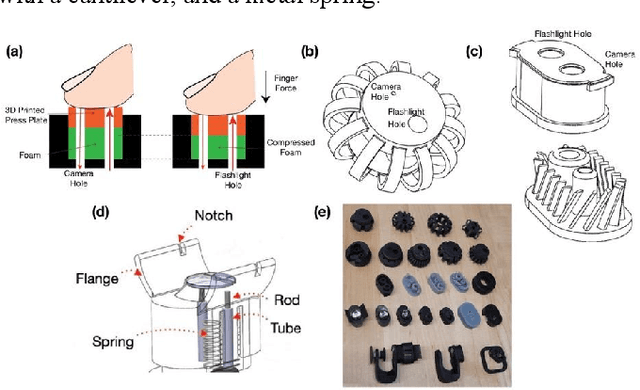
Abstract:BPClip is an ultra-low-cost cuffless blood pressure monitor. As a universal smartphone attachment, BPClip leverages the computational imaging power of smartphones to perform oscillometry based blood pressure measurements. This paper examines different design considerations in BPClip's development. The cost and accuracy of blood pressure measurements are the central design goals. Both of these requirements are achieved with the initial prototype that achieves a $0.80 USD material cost and a mean absolute error of 8.72 and 5.49 mmHg for systolic and diastolic blood pressure, respectively. Since a main motivator to develop BPClip is making blood pressure monitoring more accessible, usability is also central to the design. User studies were conducted throughout the design process to inform the most intuitive and accessible design features. In this paper, we demystify the design process to share effective design practices with future developers working towards expanding health monitoring access beyond traditional clinical settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge