E. Farrell Helbling
John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences
Hardware-in-the-Loop for Characterization of Embedded State Estimation for Flying Microrobots
Nov 10, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous flapping-wing micro-aerial vehicles (FWMAV) have a host of potential applications such as environmental monitoring, artificial pollination, and search and rescue operations. One of the challenges for achieving these applications is the implementation of an onboard sensor suite due to the small size and limited payload capacity of FWMAVs. The current solution for accurate state estimation is the use of offboard motion capture cameras, thus restricting vehicle operation to a special flight arena. In addition, the small payload capacity and highly non-linear oscillating dynamics of FWMAVs makes state estimation using onboard sensors challenging due to limited compute power and sensor noise. In this paper, we develop a novel hardware-in-the-loop (HWIL) testing pipeline that recreates flight trajectories of the Harvard RoboBee, a 100mg FWMAV. We apply this testing pipeline to evaluate a potential suite of sensors for robust altitude and attitude estimation by implementing and characterizing a Complimentary Extended Kalman Filter. The HWIL system includes a mechanical noise generator, such that both trajectories and oscillatinos can be emulated and evaluated. Our onboard sensing package works towards the future goal of enabling fully autonomous control for micro-aerial vehicles.
Scaling down an insect-size microrobot, HAMR-VI into HAMR-Jr
Mar 06, 2020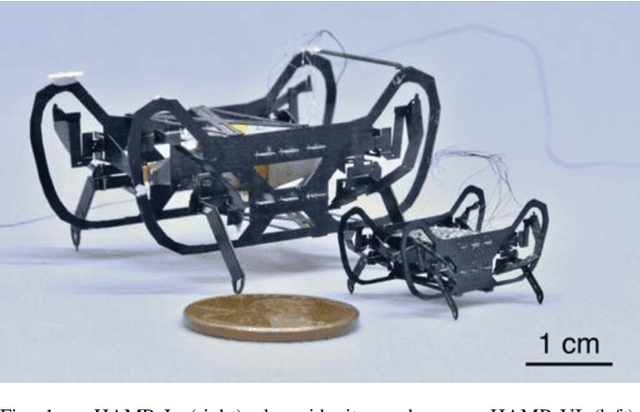
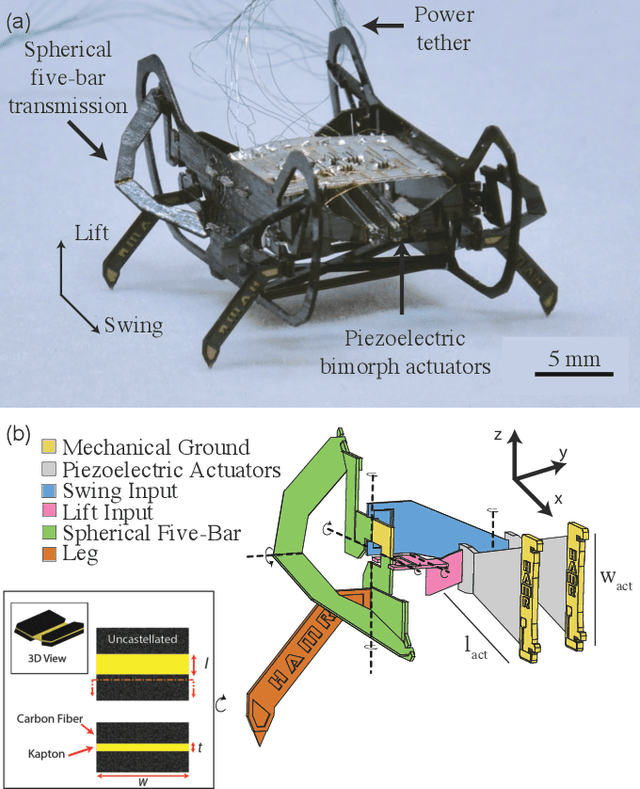
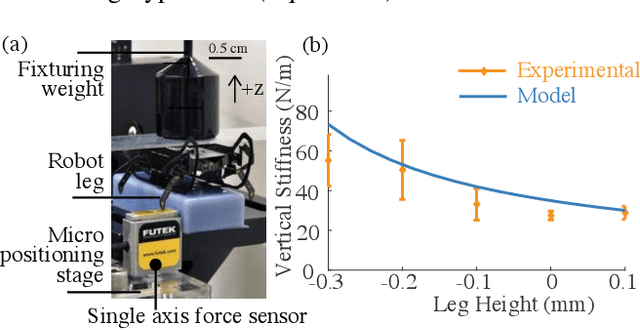
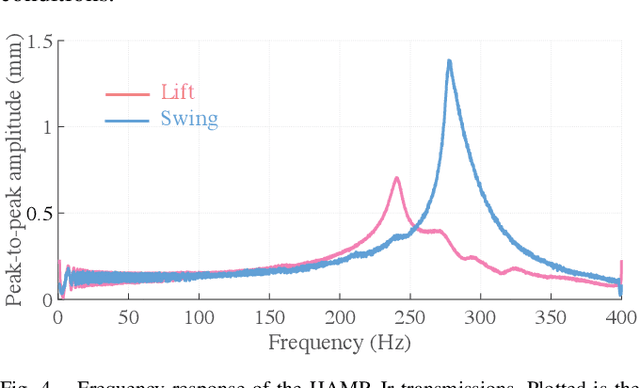
Abstract:Here we present HAMR-Jr, a \SI{22.5}{\milli\meter}, \SI{320}{\milli\gram} quadrupedal microrobot. With eight independently actuated degrees of freedom, HAMR-Jr is, to our knowledge, the most mechanically dexterous legged robot at its scale and is capable of high-speed locomotion (\SI{13.91}{bodylengths~\second^{-1}}) at a variety of stride frequencies (\SI{1}{}-\SI{200}{\hertz}) using multiple gaits. We achieved this using a design and fabrication process that is flexible, allowing scaling with minimum changes to our workflow. We further characterized HAMR-Jr's open-loop locomotion and compared it with the larger scale HAMR-VI microrobot to demonstrate the effectiveness of scaling laws in predicting running performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge