E. Adrian Henle
Non-equilibrium molecular geometries in graph neural networks
Mar 07, 2022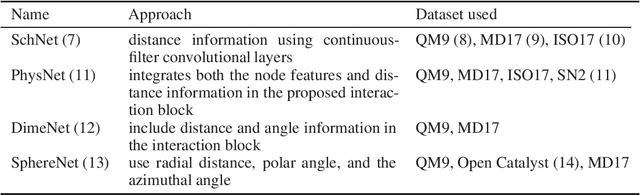
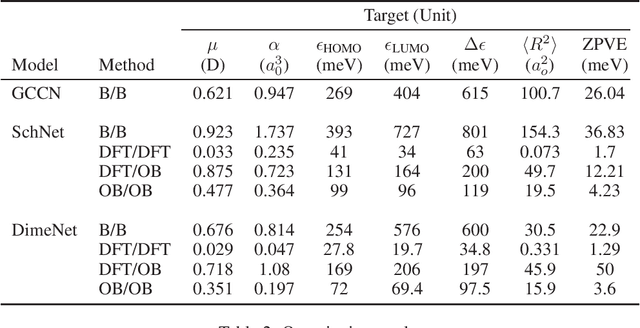
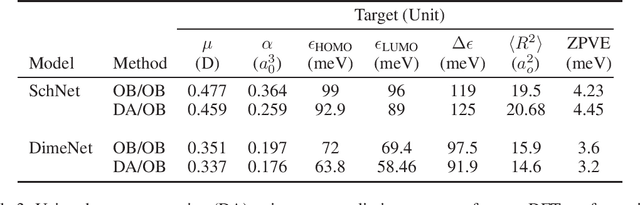
Abstract:Graph neural networks have become a powerful framework for learning complex structure-property relationships and fast screening of chemical compounds. Recently proposed methods have demonstrated that using 3D geometry information of the molecule along with the bonding structure can lead to more accurate prediction on a wide range of properties. A common practice is to use 3D geometries computed through density functional theory (DFT) for both training and testing of models. However, the computational time needed for DFT calculations can be prohibitively large. Moreover, many of the properties that we aim to predict can often be obtained with little or no overhead on top of the DFT calculations used to produce the 3D geometry information, voiding the need for a predictive model. To be practically useful for high-throughput chemical screening and drug discovery, it is desirable to work with 3D geometries obtained using less-accurate but much more efficient non-DFT methods. In this work we investigate the impact of using non-DFT conformations in the training and the testing of existing models and propose a data augmentation method for improving the prediction accuracy of classical forcefield-derived geometries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge