Dongyun Kang
Dynamic Policy Learning for Legged Robot with Simplified Model Pretraining and Model Homotopy Transfer
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Generating dynamic motions for legged robots remains a challenging problem. While reinforcement learning has achieved notable success in various legged locomotion tasks, producing highly dynamic behaviors often requires extensive reward tuning or high-quality demonstrations. Leveraging reduced-order models can help mitigate these challenges. However, the model discrepancy poses a significant challenge when transferring policies to full-body dynamics environments. In this work, we introduce a continuation-based learning framework that combines simplified model pretraining and model homotopy transfer to efficiently generate and refine complex dynamic behaviors. First, we pretrain the policy using a single rigid body model to capture core motion patterns in a simplified environment. Next, we employ a continuation strategy to progressively transfer the policy to the full-body environment, minimizing performance loss. To define the continuation path, we introduce a model homotopy from the single rigid body model to the full-body model by gradually redistributing mass and inertia between the trunk and legs. The proposed method not only achieves faster convergence but also demonstrates superior stability during the transfer process compared to baseline methods. Our framework is validated on a range of dynamic tasks, including flips and wall-assisted maneuvers, and is successfully deployed on a real quadrupedal robot.
Learning Impact-Rich Rotational Maneuvers via Centroidal Velocity Rewards and Sim-to-Real Techniques: A One-Leg Hopper Flip Case Study
May 18, 2025Abstract:Dynamic rotational maneuvers, such as front flips, inherently involve large angular momentum generation and intense impact forces, presenting major challenges for reinforcement learning and sim-to-real transfer. In this work, we propose a general framework for learning and deploying impact-rich, rotation-intensive behaviors through centroidal velocity-based rewards and actuator-aware sim-to-real techniques. We identify that conventional link-level reward formulations fail to induce true whole-body rotation and introduce a centroidal angular velocity reward that accurately captures system-wide rotational dynamics. To bridge the sim-to-real gap under extreme conditions, we model motor operating regions (MOR) and apply transmission load regularization to ensure realistic torque commands and mechanical robustness. Using the one-leg hopper front flip as a representative case study, we demonstrate the first successful hardware realization of a full front flip. Our results highlight that incorporating centroidal dynamics and actuator constraints is critical for reliably executing highly dynamic motions.
Design of a 3-DOF Hopping Robot with an Optimized Gearbox: An Intermediate Platform Toward Bipedal Robots
May 18, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a 3-DOF hopping robot with a human-like lower-limb joint configuration and a flat foot, capable of performing dynamic and repetitive jumping motions. To achieve both high torque output and a large hollow shaft diameter for efficient cable routing, a compact 3K compound planetary gearbox was designed using mixed-integer nonlinear programming for gear tooth optimization. To meet performance requirements within the constrained joint geometry, all major components-including the actuator, motor driver, and communication interface-were custom-designed. The robot weighs 12.45 kg, including a dummy mass, and measures 840 mm in length when the knee joint is fully extended. A reinforcement learning-based controller was employed, and robot's performance was validated through hardware experiments, demonstrating stable and repetitive hopping motions in response to user inputs. These experimental results indicate that the platform serves as a solid foundation for future bipedal robot development.
Online Friction Coefficient Identification for Legged Robots on Slippery Terrain Using Smoothed Contact Gradients
Feb 24, 2025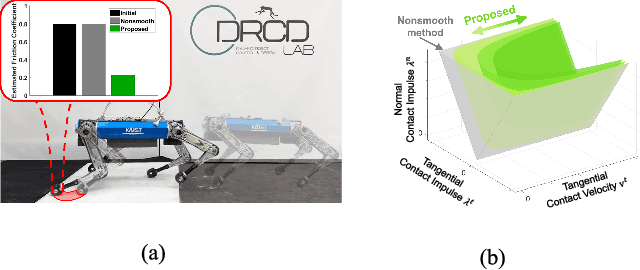
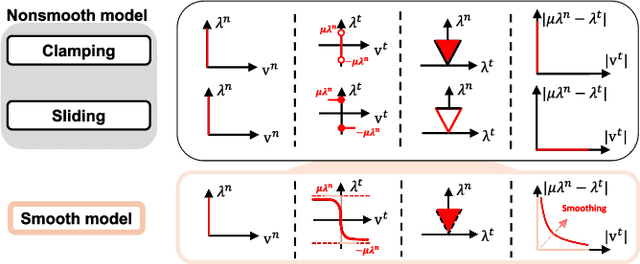
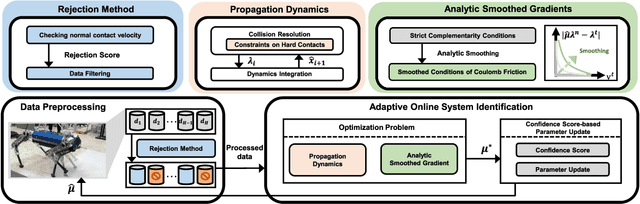
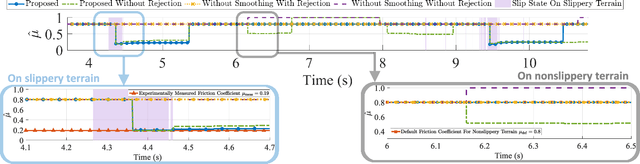
Abstract:This paper proposes an online friction coefficient identification framework for legged robots on slippery terrain. The approach formulates the optimization problem to minimize the sum of residuals between actual and predicted states parameterized by the friction coefficient in rigid body contact dynamics. Notably, the proposed framework leverages the analytic smoothed gradient of contact impulses, obtained by smoothing the complementarity condition of Coulomb friction, to solve the issue of non-informative gradients induced from the nonsmooth contact dynamics. Moreover, we introduce the rejection method to filter out data with high normal contact velocity following contact initiations during friction coefficient identification for legged robots. To validate the proposed framework, we conduct the experiments using a quadrupedal robot platform, KAIST HOUND, on slippery and nonslippery terrain. We observe that our framework achieves fast and consistent friction coefficient identification within various initial conditions.
* 8 pages, IEEE RA-L (2025) accepted
Contact-Implicit MPC: Controlling Diverse Quadruped Motions Without Pre-Planned Contact Modes or Trajectories
Dec 14, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a contact-implicit model predictive control (MPC) framework for the real-time discovery of multi-contact motions, without predefined contact mode sequences or foothold positions. This approach utilizes the contact-implicit differential dynamic programming (DDP) framework, merging the hard contact model with a linear complementarity constraint. We propose the analytical gradient of the contact impulse based on relaxed complementarity constraints to further the exploration of a variety of contact modes. By leveraging a hard contact model-based simulation and computation of search direction through a smooth gradient, our methodology identifies dynamically feasible state trajectories, control inputs, and contact forces while simultaneously unveiling new contact mode sequences. However, the broadened scope of contact modes does not always ensure real-world applicability. Recognizing this, we implemented differentiable cost terms to guide foot trajectories and make gait patterns. Furthermore, to address the challenge of unstable initial roll-outs in an MPC setting, we employ the multiple shooting variant of DDP. The efficacy of the proposed framework is validated through simulations and real-world demonstrations using a 45 kg HOUND quadruped robot, performing various tasks in simulation and showcasing actual experiments involving a forward trot and a front-leg rearing motion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge