Donald Estep
An efficient, accurate, and interpretable machine learning method for computing probability of failure
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:We introduce a novel machine learning method called the Penalized Profile Support Vector Machine based on the Gabriel edited set for the computation of the probability of failure for a complex system as determined by a threshold condition on a computer model of system behavior. The method is designed to minimize the number of evaluations of the computer model while preserving the geometry of the decision boundary that determines the probability. It employs an adaptive sampling strategy designed to strategically allocate points near the boundary determining failure and builds a locally linear surrogate boundary that remains consistent with its geometry by strategic clustering of training points. We prove two convergence results and we compare the performance of the method against a number of state of the art classification methods on four test problems. We also apply the method to determine the probability of survival using the Lotka--Volterra model for competing species.
Learning Quantities of Interest from Dynamical Systems for Observation-Consistent Inversion
Sep 15, 2020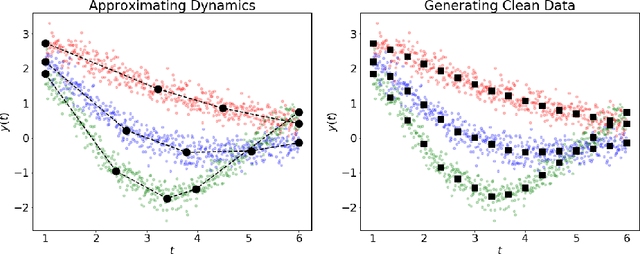

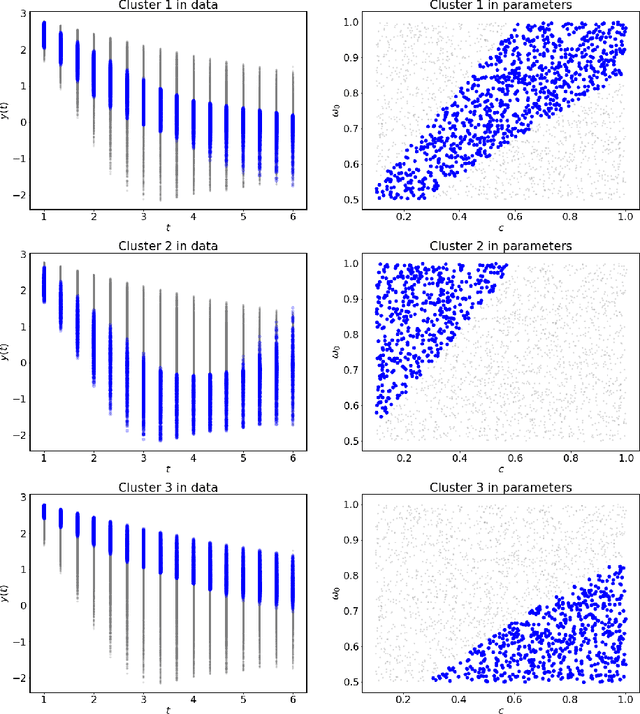

Abstract:Dynamical systems arise in a wide variety of mathematical models from science and engineering. A common challenge is to quantify uncertainties on model inputs (parameters) that correspond to a quantitative characterization of uncertainties on observable Quantities of Interest (QoI). To this end, we consider a stochastic inverse problem (SIP) with a solution described by a pullback probability measure. We call this an observation-consistent solution, as its subsequent push-forward through the QoI map matches the observed probability distribution on model outputs. A distinction is made between QoI useful for solving the SIP and arbitrary model output data. In dynamical systems, model output data are often given as a series of state variable responses recorded over a particular time window. Consequently, the dimension of output data can easily exceed $\mathcal{O}(1E4)$ or more due to the frequency of observations, and the correct choice or construction of a QoI from this data is not self-evident. We present a new framework, Learning Uncertain Quantities (LUQ), that facilitates the tractable solution of SIPs for dynamical systems. Given ensembles of predicted (simulated) time series and (noisy) observed data, LUQ provides routines for filtering data, unsupervised learning of the underlying dynamics, classifying observations, and feature extraction to learn the QoI map. Subsequently, time series data are transformed into samples of the underlying predicted and observed distributions associated with the QoI so that solutions to the SIP are computable. Following the introduction and demonstration of LUQ, numerical results from several SIPs are presented for a variety of dynamical systems arising in the life and physical sciences. For scientific reproducibility, we provide links to our Python implementation of LUQ and to all data and scripts required to reproduce the results in this manuscript.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge