Dominik Alscher
Radar-based Respiratory Rate Monitoring in Standing Position
Mar 09, 2022
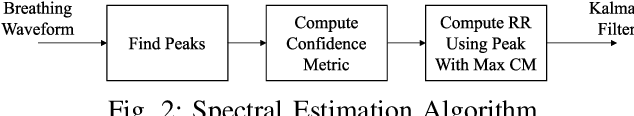
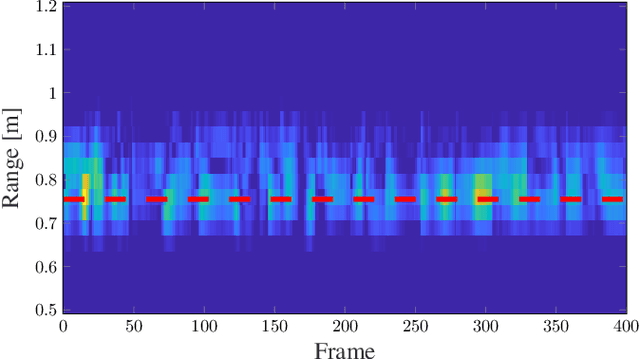
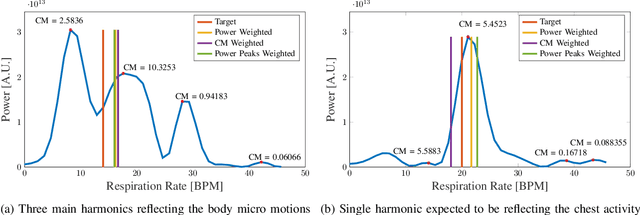
Abstract:Estimating human vital signs in a contactless non-invasive method using radar provides a convenient method in the medical field to conduct several health checkups easily and quickly. In addition to monitoring while sitting and sleeping, the standing position has aroused interest for both the industrial and medical fields. However, it is more challenging due to the micro motions induced by the body for balancing that may cause false respiratory rate estimation. In this work, we focus on the measurement of the respiratory rate of a standing person accurately with the capability of heavy breath detection and estimation. Multiple estimation approaches are presented and compared, including spectral estimation, deep-learning-based approaches, and adaptive peak selection with Kalman filtering. The latest technique is showing the best performance with an absolute error rate of 1.5 bpm, when compared to a Vernier Go Direct\textsuperscript{\textregistered} respiration belt.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge