Dirk Heimann
Quantum Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robot Navigation Tasks
Feb 24, 2022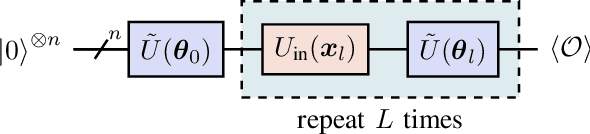
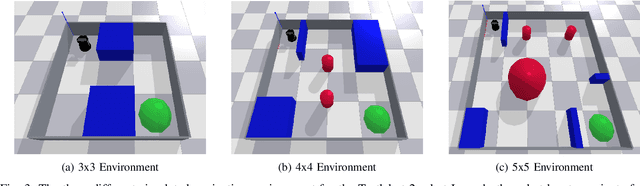
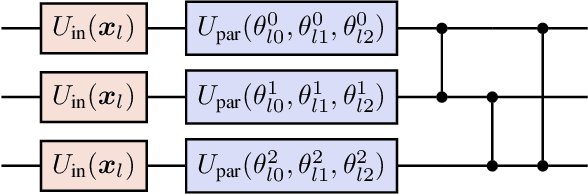
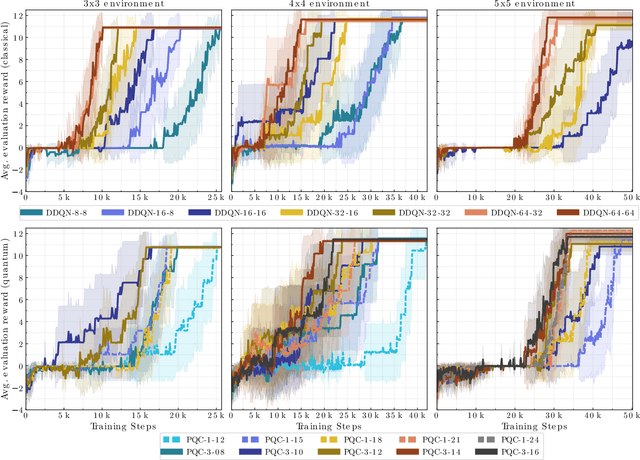
Abstract:In this work, we utilize Quantum Deep Reinforcement Learning as method to learn navigation tasks for a simple, wheeled robot in three simulated environments of increasing complexity. We show similar performance of a parameterized quantum circuit trained with well established deep reinforcement learning techniques in a hybrid quantum-classical setup compared to a classical baseline. To our knowledge this is the first demonstration of quantum machine learning (QML) for robotic behaviors. Thus, we establish robotics as a viable field of study for QML algorithms and henceforth quantum computing and quantum machine learning as potential techniques for future advancements in autonomous robotics. Beyond that, we discuss current limitations of the presented approach as well as future research directions in the field of quantum machine learning for autonomous robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge