Dirk Abel
onlineFGO: Online Continuous-Time Factor Graph Optimization with Time-Centric Multi-Sensor Fusion for Robust Localization in Large-Scale Environments
Nov 10, 2022Abstract:Accurate and consistent vehicle localization in urban areas is challenging due to the large-scale and complicated environments. In this paper, we propose onlineFGO, a novel time-centric graph-optimization-based localization method that fuses multiple sensor measurements with the continuous-time trajectory representation for vehicle localization tasks. We generalize the graph construction independent of any spatial sensor measurements by creating the states deterministically on time. As the trajectory representation in continuous-time enables querying states at arbitrary times, incoming sensor measurements can be factorized on the graph without requiring state alignment. We integrate different GNSS observations: pseudorange, deltarange, and time-differenced carrier phase (TDCP) to ensure global reference and fuse the relative motion from a LiDAR-odometry to improve the localization consistency while GNSS observations are not available. Experiments on general performance, effects of different factors, and hyper-parameter settings are conducted in a real-world measurement campaign in Aachen city that contains different urban scenarios. Our results show an average 2D error of 0.99m and consistent state estimation in urban scenarios.
Depth Camera Based Particle Filter for Robotic Osteotomy Navigation
Oct 24, 2019


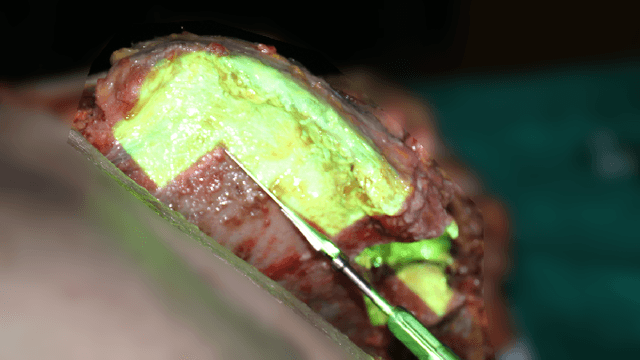
Abstract:Active surgical robots lack acceptance in clinical practice, because they do not offer the flexibility and usability required for a versatile usage: the systems require a large installation space or a complicated registration step, where the preoperative plan is aligned to the patient and transformed to the base frame of the robot. In this paper, a navigation system for robotic osteotomies is designed, which uses the raw depth images from a camera mounted on the flange of a lightweight robot arm. Consequently, the system does not require any rigid attachment of the robot or fiducials to the bone and the time-consuming registration step is eliminated. Instead, only a coarse initialization is required which improves the usability in surgery. The full six dimensional pose of the iliac crest bone is estimated with a particle filter at a maximum rate of 90 Hz. The presented method is robust against changing lighting conditions, blood or tissue on the bone surface and partial occlusions caused by the surgeons. Proof of the usability in a clinical environment is successfully provided in a corpse study, where surgeons used an augmented reality osteotomy template, which was aligned to bone via the particle filters pose estimates for the resection of transplants from the iliac crest.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge