Diganta Mukherjee
Quantitative Rule-Based Strategy modeling in Classic Indian Rummy: A Metric Optimization Approach
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:The 13-card variant of Classic Indian Rummy is a sequential game of incomplete information that requires probabilistic reasoning and combinatorial decision-making. This paper proposes a rule-based framework for strategic play, driven by a new hand-evaluation metric termed MinDist. The metric modifies the MinScore metric by quantifying the edit distance between a hand and the nearest valid configuration, thereby capturing structural proximity to completion. We design a computationally efficient algorithm derived from the MinScore algorithm, leveraging dynamic pruning and pattern caching to exactly calculate this metric during play. Opponent hand-modeling is also incorporated within a two-player zero-sum simulation framework, and the resulting strategies are evaluated using statistical hypothesis testing. Empirical results show significant improvement in win rates for MinDist-based agents over traditional heuristics, providing a formal and interpretable step toward algorithmic Rummy strategy design.
Analyzing Skill Element in Online Fantasy Cricket
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Online fantasy cricket has emerged as large-scale competitive systems in which participants construct virtual teams and compete based on real-world player performances. This massive growth has been accompanied by important questions about whether outcomes are primarily driven by skill or chance. We develop a statistical framework to assess the role of skill in determining success on these platforms. We construct and analyze a range of deterministic and stochastic team selection strategies, based on recent form, historical statistics, statistical optimization, and multi-criteria decision making. Strategy performance is evaluated based on points, ranks, and payoff under two contest structures Mega and 4x or Nothing. An extensive comparison between different strategies is made to find an optimal set of strategies. To capture adaptive behavior, we further introduce a dynamic tournament model in which agent populations evolve through a softmax reweighting mechanism proportional to positive payoff realizations. We demonstrate our work by running extensive numerical experiments on the IPL 2024 dataset. The results provide quantitative evidence in favor of the skill element present in online fantasy cricket platforms.
Significance of Anatomical Constraints in Virtual Try-On
Jan 04, 2024



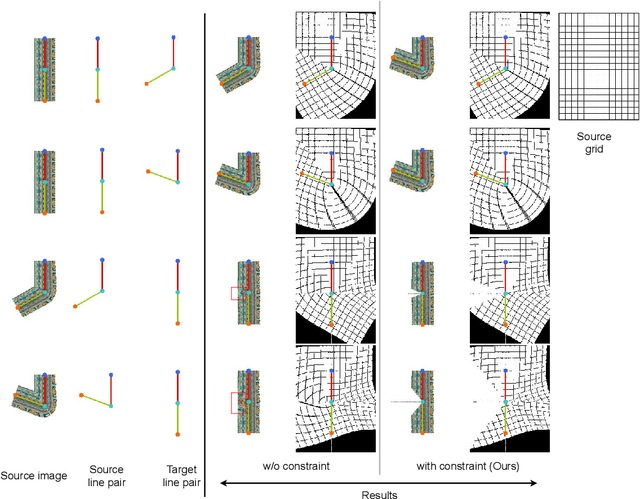
Abstract:The system of Virtual Try-ON (VTON) allows a user to try a product virtually. In general, a VTON system takes a clothing source and a person's image to predict the try-on output of the person in the given clothing. Although existing methods perform well for simple poses, in case of bent or crossed arms posture or when there is a significant difference between the alignment of the source clothing and the pose of the target person, these methods fail by generating inaccurate clothing deformations. In the VTON methods that employ Thin Plate Spline (TPS) based clothing transformations, this mainly occurs for two reasons - (1)~the second-order smoothness constraint of TPS that restricts the bending of the object plane. (2)~Overlaps among different clothing parts (e.g., sleeves and torso) can not be modeled by a single TPS transformation, as it assumes the clothing as a single planar object; therefore, disregards the independence of movement of different clothing parts. To this end, we make two major contributions. Concerning the bending limitations of TPS, we propose a human AnaTomy-Aware Geometric (ATAG) transformation. Regarding the overlap issue, we propose a part-based warping approach that divides the clothing into independently warpable parts to warp them separately and later combine them. Extensive analysis shows the efficacy of this approach.
Significance of Skeleton-based Features in Virtual Try-On
Sep 01, 2022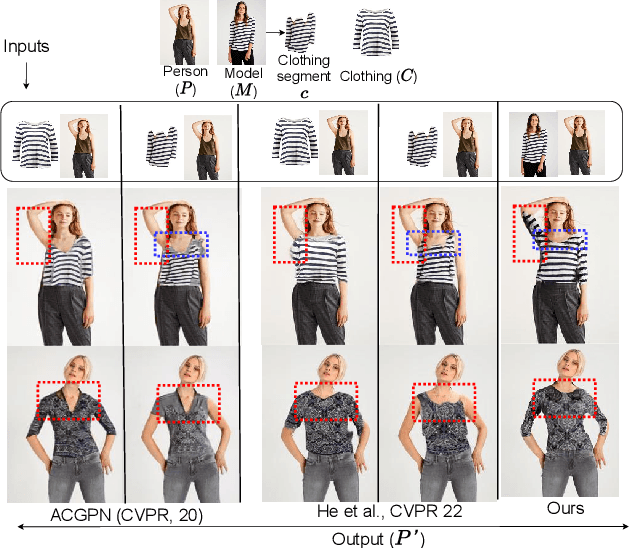
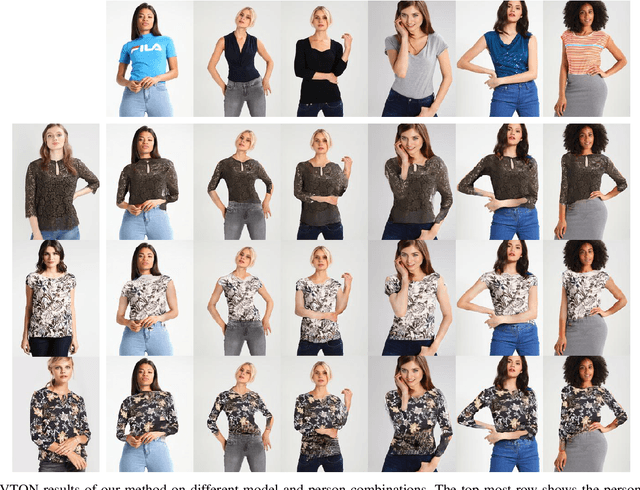


Abstract:The idea of \textit{Virtual Try-ON} (VTON) benefits e-retailing by giving an user the convenience of trying a clothing at the comfort of their home. In general, most of the existing VTON methods produce inconsistent results when a person posing with his arms folded i.e., bent or crossed, wants to try an outfit. The problem becomes severe in the case of long-sleeved outfits. As then, for crossed arm postures, overlap among different clothing parts might happen. The existing approaches, especially the warping-based methods employing \textit{Thin Plate Spline (TPS)} transform can not tackle such cases. To this end, we attempt a solution approach where the clothing from the source person is segmented into semantically meaningful parts and each part is warped independently to the shape of the person. To address the bending issue, we employ hand-crafted geometric features consistent with human body geometry for warping the source outfit. In addition, we propose two learning-based modules: a synthesizer network and a mask prediction network. All these together attempt to produce a photo-realistic, pose-robust VTON solution without requiring any paired training data. Comparison with some of the benchmark methods clearly establishes the effectiveness of the approach.
An Unsupervised Approach towards Varying Human Skin Tone Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Oct 30, 2020



Abstract:With the increasing popularity of augmented and virtual reality, retailers are now focusing more towards customer satisfaction to increase the amount of sales. Although augmented reality is not a new concept but it has gained much needed attention over the past few years. Our present work is targeted towards this direction which may be used to enhance user experience in various virtual and augmented reality based applications. We propose a model to change skin tone of a person. Given any input image of a person or a group of persons with some value indicating the desired change of skin color towards fairness or darkness, this method can change the skin tone of the persons in the image. This is an unsupervised method and also unconstrained in terms of pose, illumination, number of persons in the image etc. The goal of this work is to reduce the time and effort which is generally required for changing the skin tone using existing applications (e.g., Photoshop) by professionals or novice. To establish the efficacy of this method we have compared our result with that of some popular photo editor and also with the result of some existing benchmark method related to human attribute manipulation. Rigorous experiments on different datasets show the effectiveness of this method in terms of synthesizing perceptually convincing outputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge