Dick Carrillo Melgarejo
AsQM: Audio streaming Quality Metric based on Network Impairments and User Preferences
Sep 26, 2023Abstract:There are many users of audio streaming services because of the proliferation of cloud-based audio streaming services for different content. The complex networks that support these services do not always guarantee an acceptable quality on the end-user side. In this paper, the impact of temporal interruptions on the reproduction of audio streaming and the users preference in relation to audio contents are studied. In order to determine the key parameters in the audio streaming service, subjective tests were conducted, and their results show that users Quality-of-Experience (QoE) is highly correlated with the following application parameters, the number of temporal interruptions or stalls, its frequency and length, and the temporal location in which they occur. However, most important, experimental results demonstrated that users preference for audio content plays an important role in users QoE. Thus, a Preference Factor (PF) function is defined and considered in the formulation of the proposed metric named Audio streaming Quality Metric (AsQM). Considering that multimedia service providers are based on web servers, a framework to obtain user information is proposed. Furthermore, results show that the AsQM implemented in the audio player of an end users device presents a low impact on energy, processing and memory consumption.
* 11 pages
Incorporating Wireless Communication Parameters into the E-Model Algorithm
Mar 05, 2021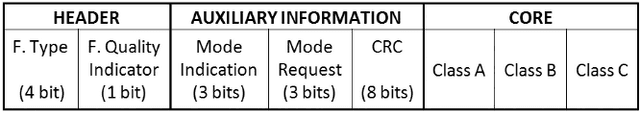



Abstract:Telecommunication service providers have to guarantee acceptable speech quality during a phone call to avoid a negative impact on the users' quality of experience. Currently, there are different speech quality assessment methods. ITU-T Recommendation G.107 describes the E-model algorithm, which is a computational model developed for network planning purposes focused on narrowband (NB) networks. Later, ITU-T Recommendations G.107.1 and G.107.2 were developed for wideband (WB) and fullband (FB) networks. These algorithms use different impairment factors, each one related to different speech communication steps. However, the NB, WB, and FB E-model algorithms do not consider wireless techniques used in these networks, such as Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output (MIMO) systems, which are used to improve the communication system robustness in the presence of different types of wireless channel degradation. In this context, the main objective of this study is to propose a general methodology to incorporate wireless network parameters into the NB and WB E-model algorithms. To accomplish this goal, MIMO and wireless channel parameters are incorporated into the E-model algorithms, specifically into the $I_{e,eff}$ and $I_{e,eff,WB}$ impairment factors. For performance validation, subjective tests were carried out, and the proposed methodology reached a Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) and a root mean square error (RMSE) of $0.9732$ and $0.2351$, respectively. It is noteworthy that our proposed methodology does not affect the rest of the E-model input parameters, and it intends to be useful for wireless network planning in speech communication services.
* 18 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge