Diana P. M. Osorio
Drone Surveillance via Coordinated Beam Sweeping in MIMO-ISAC Networks
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:This paper introduces a scheme for drone surveillance coordinated with the fifth generation (5G) synchronization signal block (SSB) cell-search procedure to simultaneously detect low-altitude drones within a volumetric surveillance grid. Herein, we consider a multistatic configuration where multiple access points (APs) collaboratively illuminate the volume while independently transmitting SSB broadcast signals. Both tasks are performed through a beam sweeping. In the proposed scheme, coordinated APs send sensing beams toward a grid of voxels within the volumetric surveillance region simultaneously with the 5G SSB burst. To prevent interference between communication and sensing signals, we propose a precoder design that guarantees orthogonality of the sensing beam and the SSB in order to maximize the sensing signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) while ensuring a specified SINR for users, as well as minimizing the impact of the direct link. The results demonstrate that the proposed precoder outperforms the non-coordinated precoder and is minimally affected by variations in drone altitude.
Joint Access Point Selection and Beamforming Design for Bistatic Backscatter Communication
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Future Internet-of-Things networks are envisioned to use small and cheap sensor nodes with extremely low power consumption to avoid the extensive use of batteries. To provide connectivity to a massive number of these nodes, backscatter communication (BC) is emerging as an energy- and cost-efficient technology exploiting the reflection of radio frequency signals. However, challenges such as round-trip path loss and direct link interference (DLI) between the carrier emitter and the reader limit its performance. To tackle these limitations, this paper proposes a joint access point role selection and a novel beamforming technique for bistatic BC in a distributed multiple-input multiple-output setup. The proposed approach boosts the received backscattered energy while effectively mitigating DLI, thereby reducing the error probability. We also propose a channel estimation method tailored to operate under DLI conditions and propose a mismatch detector using estimated channel coefficients. Furthermore, we derive a closed-form expression for the probability of error for the detectors and model the quantization noise caused by DLI. Finally, comprehensive simulation results show that the proposed method with 1-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) effectively mitigates DLI, reduces the quantization noise, and enhances backscattered signal energy, achieving performance comparable to the benchmark scenario with 8-bit ADCs.
Utilizing 5G NR SSB Blocks for Passive Detection and Localization of Low-Altitude Drones
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:With the exponential growth of the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) industry and a broad range of applications expected to appear in the coming years, the employment of traditional radar systems is becoming increasingly cumbersome for UAV supervision. Motivated by this emerging challenge, this paper investigates the feasibility of employing integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems implemented over current and future wireless networks to perform this task. We propose a sensing mechanism based on the synchronization signal block (SSB) in the fifth-generation (5G) standard that performs sensing in a passive bistatic setting. By assuming planar arrays at the sensing nodes and according to the 5G standard, we consider that the SSB signal is sent in a grid of orthogonal beams that are multiplexed in time, with some of them pointing toward a surveillance region where low-altitude drones can be flying. The Cramer-Rao Bound (CRB) is derived as the theoretical bound for range and velocity estimation. Our results demonstrate the potential of employing SSB signals for UAV-like target localization at low SNR.
Impact of Network-Controlled Repeaters in Integrated Sensing and Communication Systems
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Integrating sensing capabilities into existing massive MIMO communication networks has become crucial, stemming from a need for a more interconnected society. Improved coverage and performance can be obtained by incorporating new network components, such as reconfigurable intelligent surfaces or network-controlled repeaters (NCR). Integrating such components into modern networks brings a number of challenges. Thus, this paper contributes with the analysis of NCR impact in integrated sensing and communication networks. Particularly, the Cram\'er-Rao bound for a range estimator is derived where the interference from the repeater is taken into consideration. Additionally, a joint procedure for determining the repeater amplification factor, along with the precoders of the transmitting access point, is proposed.
Reducing Dynamic Range in Bistatic Backscatter Communication via Beamforming Design
Nov 13, 2024



Abstract:Considering the exponential growth of Internet-of-Things devices and the goals toward sustainable networks, the complexity should be focused on the infrastructure side. For a massive number of passive devices, backscatter communication (BC) is a promising technology that reduces cost and increases energy efficiency by enabling transmitting information by backscattering radio frequency signals. Two main limitations that restrict the performance of BC are the round-trip path loss effect and the direct link interference (DLI) from the carrier emitter (CE). To circumvent this, we propose a novel transmit beamforming design for a multiple antenna bistatic BC (BiBC) system that realizes both purposes: mitigation of the DLI and increasing the power towards the backscatter device (BD). Additionally, we provide a detector design and the performance is evaluated in terms of the probability of error, for which we also provide a closed-form expression. Finally, simulation results show the superiority of the proposed beamforming design in decreasing DLI over a benchmark scenario that considers maximum-ratio transmission.
Access Point Selection for Bistatic Backscatter Communication in Cell-Free MIMO
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:Backscatter communication (BC) has emerged as a key technology to satisfy the increasing need for low-cost and green Internet-of-Things (IoT) connectivity, especially in large-scale deployments. Unlike the monostatic BC (MoBC), the bistatic BC (BiBC) has the possibility to decrease the round-trip path loss by having the carrier emitter (CE) and the reader in different locations. Therefore, this work investigates the BiBC in the context of cell-free multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) networks by exploring the optimal selection of CE and reader among all access points, leveraging prior knowledge about the area where the backscatter device (BD) is located. First, a maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) detector to decode the BD information bits is derived. Then, the exact probability of error for this detector is obtained. In addition, an algorithm to select the best CE-reader pair for serving the specified area is proposed. Finally, simulation results show that the error performance of the BC is improved by the proposed algorithm compared to the benchmark scenario.
Multi-Static ISAC in Cell-Free Massive MIMO: Precoder Design and Privacy Assessment
Oct 03, 2023Abstract:A multi-static sensing-centric integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) network can take advantage of the cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output infrastructure to achieve remarkable diversity gains and reduced power consumption. While the conciliation of sensing and communication requirements is still a challenge, the privacy of the sensing information is a growing concern that should be seriously taken on the design of these systems to prevent other attacks. This paper tackles this issue by assessing the probability of an internal adversary to infer the target location information from the received signal by considering the design of transmit precoders that jointly optimizes the sensing and communication requirements in a multi-static-based cell-free ISAC network. Our results show that the multi-static setting facilitates a more precise estimation of the location of the target than the mono-static implementation.
Privacy Performance of MIMO Dual-Functional Radar-Communications with Internal Adversary
Feb 13, 2023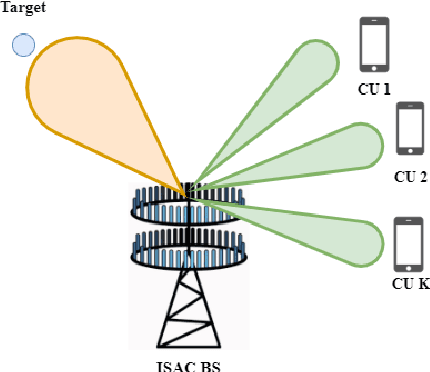
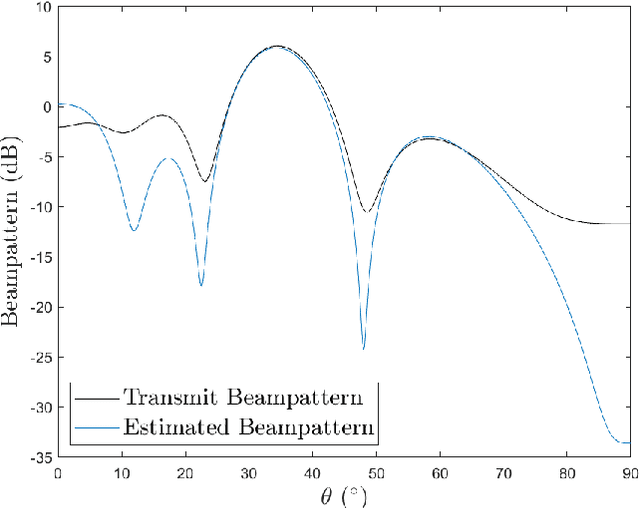
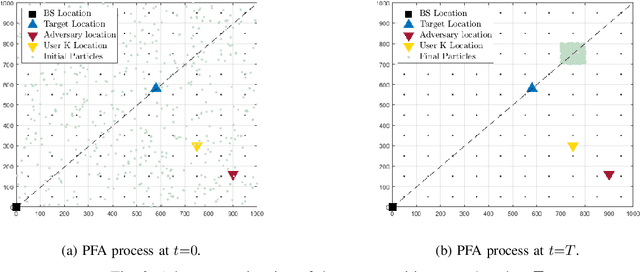
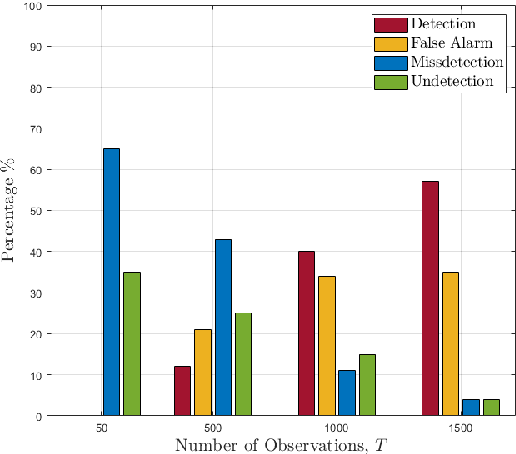
Abstract:The co-design of radar sensing and communications in dual-functional radar communication systems brings promising advantages for next generation wireless networks by providing gains in terms of the efficient and flexible use of spectrum, reduced costs, and lower energy consumption than in two separate systems. Besides the challenges associated with the conciliation of the conflicting requirements to perform wireless communication and radar sensing in a real-time cooperation, privacy issues represent a cause of concern as the co-design can let the network prone to active attacks. This paper tackles this issue by evaluating the associated privacy risks with the design of transmit precoders that simultaneously optimise both the radar transmit beampattern and the signal-to-interference-plus-noise at the communication users. Our results show that if a malicious user can infer the transmitted precoder matrix with a certain accuracy, there is a reasonable risk of exposure of the location of the target and privacy breaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge