Privacy Performance of MIMO Dual-Functional Radar-Communications with Internal Adversary
Paper and Code
Feb 13, 2023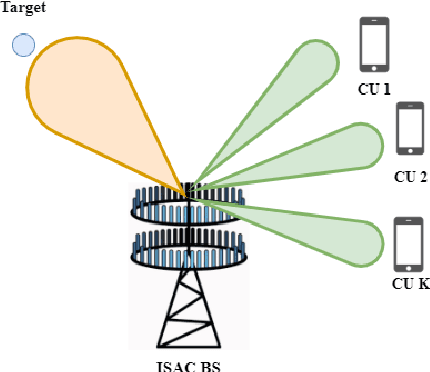
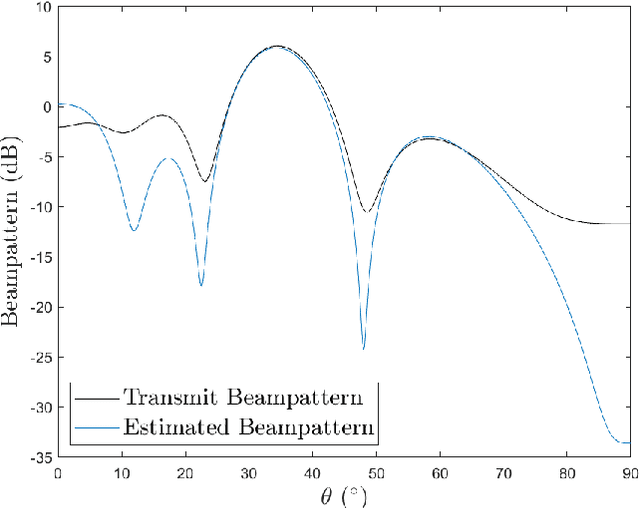
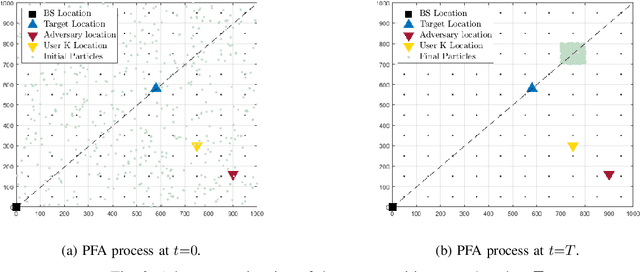
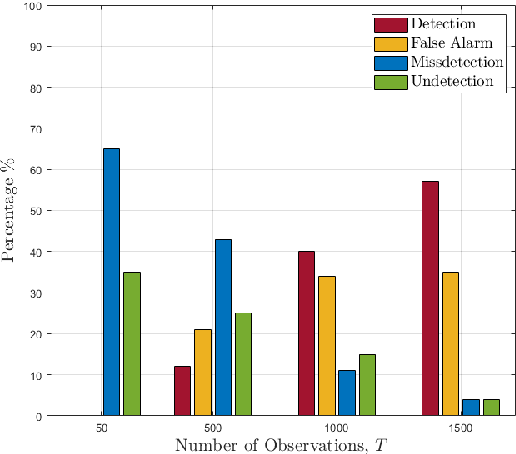
The co-design of radar sensing and communications in dual-functional radar communication systems brings promising advantages for next generation wireless networks by providing gains in terms of the efficient and flexible use of spectrum, reduced costs, and lower energy consumption than in two separate systems. Besides the challenges associated with the conciliation of the conflicting requirements to perform wireless communication and radar sensing in a real-time cooperation, privacy issues represent a cause of concern as the co-design can let the network prone to active attacks. This paper tackles this issue by evaluating the associated privacy risks with the design of transmit precoders that simultaneously optimise both the radar transmit beampattern and the signal-to-interference-plus-noise at the communication users. Our results show that if a malicious user can infer the transmitted precoder matrix with a certain accuracy, there is a reasonable risk of exposure of the location of the target and privacy breaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge