Devroop Kar
Investigating Quantum Circuit Designs Using Neuro-Evolution
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Designing effective quantum circuits remains a central challenge in quantum computing, as circuit structure strongly influences expressivity, trainability, and hardware feasibility. Current approaches, whether using manually designed circuit templates, fixed heuristics, or automated rules, face limitations in scalability, flexibility, and adaptability, often producing circuits that are poorly matched to the specific problem or quantum hardware. In this work, we propose the Evolutionary eXploration of Augmenting Quantum Circuits (EXAQC), an evolutionary approach to the automated design and training of parameterized quantum circuits (PQCs) which leverages and extends on strategies from neuroevolution and genetic programming. The proposed method jointly searches over gate types, qubit connectivity, parameterization, and circuit depth while respecting hardware and noise constraints. The method supports both Qiskit and Pennylane libraries, allowing the user to configure every aspect. This work highlights evolutionary search as a critical tool for advancing quantum machine learning and variational quantum algorithms, providing a principled pathway toward scalable, problem-aware, and hardware-efficient quantum circuit design. Preliminary results demonstrate that circuits evolved on classification tasks are able to achieve over 90% accuracy on most of the benchmark datasets with a limited computational budget, and are able to emulate target circuit quantum states with high fidelity scores.
Fuzzy Mutation Embedded Hybrids of Gravitational Search and Particle Swarm Optimization Methods for Engineering Design Problems
May 10, 2020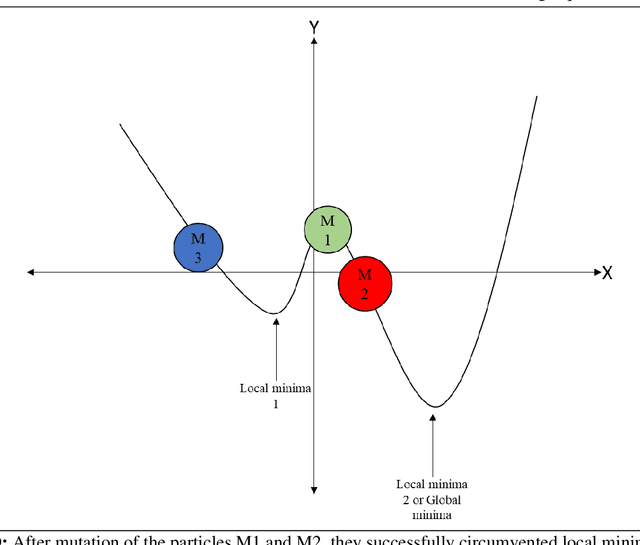

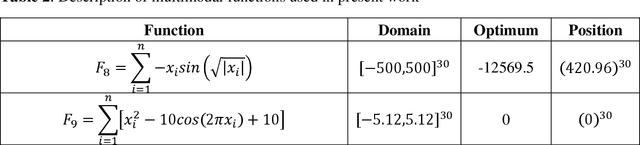
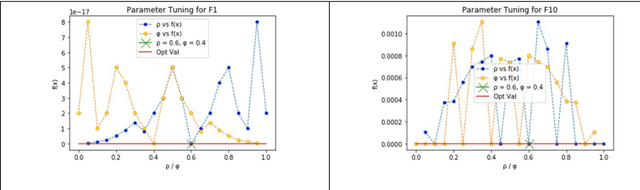
Abstract:Gravitational Search Algorithm (GSA) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) are nature-inspired, swarm-based optimization algorithms respectively. Though they have been widely used for single-objective optimization since their inception, they suffer from premature convergence. Even though the hybrids of GSA and PSO perform much better, the problem remains. Hence, to solve this issue we have proposed a fuzzy mutation model for two hybrid versions of PSO and GSA - Gravitational Particle Swarm (GPS) and PSOGSA. The developed algorithms are called Mutation based GPS (MGPS) and Mutation based PSOGSA (MPSOGSA). The mutation operator is based on a fuzzy model where the probability of mutation has been calculated based on the closeness of particle to population centroid and improvement in the particle value. We have evaluated these two new algorithms on 23 benchmark functions of three categories (unimodal, multi-modal and multi-modal with fixed dimension). The experimental outcome shows that our proposed model outperforms their corresponding ancestors, MGPS outperforms GPS 13 out of 23 times (56.52%) and MPSOGSA outperforms PSOGSA 17 times out of 23 (73.91 %). We have also compared our results against those of recent optimization algorithms such as Sine Cosine Algorithm (SCA), Opposition-Based SCA, and Volleyball Premier League Algorithm (VPL). In addition, we have applied our proposed algorithms on some classic engineering design problems and the outcomes are satisfactory. The related codes of the proposed algorithms can be found in this link: Fuzzy-Mutation-Embedded-Hybrids-of-GSA-and-PSO.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge