Dehua Tao
AEQ-Bench: Measuring Empathy of Omni-Modal Large Models
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:While the automatic evaluation of omni-modal large models (OLMs) is essential, assessing empathy remains a significant challenge due to its inherent affectivity. To investigate this challenge, we introduce AEQ-Bench (Audio Empathy Quotient Benchmark), a novel benchmark to systematically assess two core empathetic capabilities of OLMs: (i) generating empathetic responses by comprehending affective cues from multi-modal inputs (audio + text), and (ii) judging the empathy of audio responses without relying on text transcription. Compared to existing benchmarks, AEQ-Bench incorporates two novel settings that vary in context specificity and speech tone. Comprehensive assessment across linguistic and paralinguistic metrics reveals that (1) OLMs trained with audio output capabilities generally outperformed models with text-only outputs, and (2) while OLMs align with human judgments for coarse-grained quality assessment, they remain unreliable for evaluating fine-grained paralinguistic expressiveness.
DSA-Tokenizer: Disentangled Semantic-Acoustic Tokenization via Flow Matching-based Hierarchical Fusion
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Speech tokenizers serve as the cornerstone of discrete Speech Large Language Models (Speech LLMs). Existing tokenizers either prioritize semantic encoding, fuse semantic content with acoustic style inseparably, or achieve incomplete semantic-acoustic disentanglement. To achieve better disentanglement, we propose DSA-Tokenizer, which explicitly disentangles speech into discrete semantic and acoustic tokens via distinct optimization constraints. Specifically, semantic tokens are supervised by ASR to capture linguistic content, while acoustic tokens focus on mel-spectrograms restoration to encode style. To eliminate rigid length constraints between the two sequences, we introduce a hierarchical Flow-Matching decoder that further improve speech generation quality. Furthermore, We employ a joint reconstruction-recombination training strategy to enforce this separation. DSA-Tokenizer enables high fidelity reconstruction and flexible recombination through robust disentanglement, facilitating controllable generation in speech LLMs. Our analysis highlights disentangled tokenization as a pivotal paradigm for future speech modeling. Audio samples are avaialble at https://anonymous.4open.science/w/DSA_Tokenizer_demo/. The code and model will be made publicly available after the paper has been accepted.
CUEMPATHY: A Counseling Speech Dataset for Psychotherapy Research
Sep 04, 2024


Abstract:Psychotherapy or counseling is typically conducted through spoken conversation between a therapist and a client. Analyzing the speech characteristics of psychotherapeutic interactions can help understand the factors associated with effective psychotherapy. This paper introduces CUEMPATHY, a large-scale speech dataset collected from actual counseling sessions. The dataset consists of 156 counseling sessions involving 39 therapist-client dyads. The process of speech data collection, subjective ratings (one observer and two client ratings), and transcription are described. An automatic speech and text processing system is developed to locate the time stamps of speaker turns in each session. Examining the relationships among the three subjective ratings suggests that observer and client ratings have no significant correlation, while the client-rated measures are significantly correlated. The intensity similarity between the therapist and the client, measured by the averaged absolute difference of speaker-turn-level intensities, is associated with the psychotherapy outcomes. Recent studies on the acoustic and linguistic characteristics of the CUEMPATHY are introduced.
ToneUnit: A Speech Discretization Approach for Tonal Language Speech Synthesis
Jun 13, 2024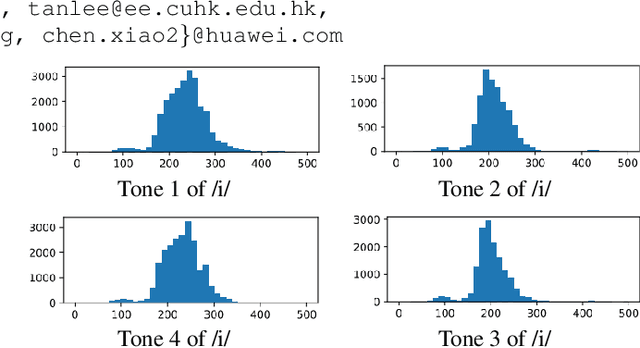
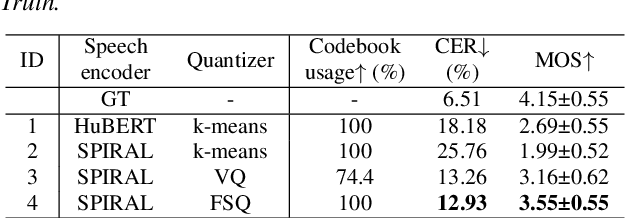
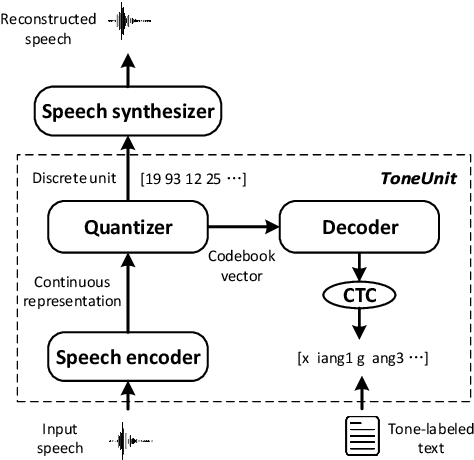
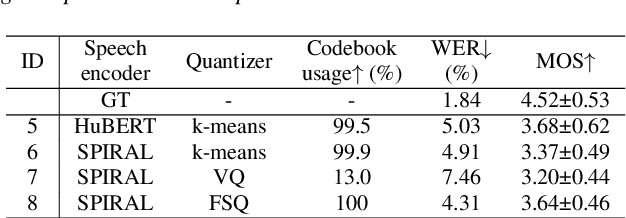
Abstract:Representing speech as discretized units has numerous benefits in supporting downstream spoken language processing tasks. However, the approach has been less explored in speech synthesis of tonal languages like Mandarin Chinese. Our preliminary experiments on Chinese speech synthesis reveal the issue of "tone shift", where a synthesized speech utterance contains correct base syllables but incorrect tones. To address the issue, we propose the ToneUnit framework, which leverages annotated data with tone labels as CTC supervision to learn tone-aware discrete speech units for Mandarin Chinese speech. Our findings indicate that the discrete units acquired through the TonUnit resolve the "tone shift" issue in synthesized Chinese speech and yield favorable results in English synthesis. Moreover, the experimental results suggest that finite scalar quantization enhances the effectiveness of ToneUnit. Notably, ToneUnit can work effectively even with minimal annotated data.
A Study on Prosodic Entrainment in Relation to Therapist Empathy in Counseling Conversation
Oct 22, 2023Abstract:Counseling is carried out as spoken conversation between a therapist and a client. The empathy level expressed by the therapist is considered an important index of the quality of counseling and often assessed by an observer or the client. This research investigates the entrainment of speech prosody in relation to subjectively rated empathy. Experimental results show that the entrainment of intensity is more influential to empathy observation than that of pitch or speech rate in client-therapist interaction. The observer and the client have different perceptions of therapist empathy with the same entrained phenomena in pitch and intensity. The client's intention to make adjustment on pitch variation and intensity of speech is considered an indicator of the client's perception of counseling quality.
Modeling Intrapersonal and Interpersonal Influences for Automatic Estimation of Therapist Empathy in Counseling Conversation
Oct 22, 2023



Abstract:Counseling is usually conducted through spoken conversation between a therapist and a client. The empathy level of therapist is a key indicator of outcomes. Presuming that therapist's empathy expression is shaped by their past behavior and their perception of the client's behavior, we propose a model to estimate the therapist empathy by considering both intrapersonal and interpersonal influences. These dynamic influences are captured by applying an attention mechanism to the therapist turn and the historical turns of both therapist and client. Our findings suggest that the integration of dynamic influences enhances empathy level estimation. The influence-derived embedding should constitute a minor portion in the target turn representation for optimal empathy estimation. The client's turns (interpersonal influence) appear to slightly surpass the therapist's own turns (intrapersonal influence) in empathy estimation effectiveness. It is noted that concentrating exclusively on recent historical turns can significantly impact the estimation of therapist empathy.
Learning Representation of Therapist Empathy in Counseling Conversation Using Siamese Hierarchical Attention Network
May 26, 2023



Abstract:Counseling is an activity of conversational speaking between a therapist and a client. Therapist empathy is an essential indicator of counseling quality and assessed subjectively by considering the entire conversation. This paper proposes to encode long counseling conversation using a hierarchical attention network. Conversations with extreme values of empathy rating are used to train a Siamese network based encoder with contrastive loss. Two-level attention mechanisms are applied to learn the importance weights of individual speaker turns and groups of turns in the conversation. Experimental results show that the use of contrastive loss is effective in encouraging the conversation encoder to learn discriminative embeddings that are related to therapist empathy. The distances between conversation embeddings positively correlate with the differences in the respective empathy scores. The learned conversation embeddings can be used to predict the subjective rating of therapist empathy.
Hierarchical Attention Network for Evaluating Therapist Empathy in Counseling Session
Mar 31, 2022



Abstract:Counseling typically takes the form of spoken conversation between a therapist and a client. The empathy level expressed by the therapist is considered to be an essential quality factor of counseling outcome. This paper proposes a hierarchical recurrent network combined with two-level attention mechanisms to determine the therapist's empathy level solely from the acoustic features of conversational speech in a counseling session. The experimental results show that the proposed model can achieve an accuracy of 72.1% in classifying the therapist's empathy level as being "high" or "low". It is found that the speech from both the therapist and the client are contributing to predicting the empathy level that is subjectively rated by an expert observer. By analyzing speaker turns assigned with high attention weights, it is observed that 2 to 6 consecutive turns should be considered together to provide useful clues for detecting empathy, and the observer tends to take the whole session into consideration when rating the therapist empathy, instead of relying on a few specific speaker turns.
Characterizing Therapist's Speaking Style in Relation to Empathy in Psychotherapy
Mar 24, 2022
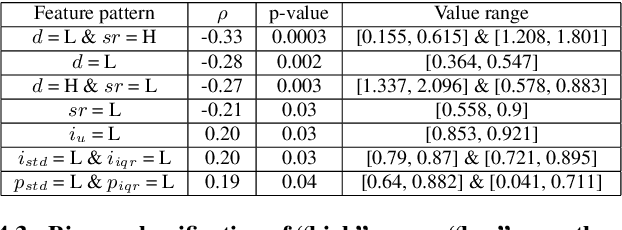
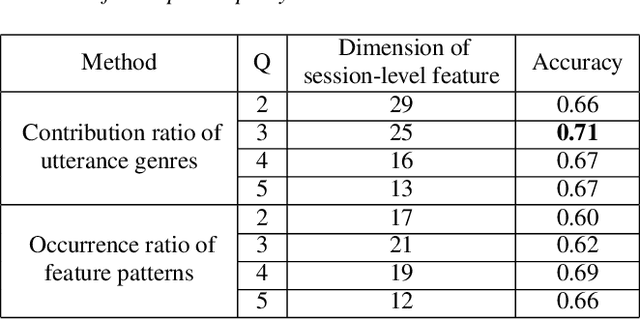
Abstract:In conversation-based psychotherapy, therapists use verbal techniques to help clients express thoughts and feelings and change behaviors. In particular, how well therapists convey empathy is an essential quality index of psychotherapy sessions and is associated with psychotherapy outcome. In this paper, we analyze the prosody of therapist speech and attempt to associate the therapist's speaking style with subjectively perceived empathy. An automatic speech and text processing system is developed to segment long recordings of psychotherapy sessions into pause-delimited utterances with text transcriptions. Data-driven clustering is applied to the utterances from different therapists in multiple sessions. For each cluster, a typological representation of utterance genre is derived based on quantized prosodic feature parameters. Prominent speaking styles of the therapist can be observed and interpreted from salient utterance genres that are correlated with empathy. Using the salient utterance genres, an accuracy of 71% is achieved in classifying psychotherapy sessions into "high" and "low" empathy level. Analysis of results suggests that empathy level tends to be (1) low if therapists speak long utterances slowly or speak short utterances quickly; and (2) high if therapists talk to clients with a steady tone and volume.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge