David M. Nicol
Assessment of System-Level Cyber Attack Vulnerability for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles Using Bayesian Networks
Nov 18, 2020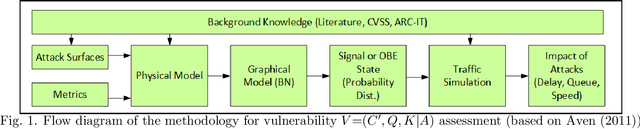
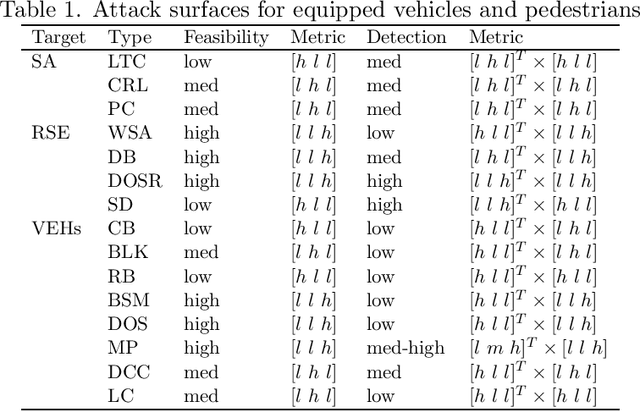
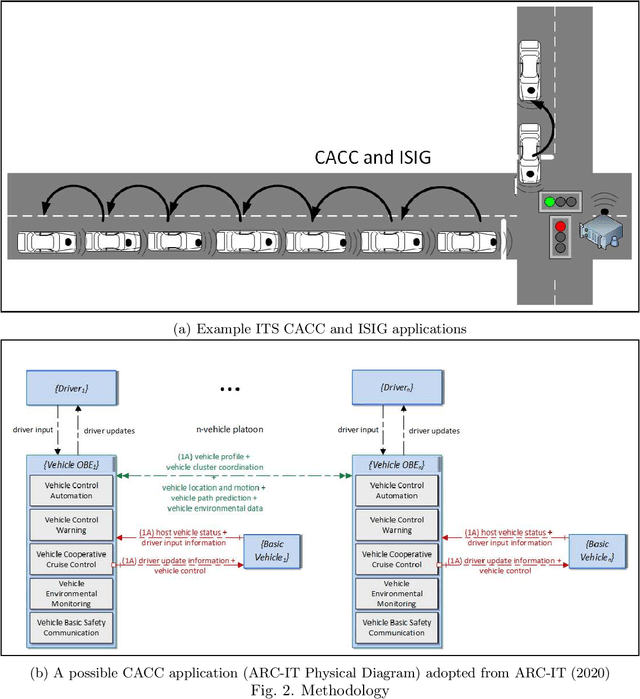
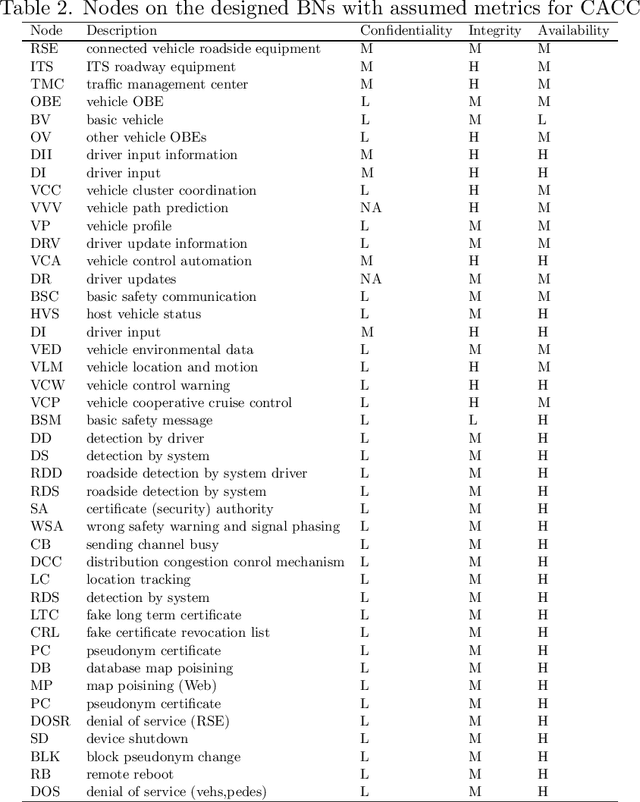
Abstract:This study presents a methodology to quantify vulnerability of cyber attacks and their impacts based on probabilistic graphical models for intelligent transportation systems under connected and autonomous vehicles framework. Cyber attack vulnerabilities from various types and their impacts are calculated for intelligent signals and cooperative adaptive cruise control (CACC) applications based on the selected performance measures. Numerical examples are given that show impact of vulnerabilities in terms of average intersection queue lengths, number of stops, average speed, and delays. At a signalized network with and without redundant systems, vulnerability can increase average queues and delays by $3\%$ and $15\%$ and $4\%$ and $17\%$, respectively. For CACC application, impact levels reach to $50\%$ delay difference on average when low amount of speed information is perturbed. When significantly different speed characteristics are inserted by an attacker, delay difference increases beyond $100\%$ of normal traffic conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge