David Kadish
Towards Situation Awareness and Attention Guidance in a Multiplayer Environment using Augmented Reality and Carcassonne
Aug 18, 2022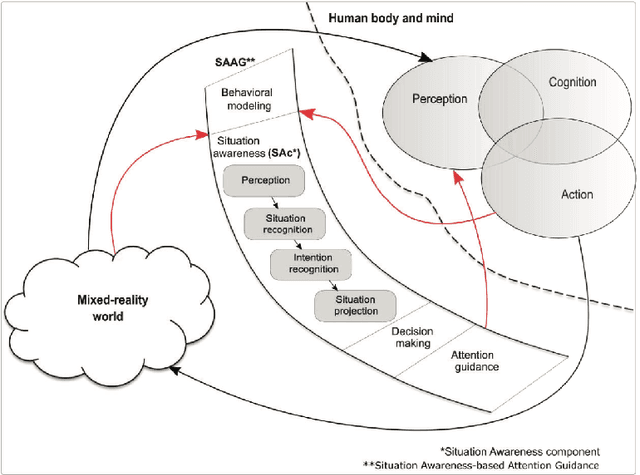

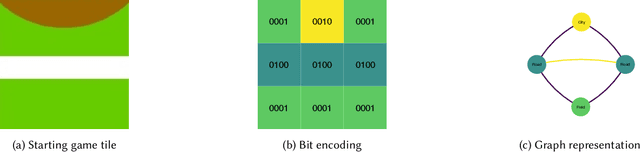
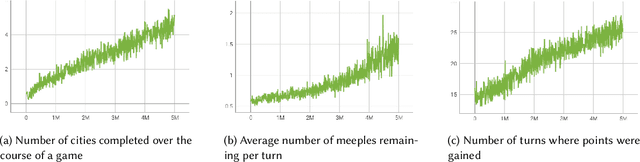
Abstract:Augmented reality (AR) games are a rich environment for researching and testing computational systems that provide subtle user guidance and training. In particular computer systems that aim to augment a user's situation awareness benefit from the range of sensors and computing power available in AR headsets. In this work-in-progress paper, we present a new environment for research into situation awareness and attention guidance (SAAG): an augmented reality version of the board game Carcassonne. We also present our initial work in producing a SAAG pipeline, including the creation of game state encodings, the development and training of a gameplay AI, and the design of situation modelling and gaze tracking systems.
Improving Object Detection in Art Images Using Only Style Transfer
Feb 12, 2021
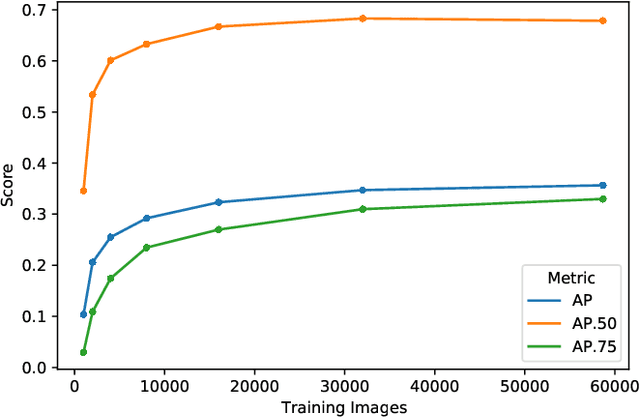

Abstract:Despite recent advances in object detection using deep learning neural networks, these neural networks still struggle to identify objects in art images such as paintings and drawings. This challenge is known as the cross depiction problem and it stems in part from the tendency of neural networks to prioritize identification of an object's texture over its shape. In this paper we propose and evaluate a process for training neural networks to localize objects - specifically people - in art images. We generate a large dataset for training and validation by modifying the images in the COCO dataset using AdaIn style transfer. This dataset is used to fine-tune a Faster R-CNN object detection network, which is then tested on the existing People-Art testing dataset. The result is a significant improvement on the state of the art and a new way forward for creating datasets to train neural networks to process art images.
An artifcial life approach to studying niche differentiation in soundscape ecology
Jul 30, 2019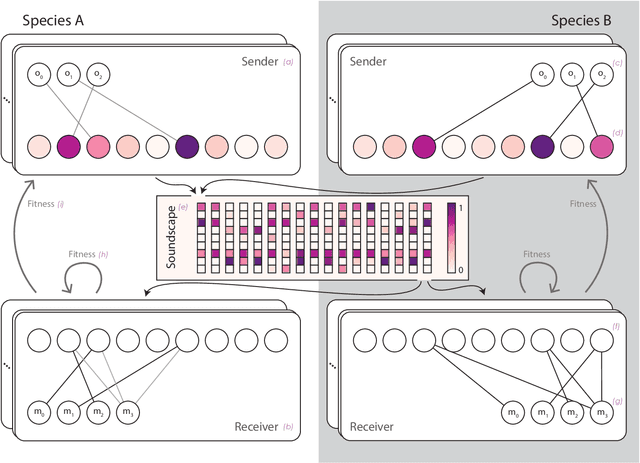
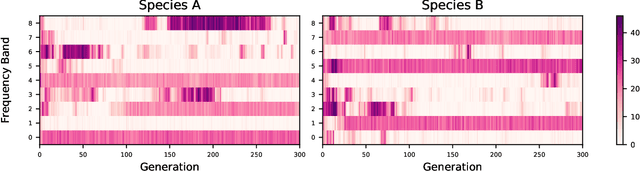
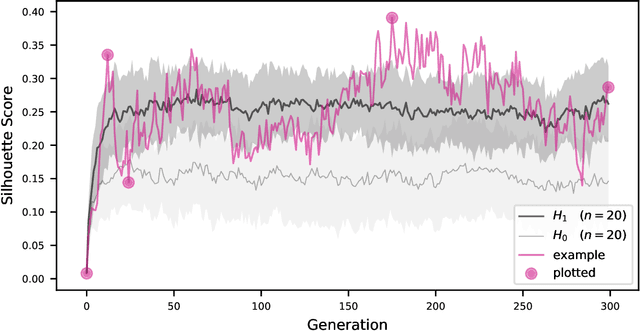
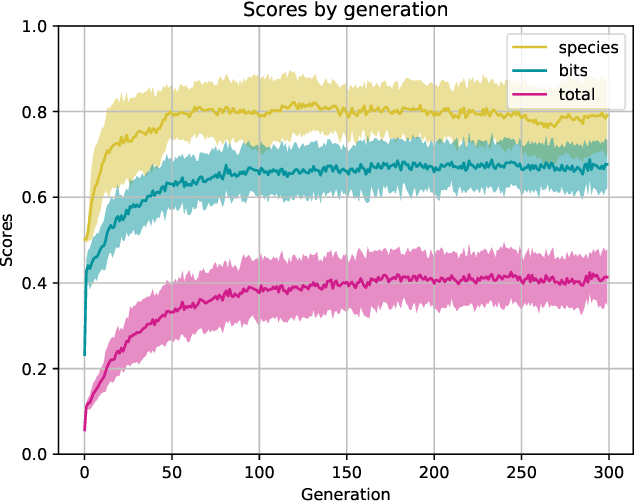
Abstract:Artificial life simulations are an important tool in the study of ecological phenomena that can be difficult to examine directly in natural environments. Recent work has established the soundscape as an ecologically important resource and it has been proposed that the differentiation of animal vocalizations within a soundscape is driven by the imperative of intraspecies communication. The experiments in this paper test that hypothesis in a simulated soundscape in order to verify the feasibility of intraspecies communication as a driver of acoustic niche differentiation. The impact of intraspecies communication is found to be a significant factor in the division of a soundscape's frequency spectrum when compared to simulations where the need to identify signals from conspecifics does not drive the evolution of signalling. The method of simulating the effects of interspecies interactions on the soundscape is positioned as a tool for developing artificial life agents that can inhabit and interact with physical ecosystems and soundscapes.
* 9 pages, 4 figures, The 2019 Conference on Artificial Life
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge