David Doukhan
Articulatory Configurations across Genders and Periods in French Radio and TV archives
Aug 08, 2024Abstract:This paper studies changes in articulatory configurations across genders and periods using an inversion from acoustic to articulatory parameters. From a diachronic corpus based on French media archives spanning 60 years from 1955 to 2015, automatic transcription and forced alignment allowed extracting the central frame of each vowel. More than one million frames were obtained from over a thousand speakers across gender and age categories. Their formants were used from these vocalic frames to fit the parameters of Maeda's articulatory model. Evaluations of the quality of these processes are provided. We focus here on two parameters of Maeda's model linked to total vocal tract length: the relative position of the larynx (higher for females) and the lips protrusion (more protruded for males). Implications for voice quality across genders are discussed. The effect across periods seems gender independent; thus, the assertion that females lowered their pitch with time is not supported.
Automatic Classification of News Subjects in Broadcast News: Application to a Gender Bias Representation Analysis
Jul 19, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a computational framework designed to delineate gender distribution biases in topics covered by French TV and radio news. We transcribe a dataset of 11.7k hours, broadcasted in 2023 on 21 French channels. A Large Language Model (LLM) is used in few-shot conversation mode to obtain a topic classification on those transcriptions. Using the generated LLM annotations, we explore the finetuning of a specialized smaller classification model, to reduce the computational cost. To evaluate the performances of these models, we construct and annotate a dataset of 804 dialogues. This dataset is made available free of charge for research purposes. We show that women are notably underrepresented in subjects such as sports, politics and conflicts. Conversely, on topics such as weather, commercials and health, women have more speaking time than their overall average across all subjects. We also observe representations differences between private and public service channels.
Detecting the terminality of speech-turn boundary for spoken interactions in French TV and Radio content
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:Transition Relevance Places are defined as the end of an utterance where the interlocutor may take the floor without interrupting the current speaker --i.e., a place where the turn is terminal. Analyzing turn terminality is useful to study the dynamic of turn-taking in spontaneous conversations. This paper presents an automatic classification of spoken utterances as Terminal or Non-Terminal in multi-speaker settings. We compared audio, text, and fusions of both approaches on a French corpus of TV and Radio extracts annotated with turn-terminality information at each speaker change. Our models are based on pre-trained self-supervised representations. We report results for different fusion strategies and varying context sizes. This study also questions the problem of performance variability by analyzing the differences in results for multiple training runs with random initialization. The measured accuracy would allow the use of these models for large-scale analysis of turn-taking.
Gender Representation in TV and Radio: Automatic Information Extraction methods versus Manual Analyses
Jun 14, 2024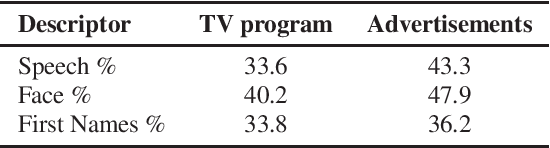



Abstract:This study investigates the relationship between automatic information extraction descriptors and manual analyses to describe gender representation disparities in TV and Radio. Automatic descriptors, including speech time, facial categorization and speech transcriptions are compared with channel reports on a vast 32,000-hour corpus of French broadcasts from 2023. Findings reveal systemic gender imbalances, with women underrepresented compared to men across all descriptors. Notably, manual channel reports show higher women's presence than automatic estimates and references to women are lower than their speech time. Descriptors share common dynamics during high and low audiences, war coverage, or private versus public channels. While women are more visible than audible in French TV, this trend is inverted in news with unseen journalists depicting male protagonists. A statistical test shows 3 main effects influencing references to women: program category, channel and speaker gender.
InaGVAD : a Challenging French TV and Radio Corpus Annotated for Speech Activity Detection and Speaker Gender Segmentation
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:InaGVAD is an audio corpus collected from 10 French radio and 18 TV channels categorized into 4 groups: generalist radio, music radio, news TV, and generalist TV. It contains 277 1-minute-long annotated recordings aimed at representing the acoustic diversity of French audiovisual programs and was primarily designed to build systems able to monitor men's and women's speaking time in media. inaGVAD is provided with Voice Activity Detection (VAD) and Speaker Gender Segmentation (SGS) annotations extended with overlap, speaker traits (gender, age, voice quality), and 10 non-speech event categories. Annotation distributions are detailed for each channel category. This dataset is partitioned into a 1h development and a 3h37 test subset, allowing fair and reproducible system evaluation. A benchmark of 6 freely available VAD software is presented, showing diverse abilities based on channel and non-speech event categories. Two existing SGS systems are evaluated on the corpus and compared against a baseline X-vector transfer learning strategy, trained on the development subset. Results demonstrate that our proposal, trained on a single - but diverse - hour of data, achieved competitive SGS results. The entire inaGVAD package; including corpus, annotations, evaluation scripts, and baseline training code; is made freely accessible, fostering future advancement in the domain.
* Voice Activity Detection (VAD), Speaker Gender Segmentation, Audiovisual Speech Resource, Speaker Traits, Speech Overlap, Benchmark, X-vector, Gender Representation in the Media, Dataset
A Semi-Automatic Approach to Create Large Gender- and Age-Balanced Speaker Corpora: Usefulness of Speaker Diarization & Identification
Apr 26, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a semi-automatic approach to create a diachronic corpus of voices balanced for speaker's age, gender, and recording period, according to 32 categories (2 genders, 4 age ranges and 4 recording periods). Corpora were selected at French National Institute of Audiovisual (INA) to obtain at least 30 speakers per category (a total of 960 speakers; only 874 have be found yet). For each speaker, speech excerpts were extracted from audiovisual documents using an automatic pipeline consisting of speech detection, background music and overlapped speech removal and speaker diarization, used to present clean speaker segments to human annotators identifying target speakers. This pipeline proved highly effective, cutting down manual processing by a factor of ten. Evaluation of the quality of the automatic processing and of the final output is provided. It shows the automatic processing compare to up-to-date process, and that the output provides high quality speech for most of the selected excerpts. This method shows promise for creating large corpora of known target speakers.
* Keywords:, semi-automatic processing, corpus creation, diarization, speaker identification, gender-balanced, age-balanced, speaker corpus, diachrony
Evolution of Voices in French Audiovisual Media Across Genders and Age in a Diachronic Perspective
Apr 24, 2024Abstract:We present a diachronic acoustic analysis of the voice of 1023 speakers from French media archives. The speakers are spread across 32 categories based on four periods (years 1955/56, 1975/76, 1995/96, 2015/16), four age groups (20-35; 36-50; 51-65, >65), and two genders. The fundamental frequency ($F_0$) and the first four formants (F1-4) were estimated. Procedures used to ensure the quality of these estimations on heterogeneous data are described. From each speaker's $F_0$ distribution, the base-$F_0$ value was calculated to estimate the register. Average vocal tract length was estimated from formant frequencies. Base-$F_0$ and vocal tract length were fit by linear mixed models to evaluate how they may have changed across time periods and genders, corrected for age effects. Results show an effect of the period with a tendency to lower voices, independently of gender. A lowering of pitch is observed with age for female but not male speakers.
* 5 pages, 2 figures, keywords:, Gender, Diachrony, Vocal Tract Resonance, Vocal register, Broadcast speech
Voice Passing : a Non-Binary Voice Gender Prediction System for evaluating Transgender voice transition
Apr 23, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a software allowing to describe voices using a continuous Voice Femininity Percentage (VFP). This system is intended for transgender speakers during their voice transition and for voice therapists supporting them in this process. A corpus of 41 French cis- and transgender speakers was recorded. A perceptual evaluation allowed 57 participants to estimate the VFP for each voice. Binary gender classification models were trained on external gender-balanced data and used on overlapping windows to obtain average gender prediction estimates, which were calibrated to predict VFP and obtained higher accuracy than $F_0$ or vocal track length-based models. Training data speaking style and DNN architecture were shown to impact VFP estimation. Accuracy of the models was affected by speakers' age. This highlights the importance of style, age, and the conception of gender as binary or not, to build adequate statistical representations of cultural concepts.
* 5 pages, 1 figure, keywords: Transgender voice, Gender perception, Speaker gender classification, CNN, X-Vector
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge