David A. Lagnado
Formalizing Neurath's Ship: Approximate Algorithms for Online Causal Learning
May 26, 2017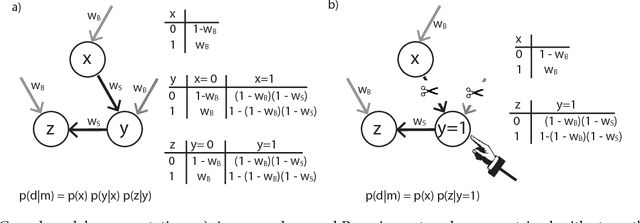
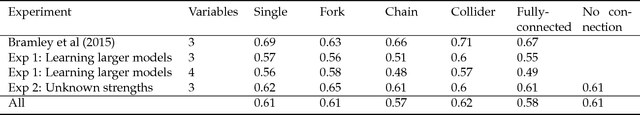
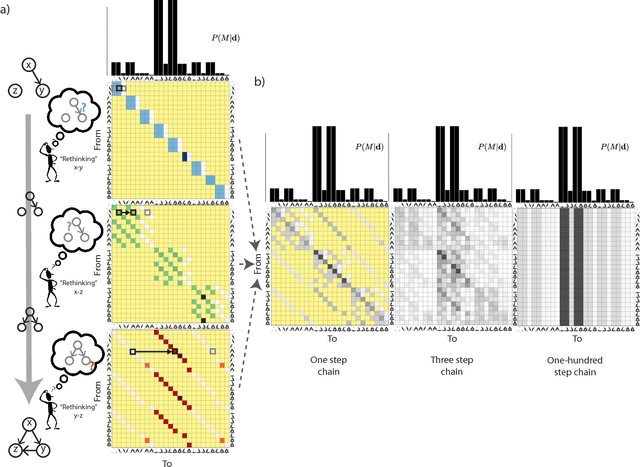
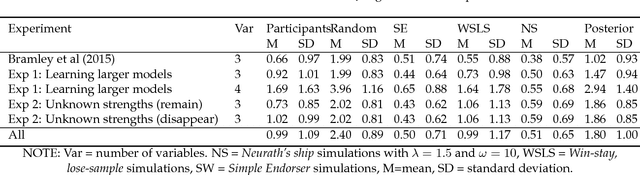
Abstract:Higher-level cognition depends on the ability to learn models of the world. We can characterize this at the computational level as a structure-learning problem with the goal of best identifying the prevailing causal relationships among a set of relata. However, the computational cost of performing exact Bayesian inference over causal models grows rapidly as the number of relata increases. This implies that the cognitive processes underlying causal learning must be substantially approximate. A powerful class of approximations that focuses on the sequential absorption of successive inputs is captured by the Neurath's ship metaphor in philosophy of science, where theory change is cast as a stochastic and gradual process shaped as much by people's limited willingness to abandon their current theory when considering alternatives as by the ground truth they hope to approach. Inspired by this metaphor and by algorithms for approximating Bayesian inference in machine learning, we propose an algorithmic-level model of causal structure learning under which learners represent only a single global hypothesis that they update locally as they gather evidence. We propose a related scheme for understanding how, under these limitations, learners choose informative interventions that manipulate the causal system to help elucidate its workings. We find support for our approach in the analysis of four experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge