Danilo Dordevic
Evidential Transformers for Improved Image Retrieval
Sep 02, 2024Abstract:We introduce the Evidential Transformer, an uncertainty-driven transformer model for improved and robust image retrieval. In this paper, we make several contributions to content-based image retrieval (CBIR). We incorporate probabilistic methods into image retrieval, achieving robust and reliable results, with evidential classification surpassing traditional training based on multiclass classification as a baseline for deep metric learning. Furthermore, we improve the state-of-the-art retrieval results on several datasets by leveraging the Global Context Vision Transformer (GC ViT) architecture. Our experimental results consistently demonstrate the reliability of our approach, setting a new benchmark in CBIR in all test settings on the Stanford Online Products (SOP) and CUB-200-2011 datasets.
Rethinking Attention: Exploring Shallow Feed-Forward Neural Networks as an Alternative to Attention Layers in Transformers
Nov 29, 2023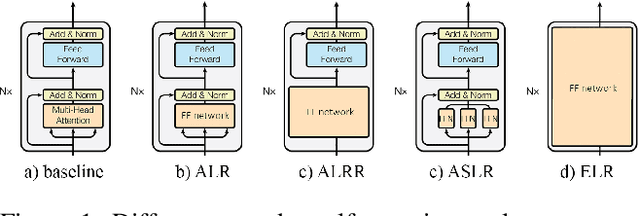



Abstract:This work presents an analysis of the effectiveness of using standard shallow feed-forward networks to mimic the behavior of the attention mechanism in the original Transformer model, a state-of-the-art architecture for sequence-to-sequence tasks. We substitute key elements of the attention mechanism in the Transformer with simple feed-forward networks, trained using the original components via knowledge distillation. Our experiments, conducted on the IWSLT2017 dataset, reveal the capacity of these "attentionless Transformers" to rival the performance of the original architecture. Through rigorous ablation studies, and experimenting with various replacement network types and sizes, we offer insights that support the viability of our approach. This not only sheds light on the adaptability of shallow feed-forward networks in emulating attention mechanisms but also underscores their potential to streamline complex architectures for sequence-to-sequence tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge