Danielle Torres
Explaining the Effectiveness of Multi-Task Learning for Efficient Knowledge Extraction from Spine MRI Reports
May 06, 2022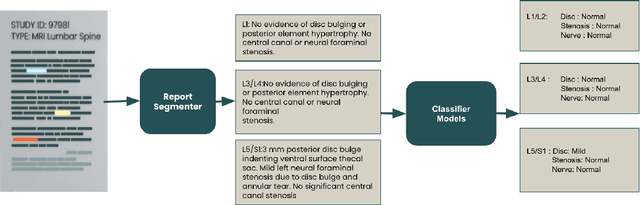
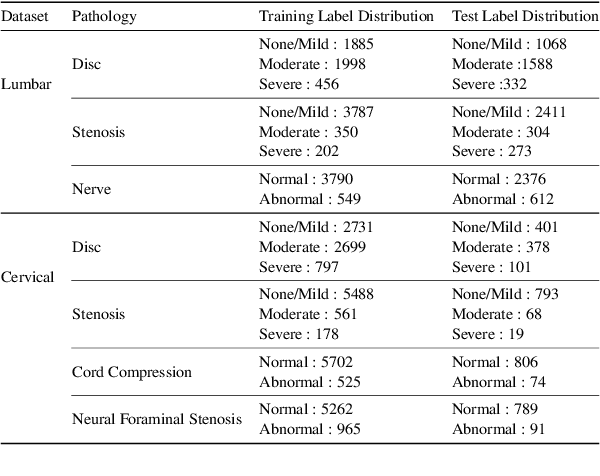
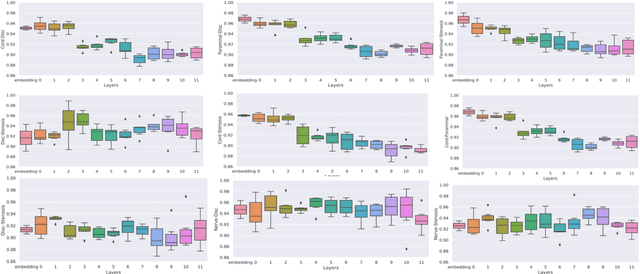
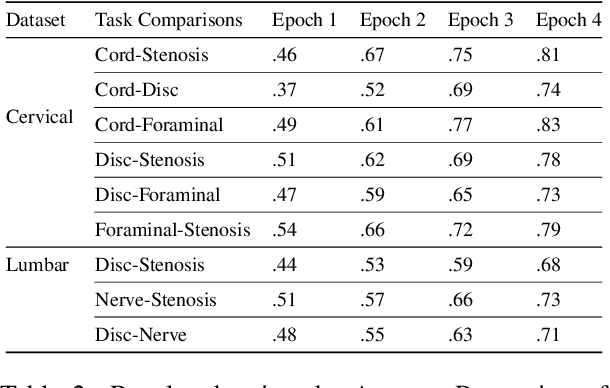
Abstract:Pretrained Transformer based models finetuned on domain specific corpora have changed the landscape of NLP. However, training or fine-tuning these models for individual tasks can be time consuming and resource intensive. Thus, a lot of current research is focused on using transformers for multi-task learning (Raffel et al.,2020) and how to group the tasks to help a multi-task model to learn effective representations that can be shared across tasks (Standley et al., 2020; Fifty et al., 2021). In this work, we show that a single multi-tasking model can match the performance of task specific models when the task specific models show similar representations across all of their hidden layers and their gradients are aligned, i.e. their gradients follow the same direction. We hypothesize that the above observations explain the effectiveness of multi-task learning. We validate our observations on our internal radiologist-annotated datasets on the cervical and lumbar spine. Our method is simple and intuitive, and can be used in a wide range of NLP problems.
Efficient Extraction of Pathologies from C-Spine Radiology Reports using Multi-Task Learning
Apr 09, 2022

Abstract:Pretrained Transformer based models finetuned on domain specific corpora have changed the landscape of NLP. Generally, if one has multiple tasks on a given dataset, one may finetune different models or use task specific adapters. In this work, we show that a multi-task model can beat or achieve the performance of multiple BERT-based models finetuned on various tasks and various task specific adapter augmented BERT-based models. We validate our method on our internal radiologist's report dataset on cervical spine. We hypothesize that the tasks are semantically close and related and thus multitask learners are powerful classifiers. Our work opens the scope of using our method to radiologist's reports on various body parts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge