Daniel Vriesman
Safe Autonomous Driving in Adverse Weather: Sensor Evaluation and Performance Monitoring
May 02, 2023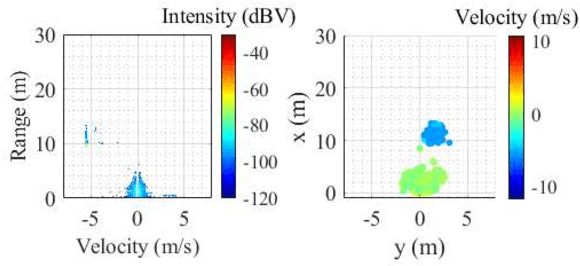
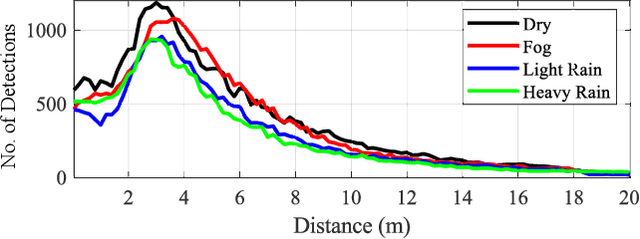
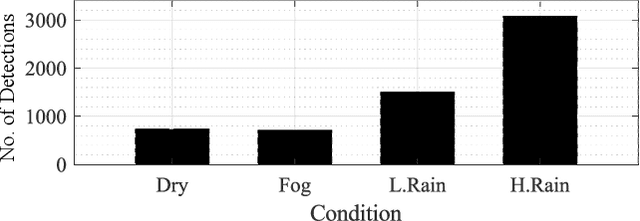
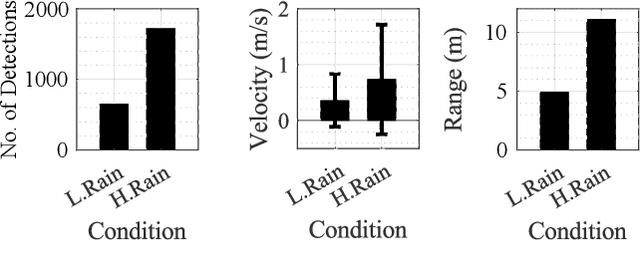
Abstract:The vehicle's perception sensors radar, lidar and camera, which must work continuously and without restriction, especially with regard to automated/autonomous driving, can lose performance due to unfavourable weather conditions. This paper analyzes the sensor signals of these three sensor technologies under rain and fog as well as day and night. A data set of a driving test vehicle as an object target under different weather conditions was recorded in a controlled environment with adjustable, defined, and reproducible weather conditions. Based on the sensor performance evaluation, a method has been developed to detect sensor degradation, including determining the affected data areas and estimating how severe they are. Through this sensor monitoring, measures can be taken in subsequent algorithms to reduce the influences or to take them into account in safety and assistance systems to avoid malfunctions.
Texture CNN for Thermoelectric Metal Pipe Image Classification
May 28, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, the concept of representation learning based on deep neural networks is applied as an alternative to the use of handcrafted features in a method for automatic visual inspection of corroded thermoelectric metallic pipes. A texture convolutional neural network (TCNN) replaces handcrafted features based on Local Phase Quantization (LPQ) and Haralick descriptors (HD) with the advantage of learning an appropriate textural representation and the decision boundaries into a single optimization process. Experimental results have shown that it is possible to reach the accuracy of 99.20% in the task of identifying different levels of corrosion in the internal surface of thermoelectric pipe walls, while using a compact network that requires much less effort in tuning parameters when compared to the handcrafted approach since the TCNN architecture is compact regarding the number of layers and connections. The observed results open up the possibility of using deep neural networks in real-time applications such as the automatic inspection of thermoelectric metal pipes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge