Daniel Rough
Mental Workload and Language Production in Non-Native Speaker IPA Interaction
Jun 11, 2020
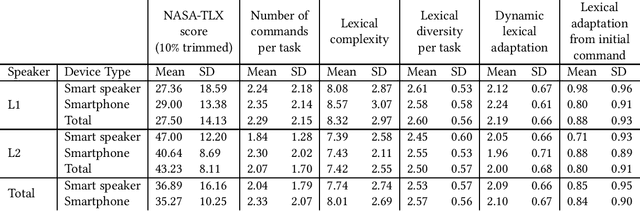
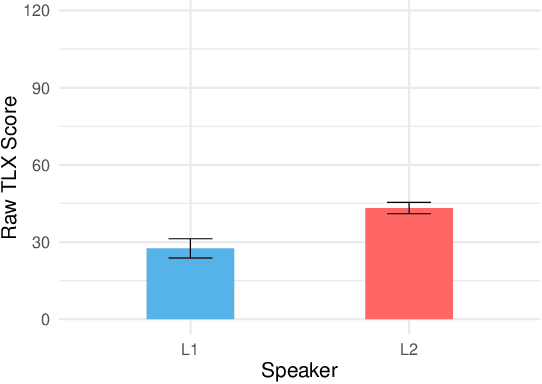
Abstract:Through proliferation on smartphones and smart speakers, intelligent personal assistants (IPAs) have made speech a common interaction modality. Yet, due to linguistic coverage and varying levels of functionality, many speakers engage with IPAs using a non-native language. This may impact the mental workload and pattern of language production displayed by non-native speakers. We present a mixed-design experiment, wherein native (L1) and non-native (L2) English speakers completed tasks with IPAs through smartphones and smart speakers. We found significantly higher mental workload for L2 speakers during IPA interactions. Contrary to our hypotheses, we found no significant differences between L1 and L2 speakers in terms of number of turns, lexical complexity, diversity, or lexical adaptation when encountering errors. These findings are discussed in relation to language production and processing load increases for L2 speakers in IPA interaction.
See what I'm saying? Comparing Intelligent Personal Assistant use for Native and Non-Native Language Speakers
Jun 11, 2020
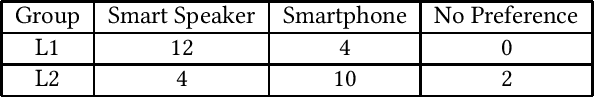
Abstract:Limited linguistic coverage for Intelligent Personal Assistants (IPAs) means that many interact in a non-native language. Yet we know little about how IPAs currently support or hinder these users. Through native (L1) and non-native (L2) English speakers interacting with Google Assistant on a smartphone and smart speaker, we aim to understand this more deeply. Interviews revealed that L2 speakers prioritised utterance planning around perceived linguistic limitations, as opposed to L1 speakers prioritising succinctness because of system limitations. L2 speakers see IPAs as insensitive to linguistic needs resulting in failed interaction. L2 speakers clearly preferred using smartphones, as visual feedback supported diagnoses of communication breakdowns whilst allowing time to process query results. Conversely, L1 speakers preferred smart speakers, with audio feedback being seen as sufficient. We discuss the need to tailor the IPA experience for L2 users, emphasising visual feedback whilst reducing the burden of language production.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge