Cuong Tuan Nguyen
Synthetic Swarm Mosquito Dataset for Acoustic Classification: A Proof of Concept
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Mosquito-borne diseases pose a serious global health threat, causing over 700,000 deaths annually. This work introduces a proof-of-concept Synthetic Swarm Mosquito Dataset for Acoustic Classification, created to simulate realistic multi-species and noisy swarm conditions. Unlike conventional datasets that require labor-intensive recording of individual mosquitoes, the synthetic approach enables scalable data generation while reducing human resource demands. Using log-mel spectrograms, we evaluated lightweight deep learning architectures for the classification of mosquito species. Experiments show that these models can effectively identify six major mosquito vectors and are suitable for deployment on embedded low-power devices. The study demonstrates the potential of synthetic swarm audio datasets to accelerate acoustic mosquito research and enable scalable real-time surveillance solutions.
Fully automatic scoring of handwritten descriptive answers in Japanese language tests
Jan 10, 2022



Abstract:This paper presents an experiment of automatically scoring handwritten descriptive answers in the trial tests for the new Japanese university entrance examination, which were made for about 120,000 examinees in 2017 and 2018. There are about 400,000 answers with more than 20 million characters. Although all answers have been scored by human examiners, handwritten characters are not labelled. We present our attempt to adapt deep neural network-based handwriting recognizers trained on a labelled handwriting dataset into this unlabeled answer set. Our proposed method combines different training strategies, ensembles multiple recognizers, and uses a language model built from a large general corpus to avoid overfitting into specific data. In our experiment, the proposed method records character accuracy of over 97% using about 2,000 verified labelled answers that account for less than 0.5% of the dataset. Then, the recognized answers are fed into a pre-trained automatic scoring system based on the BERT model without correcting misrecognized characters and providing rubric annotations. The automatic scoring system achieves from 0.84 to 0.98 of Quadratic Weighted Kappa (QWK). As QWK is over 0.8, it represents acceptable similarity of scoring between the automatic scoring system and the human examiners. These results are promising for further research on end-to-end automatic scoring of descriptive answers.
A Transformer-based Math Language Model for Handwritten Math Expression Recognition
Aug 11, 2021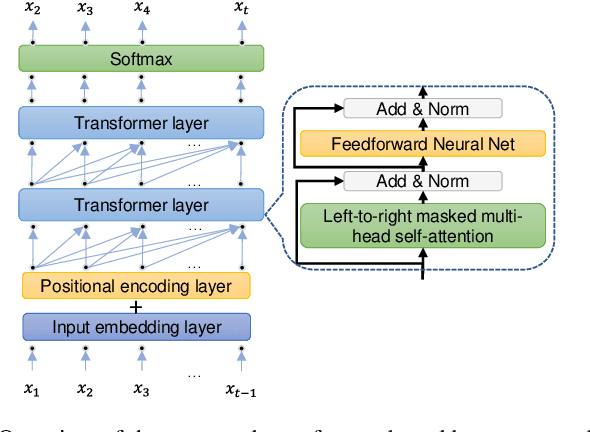
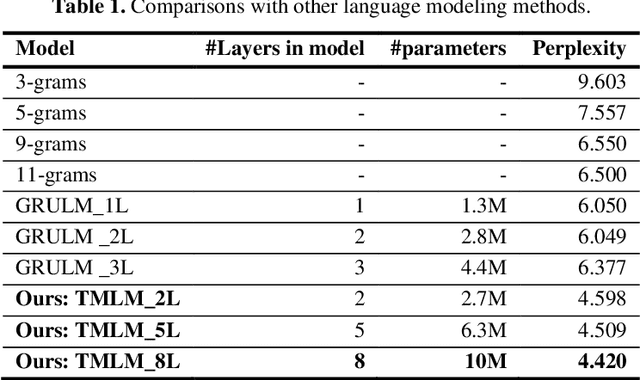
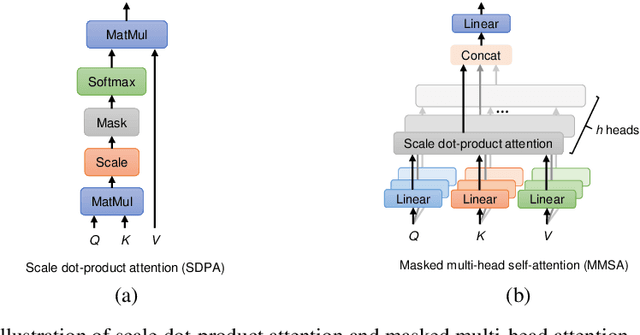

Abstract:Handwritten mathematical expressions (HMEs) contain ambiguities in their interpretations, even for humans sometimes. Several math symbols are very similar in the writing style, such as dot and comma or 0, O, and o, which is a challenge for HME recognition systems to handle without using contextual information. To address this problem, this paper presents a Transformer-based Math Language Model (TMLM). Based on the self-attention mechanism, the high-level representation of an input token in a sequence of tokens is computed by how it is related to the previous tokens. Thus, TMLM can capture long dependencies and correlations among symbols and relations in a mathematical expression (ME). We trained the proposed language model using a corpus of approximately 70,000 LaTeX sequences provided in CROHME 2016. TMLM achieved the perplexity of 4.42, which outperformed the previous math language models, i.e., the N-gram and recurrent neural network-based language models. In addition, we combine TMLM into a stochastic context-free grammar-based HME recognition system using a weighting parameter to re-rank the top-10 best candidates. The expression rates on the testing sets of CROHME 2016 and CROHME 2019 were improved by 2.97 and 0.83 percentage points, respectively.
GSSF: A Generative Sequence Similarity Function based on a Seq2Seq model for clustering online handwritten mathematical answers
May 21, 2021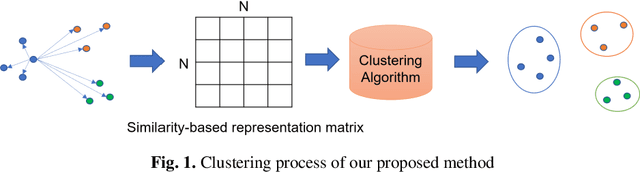
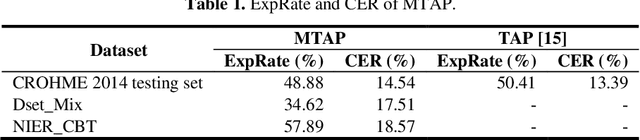
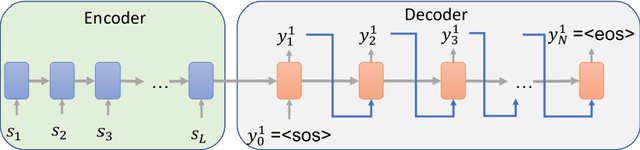
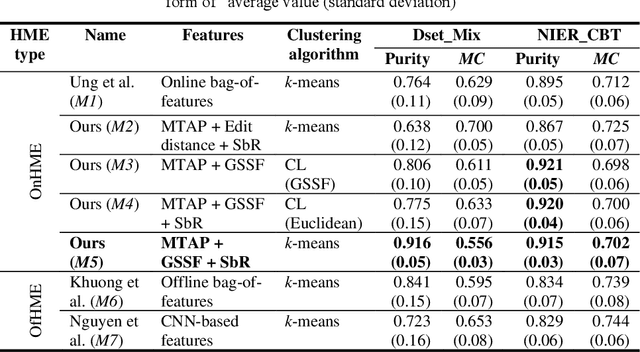
Abstract:Toward a computer-assisted marking for descriptive math questions,this paper presents clustering of online handwritten mathematical expressions (OnHMEs) to help human markers to mark them efficiently and reliably. We propose a generative sequence similarity function for computing a similarity score of two OnHMEs based on a sequence-to-sequence OnHME recognizer. Each OnHME is represented by a similarity-based representation (SbR) vector. The SbR matrix is inputted to the k-means algorithm for clustering OnHMEs. Experiments are conducted on an answer dataset (Dset_Mix) of 200 OnHMEs mixed of real patterns and synthesized patterns for each of 10 questions and a real online handwritten mathematical answer dataset of 122 student answers at most for each of 15 questions (NIER_CBT). The best clustering results achieved around 0.916 and 0.915 for purity, and around 0.556 and 0.702 for the marking cost on Dset_Mix and NIER_CBT, respectively. Our method currently outperforms the previous methods for clustering HMEs.
Global Context for improving recognition of Online Handwritten Mathematical Expressions
May 21, 2021



Abstract:This paper presents a temporal classification method for all three subtasks of symbol segmentation, symbol recognition and relation classification in online handwritten mathematical expressions (HMEs). The classification model is trained by multiple paths of symbols and spatial relations derived from the Symbol Relation Tree (SRT) representation of HMEs. The method benefits from global context of a deep bidirectional Long Short-term Memory network, which learns the temporal classification directly from online handwriting by the Connectionist Temporal Classification loss. To recognize an online HME, a symbol-level parse tree with Context-Free Grammar is constructed, where symbols and spatial relations are obtained from the temporal classification results. We show the effectiveness of the proposed method on the two latest CROHME datasets.
Learning symbol relation tree for online mathematical expression recognition
May 13, 2021



Abstract:This paper proposes a method for recognizing online handwritten mathematical expressions (OnHME) by building a symbol relation tree (SRT) directly from a sequence of strokes. A bidirectional recurrent neural network learns from multiple derived paths of SRT to predict both symbols and spatial relations between symbols using global context. The recognition system has two parts: a temporal classifier and a tree connector. The temporal classifier produces an SRT by recognizing an OnHME pattern. The tree connector splits the SRT into several sub-SRTs. The final SRT is formed by looking up the best combination among those sub-SRTs. Besides, we adopt a tree sorting method to deal with various stroke orders. Recognition experiments indicate that the proposed OnHME recognition system is competitive to other methods. The recognition system achieves 44.12% and 41.76% expression recognition rates on the Competition on Recognition of Online Handwritten Mathematical Expressions (CROHME) 2014 and 2016 testing sets.
Text-independent writer identification using convolutional neural network
Sep 10, 2020



Abstract:The text-independent approach to writer identification does not require the writer to write some predetermined text. Previous research on text-independent writer identification has been based on identifying writer-specific features designed by experts. However, in the last decade, deep learning methods have been successfully applied to learn features from data automatically. We propose here an end-to-end deep-learning method for text-independent writer identification that does not require prior identification of features. A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is trained initially to extract local features, which represent characteristics of individual handwriting in the whole character images and their sub-regions. Randomly sampled tuples of images from the training set are used to train the CNN and aggregate the extracted local features of images from the tuples to form global features. For every training epoch, the process of randomly sampling tuples is repeated, which is equivalent to a large number of training patterns being prepared for training the CNN for text-independent writer identification. We conducted experiments on the JEITA-HP database of offline handwritten Japanese character patterns. With 200 characters, our method achieved an accuracy of 99.97% to classify 100 writers. Even when using 50 characters for 100 writers or 100 characters for 400 writers, our method achieved accuracy levels of 92.80% or 93.82%, respectively. We conducted further experiments on the Firemaker and IAM databases of offline handwritten English text. Using only one page per writer to train, our method achieved over 91.81% accuracy to classify 900 writers. Overall, we achieved a better performance than the previously published best result based on handcrafted features and clustering algorithms, which demonstrates the effectiveness of our method for handwritten English text also.
* 12 pages
Online trajectory recovery from offline handwritten Japanese kanji characters
Sep 09, 2020
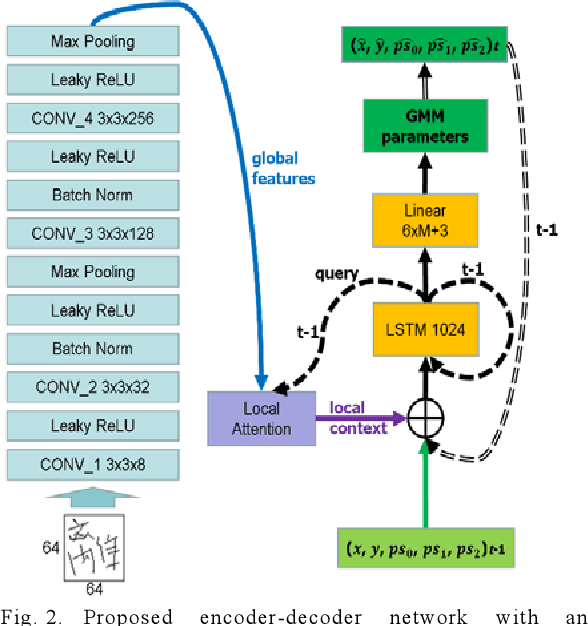
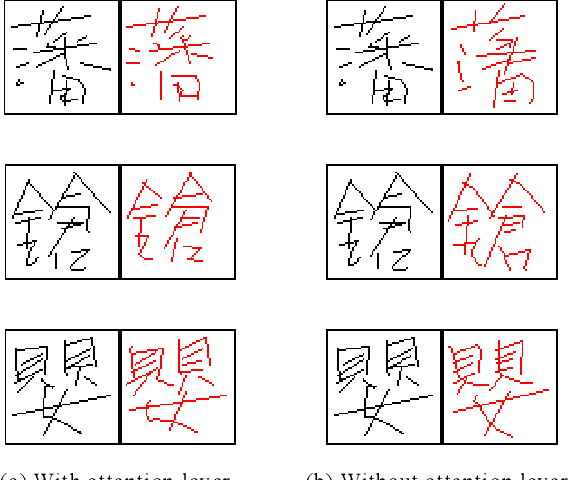
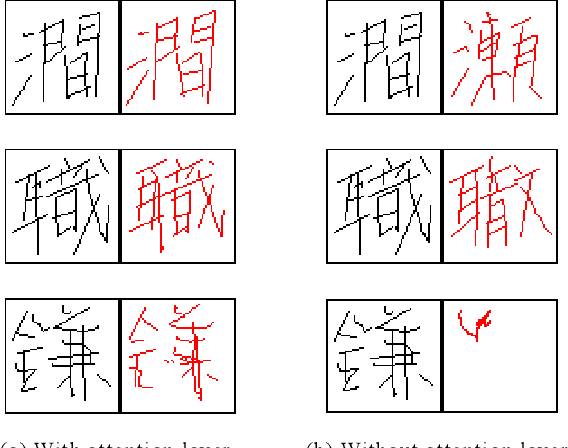
Abstract:In general, it is straightforward to render an offline handwriting image from an online handwriting pattern. However, it is challenging to reconstruct an online handwriting pattern given an offline handwriting image, especially for multiple-stroke character as Japanese kanji. The multiple-stroke character requires not only point coordinates but also stroke orders whose difficulty is exponential growth by the number of strokes. Besides, several crossed and touch points might increase the difficulty of the recovered task. We propose a deep neural network-based method to solve the recovered task using a large online handwriting database. Our proposed model has two main components: Convolutional Neural Network-based encoder and Long Short-Term Memory Network-based decoder with an attention layer. The encoder focuses on feature extraction while the decoder refers to the extracted features and generates the time-sequences of coordinates. We also demonstrate the effect of the attention layer to guide the decoder during the reconstruction. We evaluate the performance of the proposed method by both visual verification and handwritten character recognition. Although the visual verification reveals some problems, the recognition experiments demonstrate the effect of trajectory recovery in improving the accuracy of offline handwritten character recognition when online recognition for the recovered trajectories are combined.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge