Cristina Tîrnăucă
Learning Definite Horn Formulas from Closure Queries
Nov 09, 2015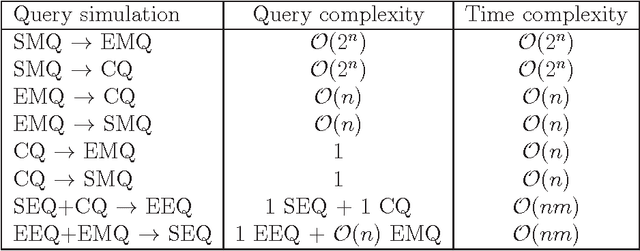
Abstract:A definite Horn theory is a set of n-dimensional Boolean vectors whose characteristic function is expressible as a definite Horn formula, that is, as conjunction of definite Horn clauses. The class of definite Horn theories is known to be learnable under different query learning settings, such as learning from membership and equivalence queries or learning from entailment. We propose yet a different type of query: the closure query. Closure queries are a natural extension of membership queries and also a variant, appropriate in the context of definite Horn formulas, of the so-called correction queries. We present an algorithm that learns conjunctions of definite Horn clauses in polynomial time, using closure and equivalence queries, and show how it relates to the canonical Guigues-Duquenne basis for implicational systems. We also show how the different query models mentioned relate to each other by either showing full-fledged reductions by means of query simulation (where possible), or by showing their connections in the context of particular algorithms that use them for learning definite Horn formulas.
Closed-set-based Discovery of Bases of Association Rules
Mar 24, 2011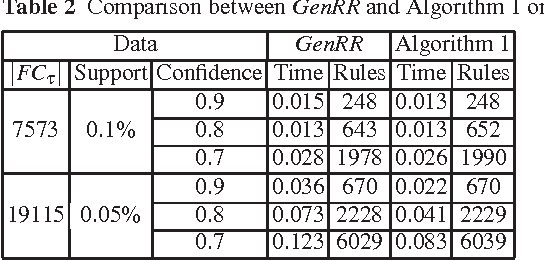
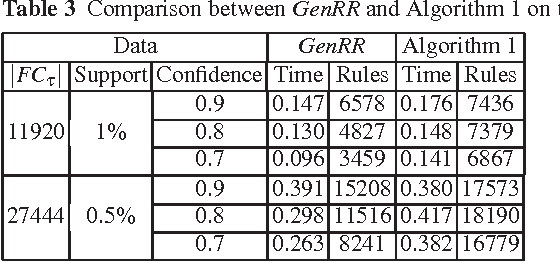
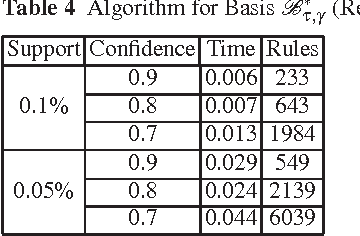
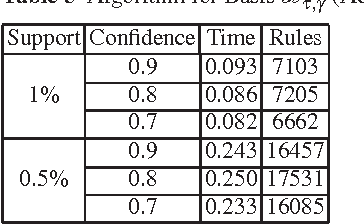
Abstract:The output of an association rule miner is often huge in practice. This is why several concise lossless representations have been proposed, such as the "essential" or "representative" rules. We revisit the algorithm given by Kryszkiewicz (Int. Symp. Intelligent Data Analysis 2001, Springer-Verlag LNCS 2189, 350-359) for mining representative rules. We show that its output is sometimes incomplete, due to an oversight in its mathematical validation. We propose alternative complete generators and we extend the approach to an existing closure-aware basis similar to, and often smaller than, the representative rules, namely the basis B*.
* Shorter version in: Ali Khenchaf and Pascal Poncelet (eds.), Extraction et gestion des connaissances (EGC'2011)
Border Algorithms for Computing Hasse Diagrams of Arbitrary Lattices
Dec 03, 2010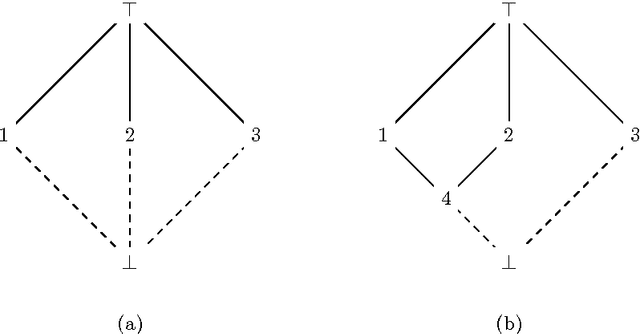
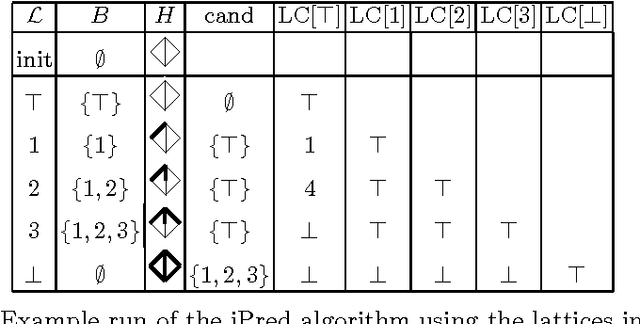
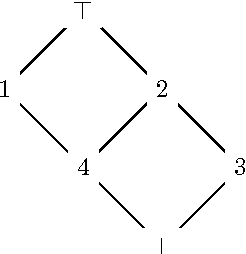
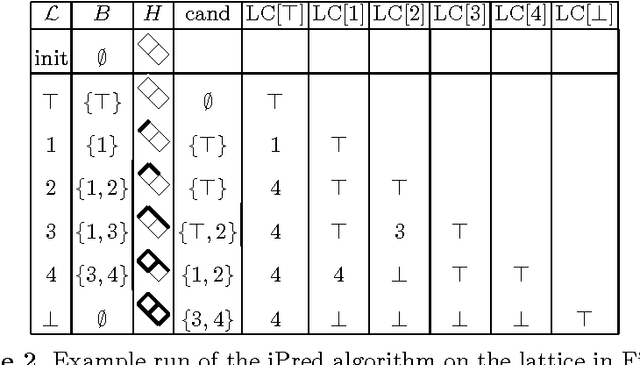
Abstract:The Border algorithm and the iPred algorithm find the Hasse diagrams of FCA lattices. We show that they can be generalized to arbitrary lattices. In the case of iPred, this requires the identification of a join-semilattice homomorphism into a distributive lattice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge