Chuwen Wang
Large Language Models Need Consultants for Reasoning: Becoming an Expert in a Complex Human System Through Behavior Simulation
Mar 27, 2024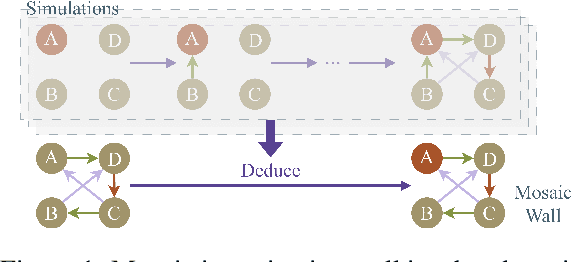
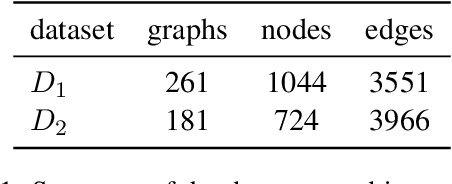
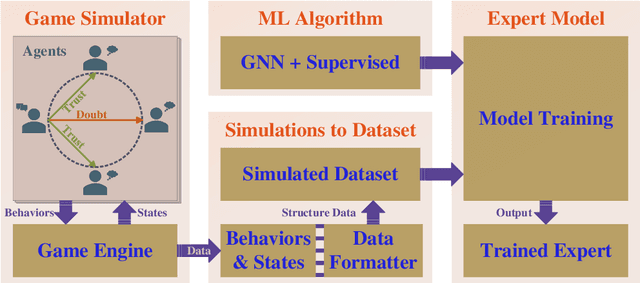
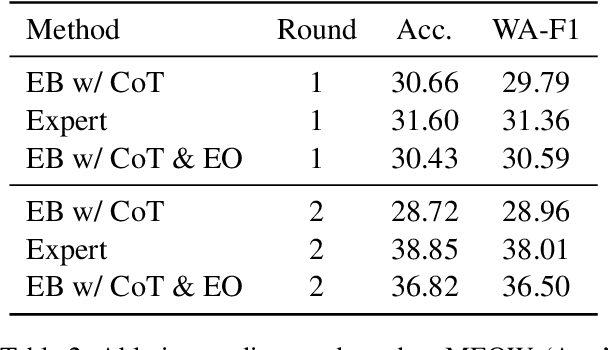
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), in conjunction with various reasoning reinforcement methodologies, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities comparable to humans in fields such as mathematics, law, coding, common sense, and world knowledge. In this paper, we delve into the reasoning abilities of LLMs within complex human systems. We propose a novel reasoning framework, termed ``Mosaic Expert Observation Wall'' (MEOW) exploiting generative-agents-based simulation technique. In the MEOW framework, simulated data are utilized to train an expert model concentrating ``experience'' about a specific task in each independent time of simulation. It is the accumulated ``experience'' through the simulation that makes for an expert on a task in a complex human system. We conduct the experiments within a communication game that mirrors real-world security scenarios. The results indicate that our proposed methodology can cooperate with existing methodologies to enhance the reasoning abilities of LLMs in complex human systems.
Behavioral Simulation: Exploring A Possible Next Paradigm for Science
Jan 18, 2024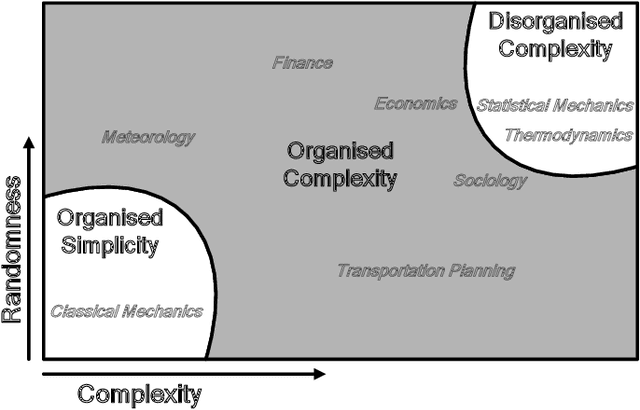
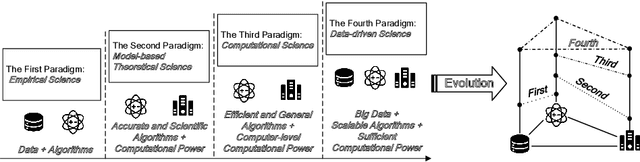
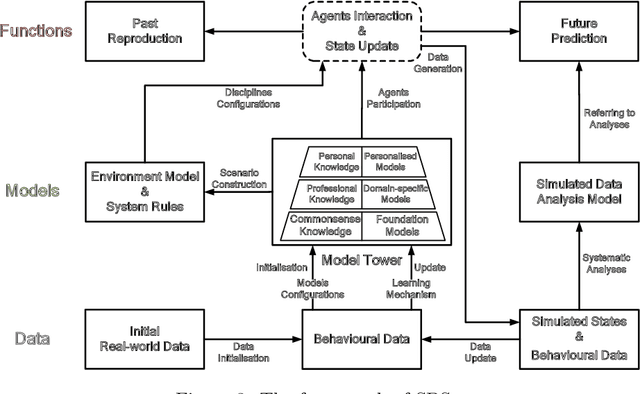
Abstract:Simulation technologies have been widely utilized in many scientific research fields such as weather forecasting, fluid mechanics and biological populations. It is the best tool to handle problems in complex systems, where closed-form expressions are unavailable and the target distribution in the representation space is too complex to be fully represented by a deep learning (DL) model. We believe that the development of simulation technologies is consistent with scientific paradigms. This paper induces the evolution of scientific paradigms from the perspective of data, algorithms, and computational power. Building upon this perspective, we divide simulation technologies into three stages aligning with the emergence of new paradigms, and find that advanced simulation technologies are typical instances of paradigms integration. Moreover, we propose the concept of behavioral simulation (BS), specifically sophisticated behavioral simulation (SBS), representing a higher degree of paradigms integration based on foundation models to simulate complex social systems involving sophisticated human strategies and behaviors. BS and further SBS are designed to tackle challenges concerning the complex human system that surpasses the capacity of traditional agent-based modeling simulation (ABMS), which can be regarded as a possible next paradigm for science. Through this work, we look forward to more powerful BS and SBS applications in scientific research branches within social science.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge