Chunhao Cai
Uncertainty-based Network for Few-shot Image Classification
May 17, 2022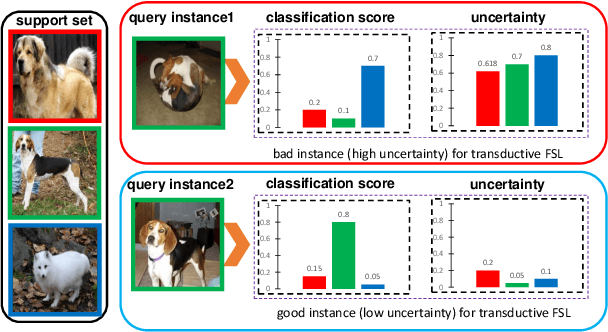
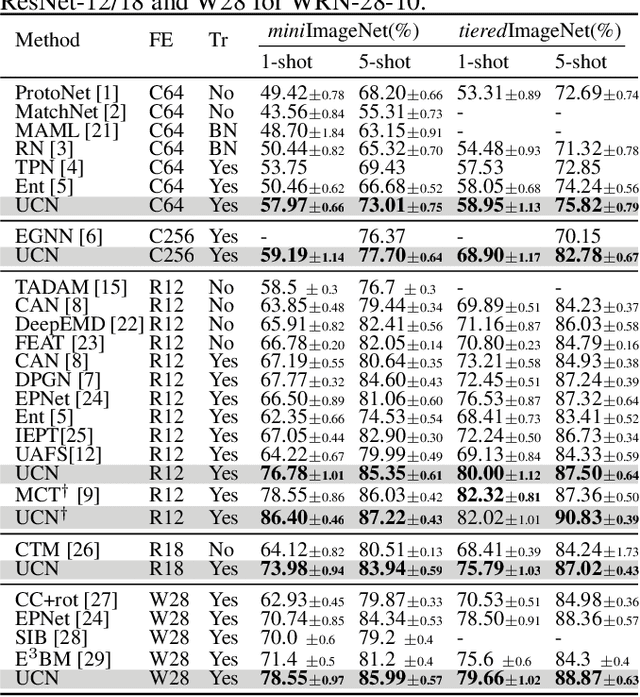
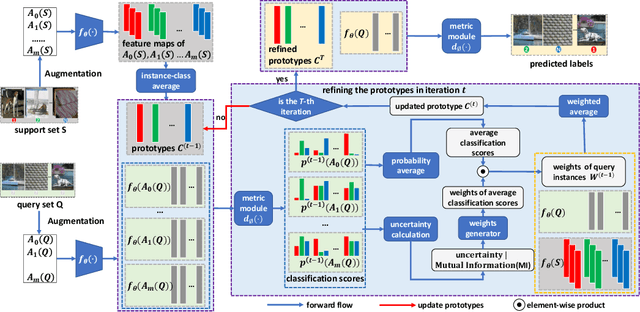
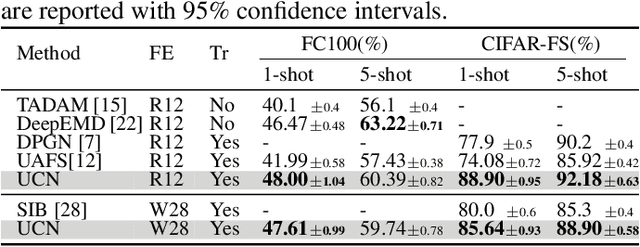
Abstract:The transductive inference is an effective technique in the few-shot learning task, where query sets update prototypes to improve themselves. However, these methods optimize the model by considering only the classification scores of the query instances as confidence while ignoring the uncertainty of these classification scores. In this paper, we propose a novel method called Uncertainty-Based Network, which models the uncertainty of classification results with the help of mutual information. Specifically, we first data augment and classify the query instance and calculate the mutual information of these classification scores. Then, mutual information is used as uncertainty to assign weights to classification scores, and the iterative update strategy based on classification scores and uncertainties assigns the optimal weights to query instances in prototype optimization. Extensive results on four benchmarks show that Uncertainty-Based Network achieves comparable performance in classification accuracy compared to state-of-the-art method.
Learning Class-level Prototypes for Few-shot Learning
Aug 25, 2021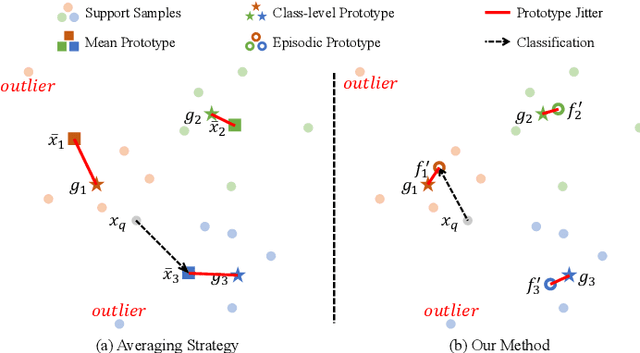
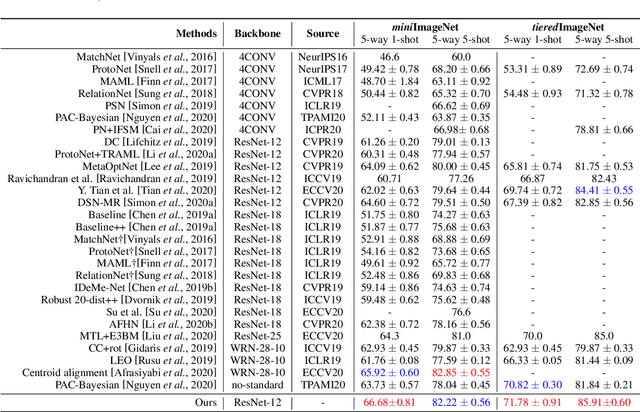
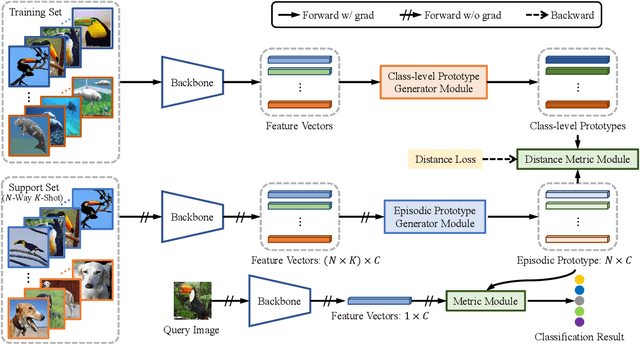
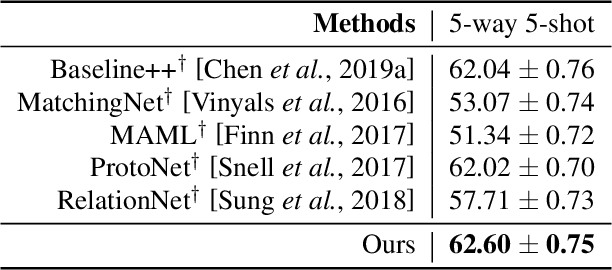
Abstract:Few-shot learning aims to recognize new categories using very few labeled samples. Although few-shot learning has witnessed promising development in recent years, most existing methods adopt an average operation to calculate prototypes, thus limited by the outlier samples. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective framework for few-shot classification, which can learn to generate preferable prototypes from few support data, with the help of an episodic prototype generator module. The generated prototype is meant to be close to a certain \textit{\targetproto{}} and is less influenced by outlier samples. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of this module, and our approach gets a significant raise over baseline models, and get a competitive result compared to previous methods on \textit{mini}ImageNet, \textit{tiered}ImageNet, and cross-domain (\textit{mini}ImageNet $\rightarrow$ CUB-200-2011) datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge