Christopher X. Ren
Learning Continuous Exponential Families Beyond Gaussian
Feb 18, 2021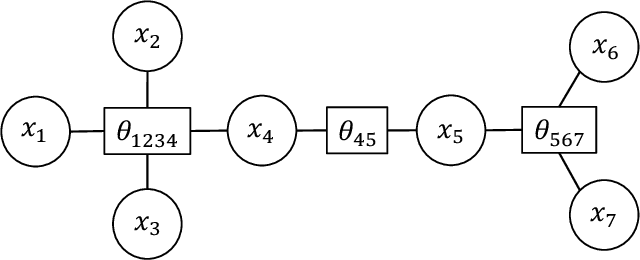
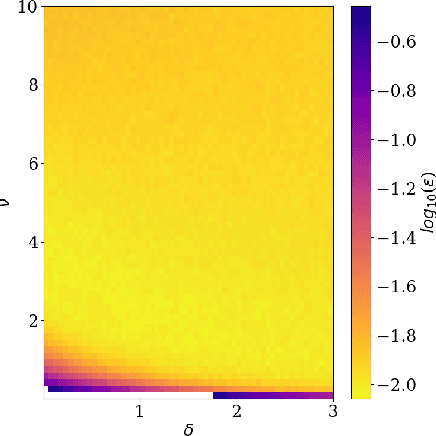
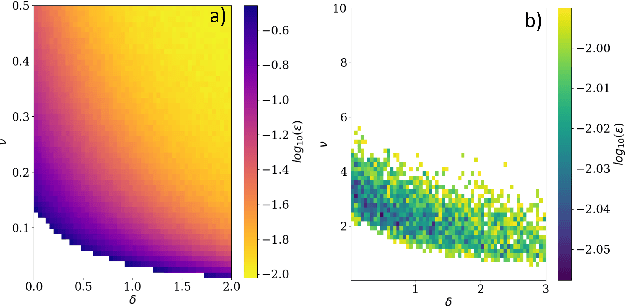
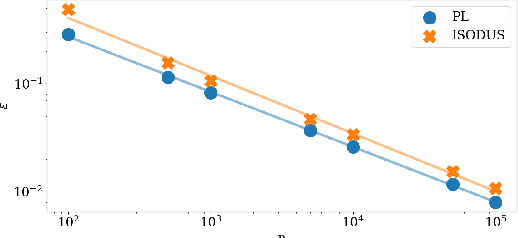
Abstract:We address the problem of learning of continuous exponential family distributions with unbounded support. While a lot of progress has been made on learning of Gaussian graphical models, we are still lacking scalable algorithms for reconstructing general continuous exponential families modeling higher-order moments of the data beyond the mean and the covariance. Here, we introduce a computationally efficient method for learning continuous graphical models based on the Interaction Screening approach. Through a series of numerical experiments, we show that our estimator maintains similar requirements in terms of accuracy and sample complexity compared to alternative approaches such as maximization of conditional likelihood, while considerably improving upon the algorithm's run-time.
Deep Snow: Synthesizing Remote Sensing Imagery with Generative Adversarial Nets
May 18, 2020Abstract:In this work we demonstrate that generative adversarial networks (GANs) can be used to generate realistic pervasive changes in remote sensing imagery, even in an unpaired training setting. We investigate some transformation quality metrics based on deep embedding of the generated and real images which enable visualization and understanding of the training dynamics of the GAN, and may provide a useful measure in terms of quantifying how distinguishable the generated images are from real images. We also identify some artifacts introduced by the GAN in the generated images, which are likely to contribute to the differences seen between the real and generated samples in the deep embedding feature space even in cases where the real and generated samples appear perceptually similar.
Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks for Realistic Pervasive Change Generation in Remote Sensing Imagery
Dec 08, 2019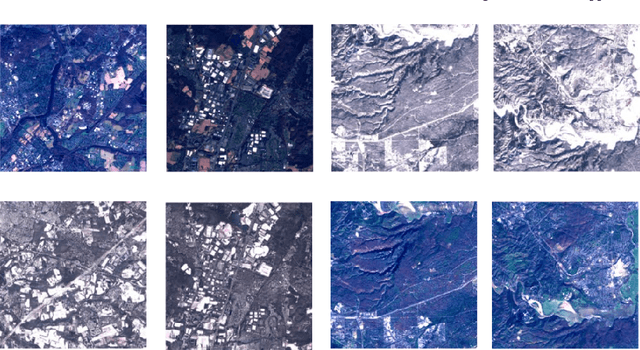
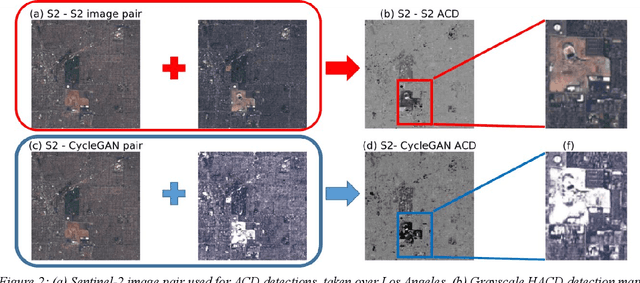
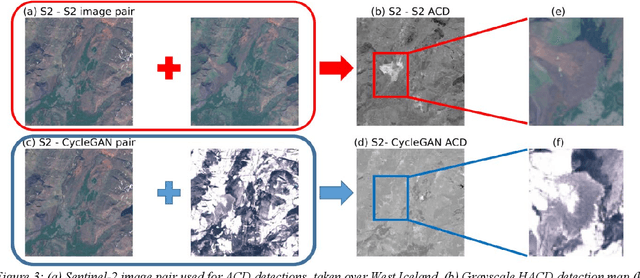
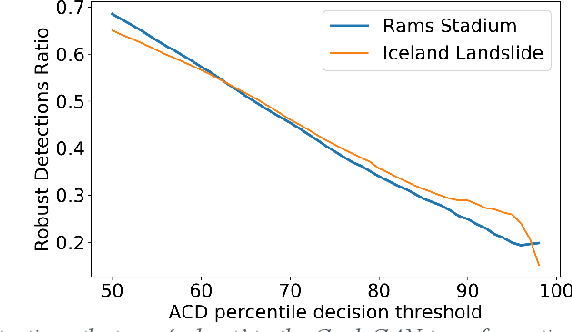
Abstract:This paper introduces a new method of generating realistic pervasive changes in the context of evaluating the effectiveness of change detection algorithms in controlled settings. The method, a cycle-consistent adversarial network (CycleGAN), requires low quantities of training data to generate realistic changes. Here we show an application of CycleGAN in creating realistic snow-covered scenes of multispectral Sentinel-2 imagery, and demonstrate how these images can be used as a test bed for anomalous change detection algorithms.
Feature Augmentation Improves Anomalous Change Detection for Human Activity Identification in Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery
Dec 07, 2019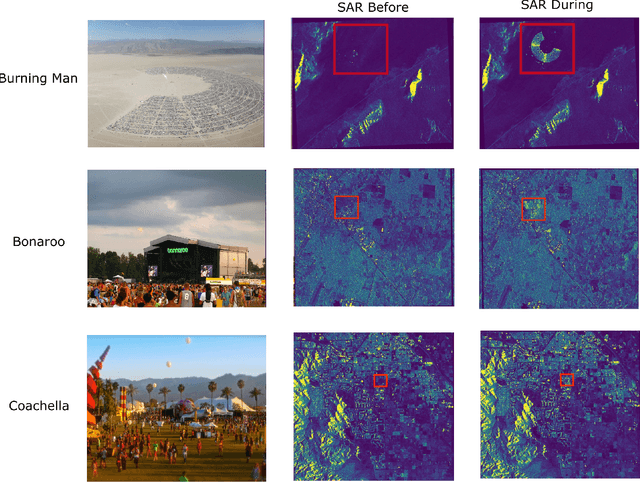
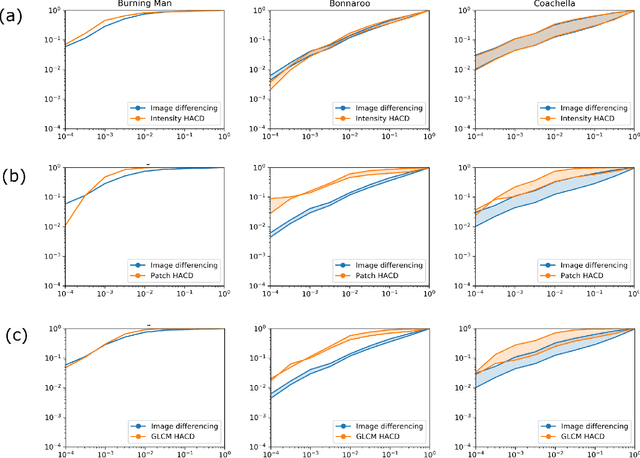
Abstract:Anomalous change detection (ACD) methods separate common, uninteresting changes from rare, significant changes in co-registered images collected at different points in time. In this paper we evaluate methods to improve the performance of ACD in detecting human activity in SAR imagery using outdoor music festivals as a target. Our results show that the low dimensionality of SAR data leads to poor performance of ACD when compared to simpler methods such as image differencing, but augmenting the dimensionality of our input feature space by incorporating local spatial information leads to enhanced performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge