Christopher Hench
The Massively Multilingual Natural Language Understanding 2022 (MMNLU-22) Workshop and Competition
Dec 13, 2022Abstract:Despite recent progress in Natural Language Understanding (NLU), the creation of multilingual NLU systems remains a challenge. It is common to have NLU systems limited to a subset of languages due to lack of available data. They also often vary widely in performance. We launch a three-phase approach to address the limitations in NLU and help propel NLU technology to new heights. We release a 52 language dataset called the Multilingual Amazon SLU resource package (SLURP) for Slot-filling, Intent classification, and Virtual assistant Evaluation, or MASSIVE, in an effort to address parallel data availability for voice assistants. We organize the Massively Multilingual NLU 2022 Challenge to provide a competitive environment and push the state-of-the art in the transferability of models into other languages. Finally, we host the first Massively Multilingual NLU workshop which brings these components together. The MMNLU workshop seeks to advance the science behind multilingual NLU by providing a platform for the presentation of new research in the field and connecting teams working on this research direction. This paper summarizes the dataset, workshop and the competition and the findings of each phase.
* 5 pages
MASSIVE: A 1M-Example Multilingual Natural Language Understanding Dataset with 51 Typologically-Diverse Languages
Apr 18, 2022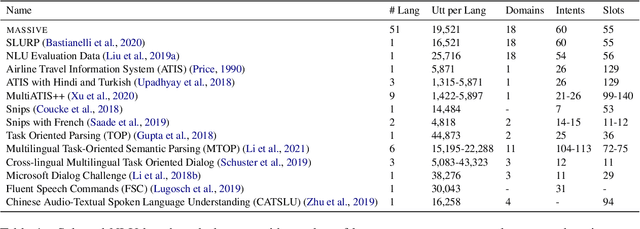
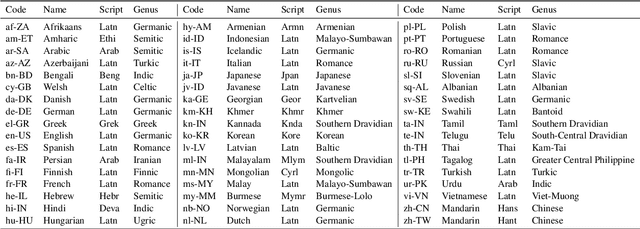
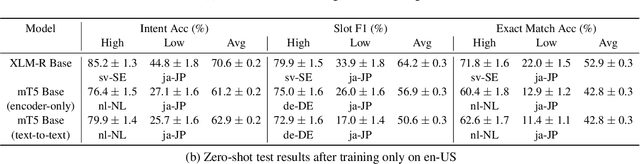

Abstract:We present the MASSIVE dataset--Multilingual Amazon Slu resource package (SLURP) for Slot-filling, Intent classification, and Virtual assistant Evaluation. MASSIVE contains 1M realistic, parallel, labeled virtual assistant utterances spanning 51 languages, 18 domains, 60 intents, and 55 slots. MASSIVE was created by tasking professional translators to localize the English-only SLURP dataset into 50 typologically diverse languages from 29 genera. We also present modeling results on XLM-R and mT5, including exact match accuracy, intent classification accuracy, and slot-filling F1 score. We have released our dataset, modeling code, and models publicly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge