Christian Straßer
Ranking-based Argumentation Semantics Applied to Logical Argumentation (full version)
Jul 31, 2023

Abstract:In formal argumentation, a distinction can be made between extension-based semantics, where sets of arguments are either (jointly) accepted or not, and ranking-based semantics, where grades of acceptability are assigned to arguments. Another important distinction is that between abstract approaches, that abstract away from the content of arguments, and structured approaches, that specify a method of constructing argument graphs on the basis of a knowledge base. While ranking-based semantics have been extensively applied to abstract argumentation, few work has been done on ranking-based semantics for structured argumentation. In this paper, we make a systematic investigation into the behaviour of ranking-based semantics applied to existing formalisms for structured argumentation. We show that a wide class of ranking-based semantics gives rise to so-called culpability measures, and are relatively robust to specific choices in argument construction methods.
Relevance in Structured Argumentation
Sep 13, 2018Abstract:We study properties related to relevance in non-monotonic consequence relations obtained by systems of structured argumentation. Relevance desiderata concern the robustness of a consequence relation under the addition of irrelevant information. For an account of what (ir)relevance amounts to we use syntactic and semantic considerations. Syntactic criteria have been proposed in the domain of relevance logic and were recently used in argumentation theory under the names of non-interference and crash-resistance. The basic idea is that the conclusions of a given argumentative theory should be robust under adding information that shares no propositional variables with the original database. Some semantic relevance criteria are known from non-monotonic logic. For instance, cautious monotony states that if we obtain certain conclusions from an argumentation theory, we may expect to still obtain the same conclusions if we add some of them to the given database. In this paper we investigate properties of structured argumentation systems that warrant relevance desiderata.
Assumption-Based Approaches to Reasoning with Priorities
Sep 29, 2017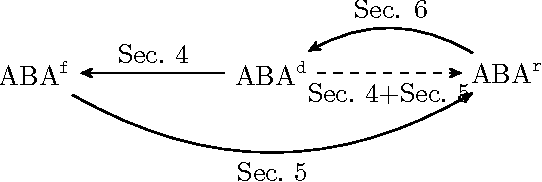
Abstract:This paper maps out the relation between different approaches for handling preferences in argumentation with strict rules and defeasible assumptions by offering translations between them. The systems we compare are: non-prioritized defeats i.e. attacks, preference-based defeats, and preference-based defeats extended with reverse defeat.
Reasoning by Cases in Structured Argumentation
Mar 24, 2017Abstract:We extend the $ASPIC^+$ framework for structured argumentation so as to allow applications of the reasoning by cases inference scheme for defeasible arguments. Given an argument with conclusion `$A$ or $B$', an argument based on $A$ with conclusion $C$, and an argument based on $B$ with conclusion $C$, we allow the construction of an argument with conclusion $C$. We show how our framework leads to different results than other approaches in non-monotonic logic for dealing with disjunctive information, such as disjunctive default theory or approaches based on the OR-rule (which allows to derive a defeasible rule `If ($A$ or $B$) then $C$', given two defeasible rules `If $A$ then $C$' and `If $B$ then $C$'). We raise new questions regarding the subtleties of reasoning defeasibly with disjunctive information, and show that its formalization is more intricate than one would presume.
An argumentative agent-based model of scientific inquiry
Dec 13, 2016


Abstract:In this paper we present an agent-based model (ABM) of scientific inquiry aimed at investigating how different social networks impact the efficiency of scientists in acquiring knowledge. As such, the ABM is a computational tool for tackling issues in the domain of scientific methodology and science policy. In contrast to existing ABMs of science, our model aims to represent the argumentative dynamics that underlies scientific practice. To this end we employ abstract argumentation theory as the core design feature of the model. This helps to avoid a number of problematic idealizations which are present in other ABMs of science and which impede their relevance for actual scientific practice.
A structured argumentation framework for detaching conditional obligations
Jun 01, 2016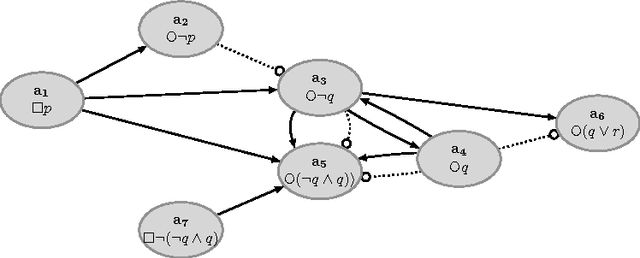
Abstract:We present a general formal argumentation system for dealing with the detachment of conditional obligations. Given a set of facts, constraints, and conditional obligations, we answer the question whether an unconditional obligation is detachable by considering reasons for and against its detachment. For the evaluation of arguments in favor of detaching obligations we use a Dung-style argumentation-theoretical semantics. We illustrate the modularity of the general framework by considering some extensions, and we compare the framework to some related approaches from the literature.
Relations between assumption-based approaches in nonmonotonic logic and formal argumentation
Apr 01, 2016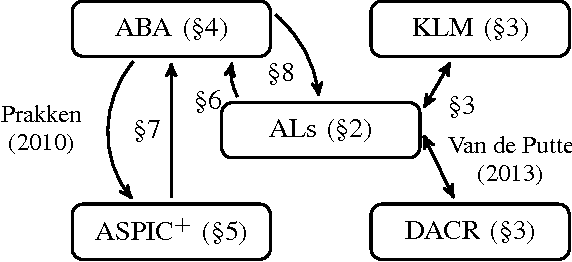
Abstract:In this paper we make a contribution to the unification of formal models of defeasible reasoning. We present several translations between formal argumentation frameworks and nonmonotonic logics for reasoning with plausible assumptions. More specifically, we translate adaptive logics into assumption-based argumentation and ASPIC+, ASPIC+ into assumption-based argumentation and a fragment of assumption-based argumentation into adaptive logics. Adaptive logics are closely related to Makinson's default assumptions and to a significant class of systems within the tradition of preferential semantics in the vein of KLM and Shoham. Thus, our results also provide close links between formal argumentation and the latter approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge