Chrisantus Eze
Data-Driven Fairness Generalization for Deepfake Detection
Dec 31, 2024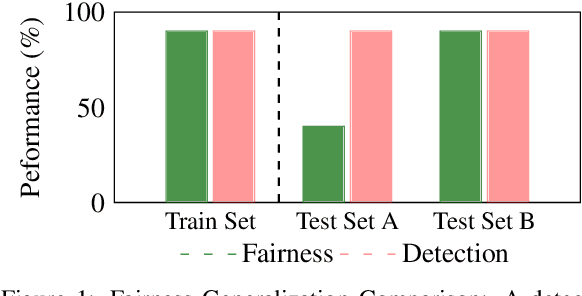
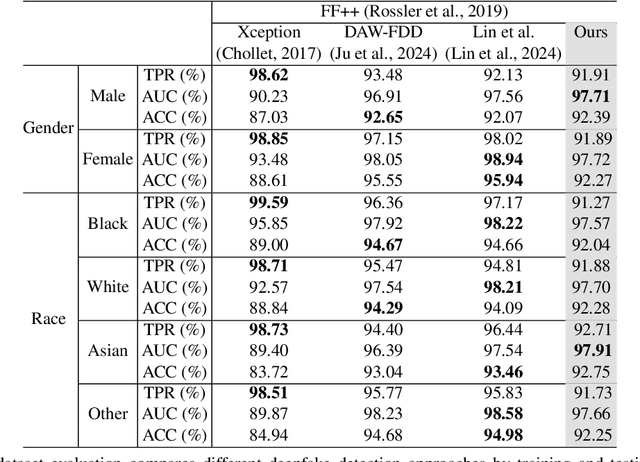

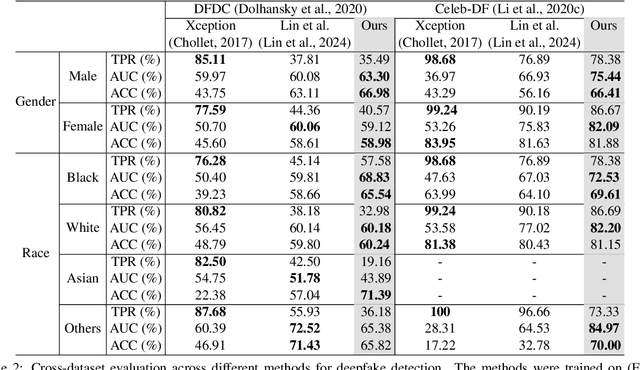
Abstract:Despite the progress made in deepfake detection research, recent studies have shown that biases in the training data for these detectors can result in varying levels of performance across different demographic groups, such as race and gender. These disparities can lead to certain groups being unfairly targeted or excluded. Traditional methods often rely on fair loss functions to address these issues, but they under-perform when applied to unseen datasets, hence, fairness generalization remains a challenge. In this work, we propose a data-driven framework for tackling the fairness generalization problem in deepfake detection by leveraging synthetic datasets and model optimization. Our approach focuses on generating and utilizing synthetic data to enhance fairness across diverse demographic groups. By creating a diverse set of synthetic samples that represent various demographic groups, we ensure that our model is trained on a balanced and representative dataset. This approach allows us to generalize fairness more effectively across different domains. We employ a comprehensive strategy that leverages synthetic data, a loss sharpness-aware optimization pipeline, and a multi-task learning framework to create a more equitable training environment, which helps maintain fairness across both intra-dataset and cross-dataset evaluations. Extensive experiments on benchmark deepfake detection datasets demonstrate the efficacy of our approach, surpassing state-of-the-art approaches in preserving fairness during cross-dataset evaluation. Our results highlight the potential of synthetic datasets in achieving fairness generalization, providing a robust solution for the challenges faced in deepfake detection.
Deepfake detection, image manipulation detection, fairness, generalization
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:Despite the progress made in deepfake detection research, recent studies have shown that biases in the training data for these detectors can result in varying levels of performance across different demographic groups, such as race and gender. These disparities can lead to certain groups being unfairly targeted or excluded. Traditional methods often rely on fair loss functions to address these issues, but they under-perform when applied to unseen datasets, hence, fairness generalization remains a challenge. In this work, we propose a data-driven framework for tackling the fairness generalization problem in deepfake detection by leveraging synthetic datasets and model optimization. Our approach focuses on generating and utilizing synthetic data to enhance fairness across diverse demographic groups. By creating a diverse set of synthetic samples that represent various demographic groups, we ensure that our model is trained on a balanced and representative dataset. This approach allows us to generalize fairness more effectively across different domains. We employ a comprehensive strategy that leverages synthetic data, a loss sharpness-aware optimization pipeline, and a multi-task learning framework to create a more equitable training environment, which helps maintain fairness across both intra-dataset and cross-dataset evaluations. Extensive experiments on benchmark deepfake detection datasets demonstrate the efficacy of our approach, surpassing state-of-the-art approaches in preserving fairness during cross-dataset evaluation. Our results highlight the potential of synthetic datasets in achieving fairness generalization, providing a robust solution for the challenges faced in deepfake detection.
A3: Active Adversarial Alignment for Source-Free Domain Adaptation
Sep 27, 2024



Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) aims to transfer knowledge from a labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain. Recent works have focused on source-free UDA, where only target data is available. This is challenging as models rely on noisy pseudo-labels and struggle with distribution shifts. We propose Active Adversarial Alignment (A3), a novel framework combining self-supervised learning, adversarial training, and active learning for robust source-free UDA. A3 actively samples informative and diverse data using an acquisition function for training. It adapts models via adversarial losses and consistency regularization, aligning distributions without source data access. A3 advances source-free UDA through its synergistic integration of active and adversarial learning for effective domain alignment and noise reduction.
Learning by Watching: A Review of Video-based Learning Approaches for Robot Manipulation
Feb 11, 2024Abstract:Robot learning of manipulation skills is hindered by the scarcity of diverse, unbiased datasets. While curated datasets can help, challenges remain in generalizability and real-world transfer. Meanwhile, large-scale "in-the-wild" video datasets have driven progress in computer vision through self-supervised techniques. Translating this to robotics, recent works have explored learning manipulation skills by passively watching abundant videos sourced online. Showing promising results, such video-based learning paradigms provide scalable supervision while reducing dataset bias. This survey reviews foundations such as video feature representation learning techniques, object affordance understanding, 3D hand/body modeling, and large-scale robot resources, as well as emerging techniques for acquiring robot manipulation skills from uncontrolled video demonstrations. We discuss how learning only from observing large-scale human videos can enhance generalization and sample efficiency for robotic manipulation. The survey summarizes video-based learning approaches, analyses their benefits over standard datasets, survey metrics, and benchmarks, and discusses open challenges and future directions in this nascent domain at the intersection of computer vision, natural language processing, and robot learning.
Internet of Things Meets Robotics: A Survey of Cloud-based Robots
Jun 08, 2023Abstract:This work presents a survey of existing literature on the fusion of the Internet of Things (IoT) with robotics and explores the integration of these technologies for the development of the Internet of Robotics Things (IoRT). The survey focuses on the applications of IoRT in healthcare and agriculture, while also addressing key concerns regarding the adoption of IoT and robotics. Additionally, an online survey was conducted to examine how companies utilize IoT technology in their organizations. The findings highlight the benefits of IoT in improving customer experience, reducing costs, and accelerating product development. However, concerns regarding unauthorized access, data breaches, and privacy need to be addressed for successful IoT deployment.
Enhancing Human-robot Collaboration by Exploring Intuitive Augmented Reality Design Representations
Mar 09, 2023



Abstract:As the use of Augmented Reality (AR) to enhance interactions between human agents and robotic systems in a work environment continues to grow, robots must communicate their intents in informative yet straightforward ways. This improves the human agent's feeling of trust and safety in the work environment while also reducing task completion time. To this end, we discuss a set of guidelines for the systematic design of AR interfaces for Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) systems. Furthermore, we develop design frameworks that would ride on these guidelines and serve as a base for researchers seeking to explore this direction further. We develop a series of designs for visually representing the robot's planned path and reactions, which we evaluate by conducting a user survey involving 14 participants. Subjects were given different design representations to review and rate based on their intuitiveness and informativeness. The collated results showed that our design representations significantly improved the participants' ease of understanding the robot's intents over the baselines for the robot's proposed navigation path, planned arm trajectory, and reactions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge