Chengzuo Qi
Unsupervised Semantic-based Aggregation of Deep Convolutional Features
Apr 03, 2018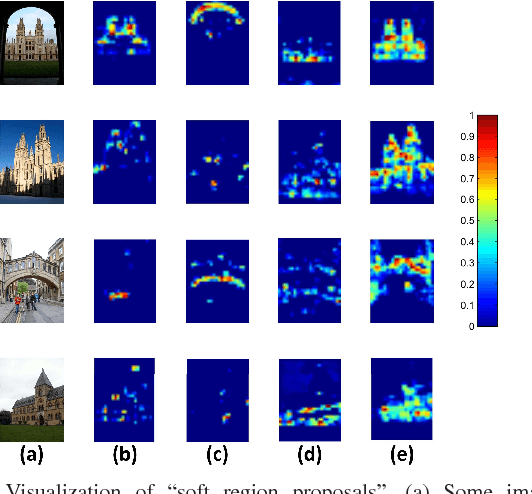
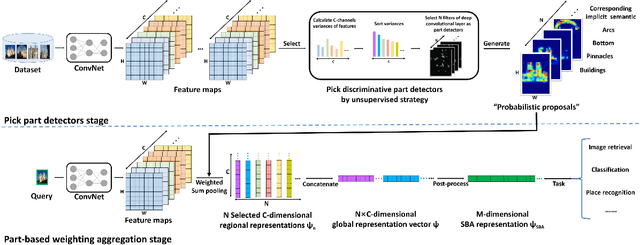

Abstract:In this paper, we propose a simple but effective semantic-based aggregation (SBA) method. The proposed SBA utilizes the discriminative filters of deep convolutional layers as semantic detectors. Moreover, we propose the effective unsupervised strategy to select some semantic detectors to generate the "probabilistic proposals", which highlight certain discriminative pattern of objects and suppress the noise of background. The final global SBA representation could then be acquired by aggregating the regional representations weighted by the selected "probabilistic proposals" corresponding to various semantic content. Our unsupervised SBA is easy to generalize and achieves excellent performance on various tasks. We conduct comprehensive experiments and show that our unsupervised SBA outperforms the state-of-the-art unsupervised and supervised aggregation methods on image retrieval, place recognition and cloud classification.
Iterative Manifold Embedding Layer Learned by Incomplete Data for Large-scale Image Retrieval
Apr 03, 2018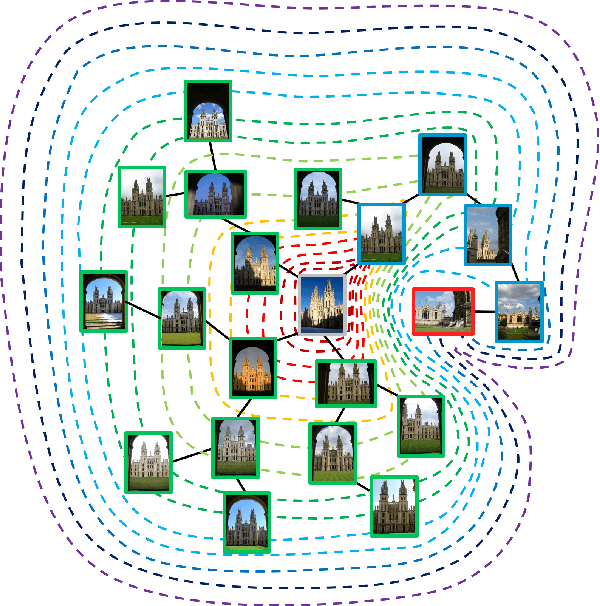
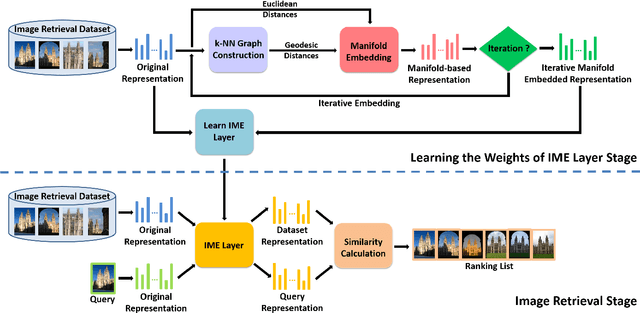
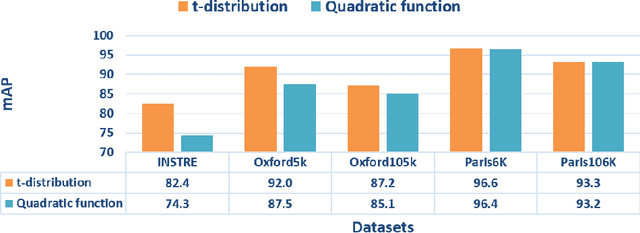
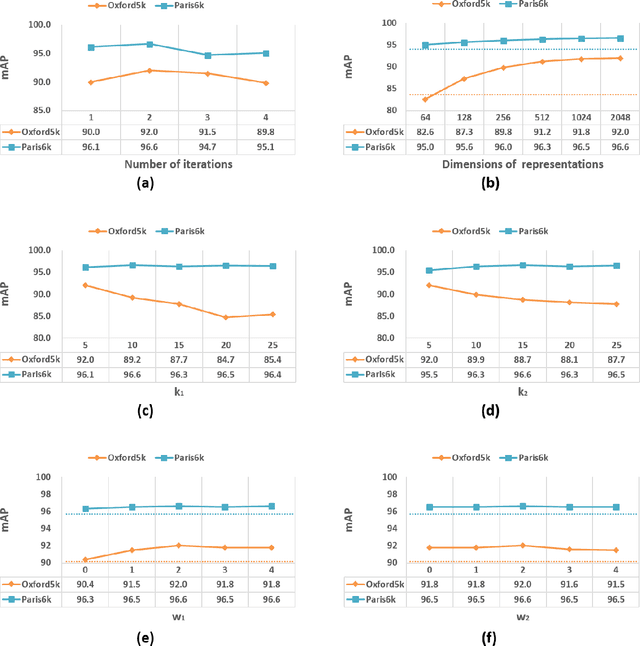
Abstract:Existing manifold learning methods are not appropriate for image retrieval task, because most of them are unable to process query image and they have much additional computational cost especially for large scale database. Therefore, we propose the iterative manifold embedding (IME) layer, of which the weights are learned off-line by unsupervised strategy, to explore the intrinsic manifolds by incomplete data. On the large scale database that contains 27000 images, IME layer is more than 120 times faster than other manifold learning methods to embed the original representations at query time. We embed the original descriptors of database images which lie on manifold in a high dimensional space into manifold-based representations iteratively to generate the IME representations in off-line learning stage. According to the original descriptors and the IME representations of database images, we estimate the weights of IME layer by ridge regression. In on-line retrieval stage, we employ the IME layer to map the original representation of query image with ignorable time cost (2 milliseconds). We experiment on five public standard datasets for image retrieval. The proposed IME layer significantly outperforms related dimension reduction methods and manifold learning methods. Without post-processing, Our IME layer achieves a boost in performance of state-of-the-art image retrieval methods with post-processing on most datasets, and needs less computational cost.
Unsupervised Part-based Weighting Aggregation of Deep Convolutional Features for Image Retrieval
Nov 29, 2017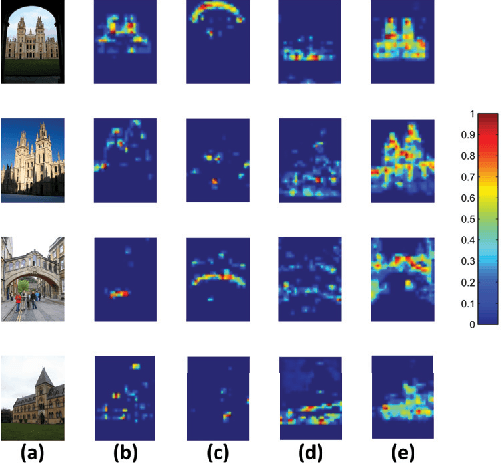
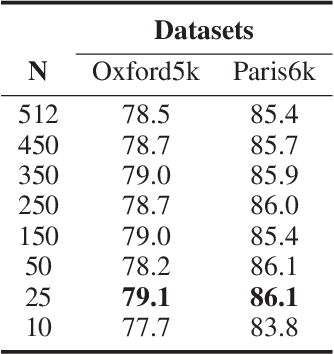
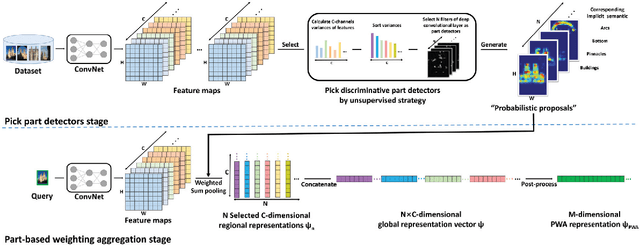
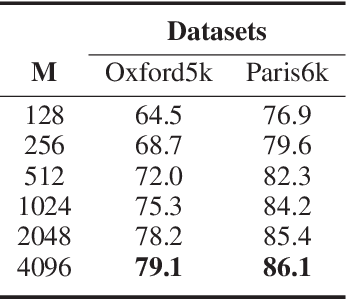
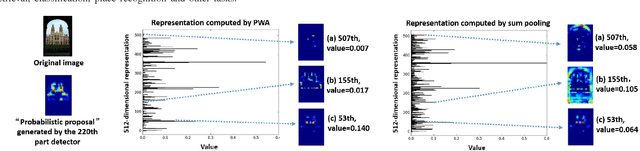
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a simple but effective semantic part-based weighting aggregation (PWA) for image retrieval. The proposed PWA utilizes the discriminative filters of deep convolutional layers as part detectors. Moreover, we propose the effective unsupervised strategy to select some part detectors to generate the "probabilistic proposals", which highlight certain discriminative parts of objects and suppress the noise of background. The final global PWA representation could then be acquired by aggregating the regional representations weighted by the selected "probabilistic proposals" corresponding to various semantic content. We conduct comprehensive experiments on four standard datasets and show that our unsupervised PWA outperforms the state-of-the-art unsupervised and supervised aggregation methods. Code is available at https://github.com/XJhaoren/PWA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge