Chenggong Zhang
Web World Models
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Language agents increasingly require persistent worlds in which they can act, remember, and learn. Existing approaches sit at two extremes: conventional web frameworks provide reliable but fixed contexts backed by databases, while fully generative world models aim for unlimited environments at the expense of controllability and practical engineering. In this work, we introduce the Web World Model (WWM), a middle ground where world state and ``physics'' are implemented in ordinary web code to ensure logical consistency, while large language models generate context, narratives, and high-level decisions on top of this structured latent state. We build a suite of WWMs on a realistic web stack, including an infinite travel atlas grounded in real geography, fictional galaxy explorers, web-scale encyclopedic and narrative worlds, and simulation- and game-like environments. Across these systems, we identify practical design principles for WWMs: separating code-defined rules from model-driven imagination, representing latent state as typed web interfaces, and utilizing deterministic generation to achieve unlimited but structured exploration. Our results suggest that web stacks themselves can serve as a scalable substrate for world models, enabling controllable yet open-ended environments. Project Page: https://github.com/Princeton-AI2-Lab/Web-World-Models.
Hallucination Detection and Evaluation of Large Language Model
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Hallucinations in Large Language Models (LLMs) pose a significant challenge, generating misleading or unverifiable content that undermines trust and reliability. Existing evaluation methods, such as KnowHalu, employ multi-stage verification but suffer from high computational costs. To address this, we integrate the Hughes Hallucination Evaluation Model (HHEM), a lightweight classification-based framework that operates independently of LLM-based judgments, significantly improving efficiency while maintaining high detection accuracy. We conduct a comparative analysis of hallucination detection methods across various LLMs, evaluating True Positive Rate (TPR), True Negative Rate (TNR), and Accuracy on question-answering (QA) and summarization tasks. Our results show that HHEM reduces evaluation time from 8 hours to 10 minutes, while HHEM with non-fabrication checking achieves the highest accuracy \(82.2\%\) and TPR \(78.9\%\). However, HHEM struggles with localized hallucinations in summarization tasks. To address this, we introduce segment-based retrieval, improving detection by verifying smaller text components. Additionally, our cumulative distribution function (CDF) analysis indicates that larger models (7B-9B parameters) generally exhibit fewer hallucinations, while intermediate-sized models show higher instability. These findings highlight the need for structured evaluation frameworks that balance computational efficiency with robust factual validation, enhancing the reliability of LLM-generated content.
Teacher-Student Network for Real-World Face Super-Resolution with Progressive Embedding of Edge Information
May 08, 2024



Abstract:Traditional face super-resolution (FSR) methods trained on synthetic datasets usually have poor generalization ability for real-world face images. Recent work has utilized complex degradation models or training networks to simulate the real degradation process, but this limits the performance of these methods due to the domain differences that still exist between the generated low-resolution images and the real low-resolution images. Moreover, because of the existence of a domain gap, the semantic feature information of the target domain may be affected when synthetic data and real data are utilized to train super-resolution models simultaneously. In this study, a real-world face super-resolution teacher-student model is proposed, which considers the domain gap between real and synthetic data and progressively includes diverse edge information by using the recurrent network's intermediate outputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed approach surpasses state-of-the-art methods in obtaining high-quality face images for real-world FSR.
Face Super-Resolution with Progressive Embedding of Multi-scale Face Priors
Oct 12, 2022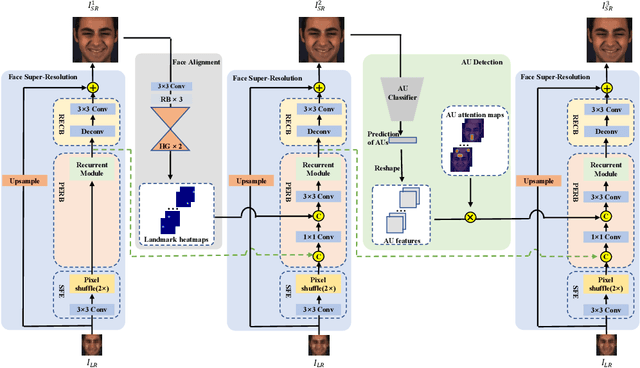
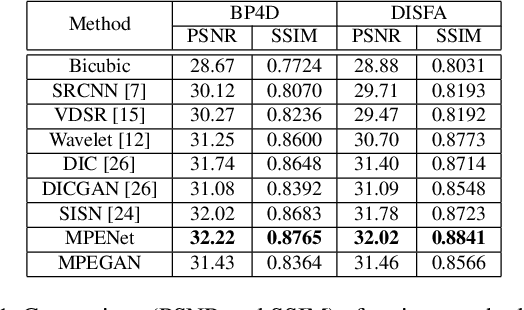

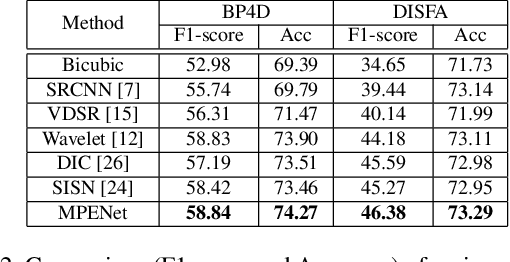
Abstract:The face super-resolution (FSR) task is to reconstruct high-resolution face images from low-resolution inputs. Recent works have achieved success on this task by utilizing facial priors such as facial landmarks. Most existing methods pay more attention to global shape and structure information, but less to local texture information, which makes them cannot recover local details well. In this paper, we propose a novel recurrent convolutional network based framework for face super-resolution, which progressively introduces both global shape and local texture information. We take full advantage of the intermediate outputs of the recurrent network, and landmarks information and facial action units (AUs) information are extracted in the output of the first and second steps respectively, rather than low-resolution input. Moreover, we introduced AU classification results as a novel quantitative metric for facial details restoration. Extensive experiments show that our proposed method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art FSR methods in terms of image quality and facial details restoration.
Action Unit Detection with Joint Adaptive Attention and Graph Relation
Jul 09, 2021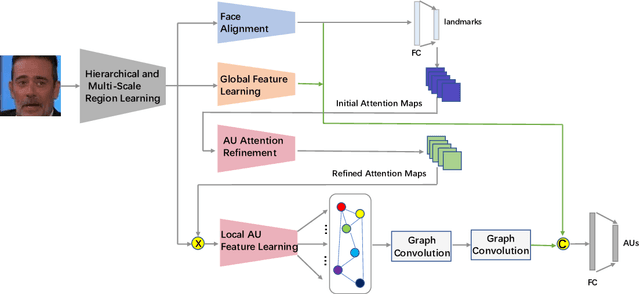
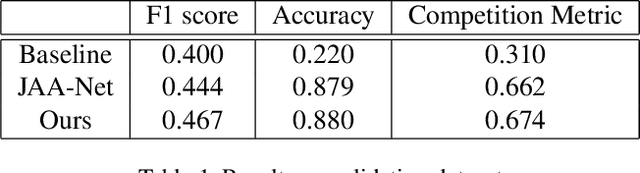
Abstract:This paper describes an approach to the facial action unit (AU) detection. In this work, we present our submission to the Field Affective Behavior Analysis (ABAW) 2021 competition. The proposed method uses the pre-trained JAA model as the feature extractor, and extracts global features, face alignment features and AU local features on the basis of multi-scale features. We take the AU local features as the input of the graph convolution to further consider the correlation between AU, and finally use the fused features to classify AU. The detected accuracy was evaluated by 0.5*accuracy + 0.5*F1. Our model achieves 0.674 on the challenging Aff-Wild2 database.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge