Changan Niu
CrossCodeBench: Benchmarking Cross-Task Generalization of Source Code Models
Feb 10, 2023



Abstract:Despite the recent advances showing that a model pre-trained on large-scale source code data is able to gain appreciable generalization capability, it still requires a sizeable amount of data on the target task for fine-tuning. And the effectiveness of the model generalization is largely affected by the size and quality of the fine-tuning data, which is detrimental for target tasks with limited or unavailable resources. Therefore, cross-task generalization, with the goal of improving the generalization of the model to unseen tasks that have not been seen before, is of strong research and application value. In this paper, we propose a large-scale benchmark that includes 216 existing code-related tasks. Then, we annotate each task with the corresponding meta information such as task description and instruction, which contains detailed information about the task and a solution guide. This also helps us to easily create a wide variety of ``training/evaluation'' task splits to evaluate the various cross-task generalization capabilities of the model. Then we perform some preliminary experiments to demonstrate that the cross-task generalization of models can be largely improved by in-context learning methods such as few-shot learning and learning from task instructions, which shows the promising prospects of conducting cross-task learning research on our benchmark. We hope that the collection of the datasets and our benchmark will facilitate future work that is not limited to cross-task generalization.
Deep Learning Meets Software Engineering: A Survey on Pre-Trained Models of Source Code
May 24, 2022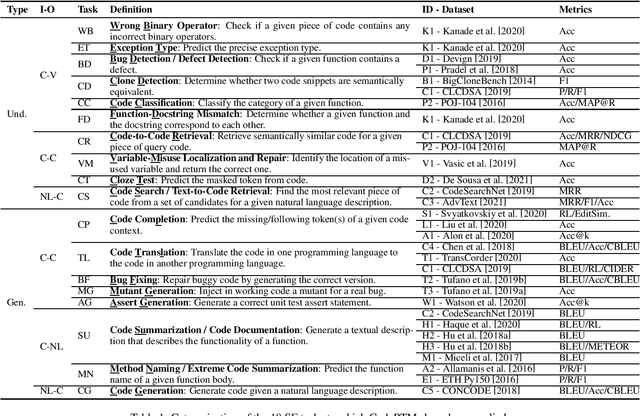
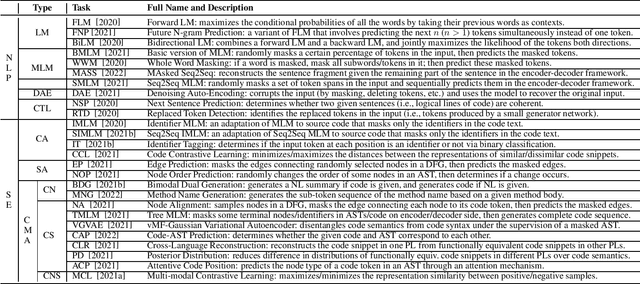

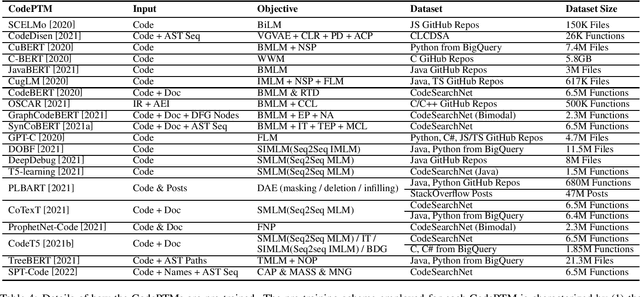
Abstract:Recent years have seen the successful application of deep learning to software engineering (SE). In particular, the development and use of pre-trained models of source code has enabled state-of-the-art results to be achieved on a wide variety of SE tasks. This paper provides an overview of this rapidly advancing field of research and reflects on future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge