Chandra Sekhara Rao Annavarapu
A Graph Convolutional Neural Network based Framework for Estimating Future Citations Count of Research Articles
Apr 11, 2021



Abstract:Scientific publications play a vital role in the career of a researcher. However, some articles become more popular than others among the research community and subsequently drive future research directions. One of the indicative signs of popular articles is the number of citations an article receives. The citation count, which is also the basis with various other metrics, such as the journal impact factor score, the $h$-index, is an essential measure for assessing a scientific paper's quality. In this work, we proposed a Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) based framework for estimating future research publication citations for both the short-term (1-year) and long-term (for 5-years and 10-years) duration. We have tested our proposed approach over the AMiner dataset, specifically on research articles from the computer science domain, consisting of more than 0.8 million articles.
U-Det: A Modified U-Net architecture with bidirectional feature network for lung nodule segmentation
Mar 20, 2020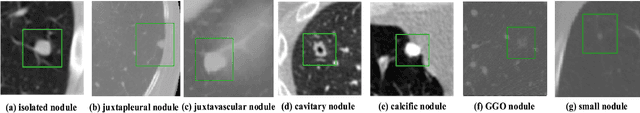
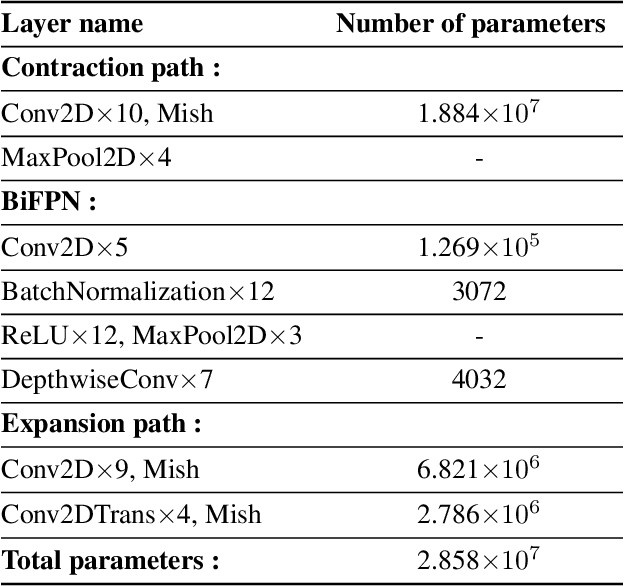
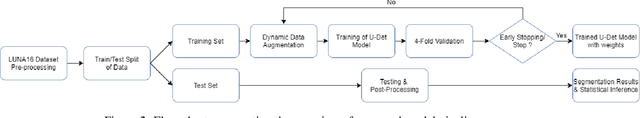
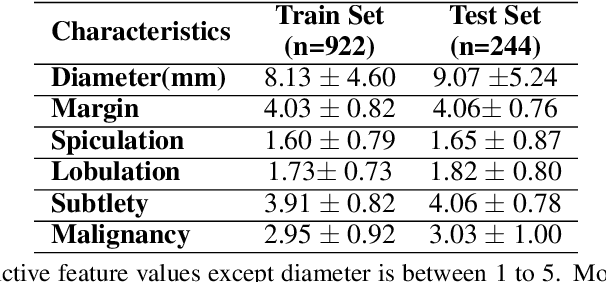
Abstract:Early diagnosis and analysis of lung cancer involve a precise and efficient lung nodule segmentation in computed tomography (CT) images. However, the anonymous shapes, visual features, and surroundings of the nodule in the CT image pose a challenging problem to the robust segmentation of the lung nodules. This article proposes U-Det, a resource-efficient model architecture, which is an end to end deep learning approach to solve the task at hand. It incorporates a Bi-FPN (bidirectional feature network) between the encoder and decoder. Furthermore, it uses Mish activation function and class weights of masks to enhance segmentation efficiency. The proposed model is extensively trained and evaluated on the publicly available LUNA-16 dataset consisting of 1186 lung nodules. The U-Det architecture outperforms the existing U-Net model with the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 82.82% and achieves results comparable to human experts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge