Canyu Yang
Semi- and Self-Supervised Multi-View Fusion of 3D Microscopy Images using Generative Adversarial Networks
Aug 05, 2021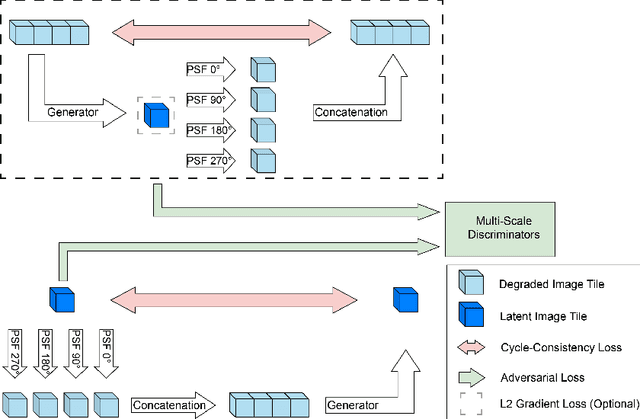
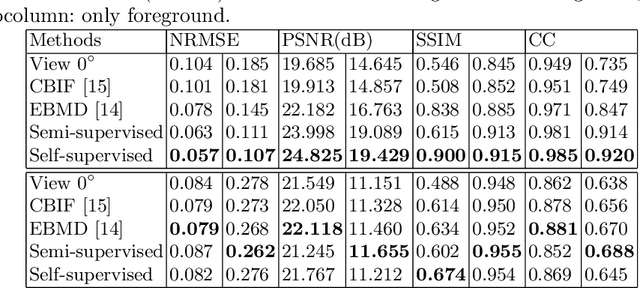
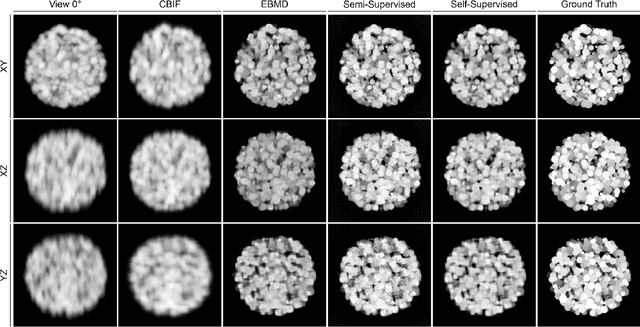
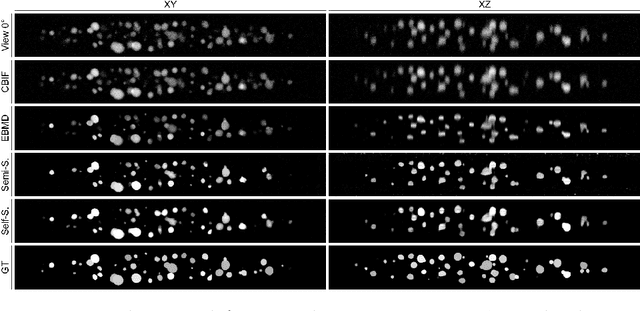
Abstract:Recent developments in fluorescence microscopy allow capturing high-resolution 3D images over time for living model organisms. To be able to image even large specimens, techniques like multi-view light-sheet imaging record different orientations at each time point that can then be fused into a single high-quality volume. Based on measured point spread functions (PSF), deconvolution and content fusion are able to largely revert the inevitable degradation occurring during the imaging process. Classical multi-view deconvolution and fusion methods mainly use iterative procedures and content-based averaging. Lately, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have been deployed to approach 3D single-view deconvolution microscopy, but the multi-view case waits to be studied. We investigated the efficacy of CNN-based multi-view deconvolution and fusion with two synthetic data sets that mimic developing embryos and involve either two or four complementary 3D views. Compared with classical state-of-the-art methods, the proposed semi- and self-supervised models achieve competitive and superior deconvolution and fusion quality in the two-view and quad-view cases, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge