C. Emre Koksal
Bi-Level Online Provisioning and Scheduling with Switching Costs and Cross-Level Constraints
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:We study a bi-level online provisioning and scheduling problem motivated by network resource allocation, where provisioning decisions are made at a slow time scale while queue-/state-dependent scheduling is performed at a fast time scale. We model this two-time-scale interaction using an upper-level online convex optimization (OCO) problem and a lower-level constrained Markov decision process (CMDP). Existing OCO typically assumes stateless decisions and thus cannot capture MDP network dynamics such as queue evolution. Meanwhile, CMDP algorithms typically assume a fixed constraint threshold, whereas in provisioning-and-scheduling systems, the threshold varies with online budget decisions. To address these gaps, we study bi-level OCO-CMDP learning under switching costs (budget reprovisioning/system reconfiguration) and cross-level constraints that couple budgets to scheduling decisions. Our new algorithm solves this learning problem via several non-trivial developments, including a carefully designed dual feedback that returns the budget multiplier as sensitivity information for the upper-level update and a lower level that solves a budget-adaptive safe exploration problem via an extended occupancy-measure linear program. We establish near-optimal regret and high-probability satisfaction of the cross-level constraints.
Quickest Detection over Sensor Networks with Unknown Post-Change Distribution
Dec 23, 2020
Abstract:We propose a quickest change detection problem over sensor networks where both the subset of sensors undergoing a change and the local post-change distributions are unknown. Each sensor in the network observes a local discrete time random process over a finite alphabet. Initially, the observations are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) with known pre-change distributions independent from other sensors. At a fixed but unknown change point, a fixed but unknown subset of the sensors undergo a change and start observing samples from an unknown distribution. We assume the change can be quantified using concave (or convex) local statistics over the space of distributions. We propose an asymptotically optimal and computationally tractable stopping time for Lorden's criterion. Under this scenario, our proposed method uses a concave global cumulative sum (CUSUM) statistic at the fusion center and suppresses the most likely false alarms using information projection. Finally, we show some numerical results of the simulation of our algorithm for the problem described.
Source Coding Based mmWave Channel Estimation with Deep Learning Based Decoding
Apr 30, 2019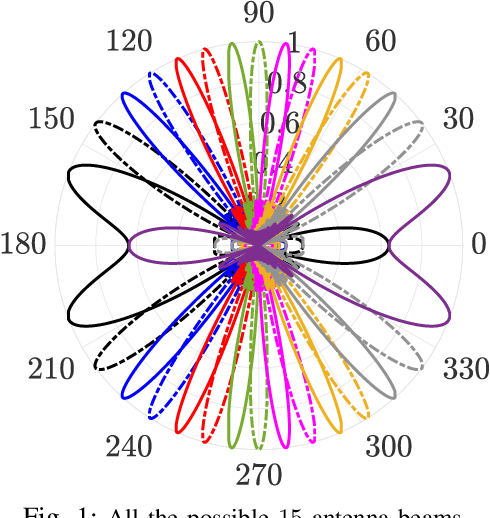
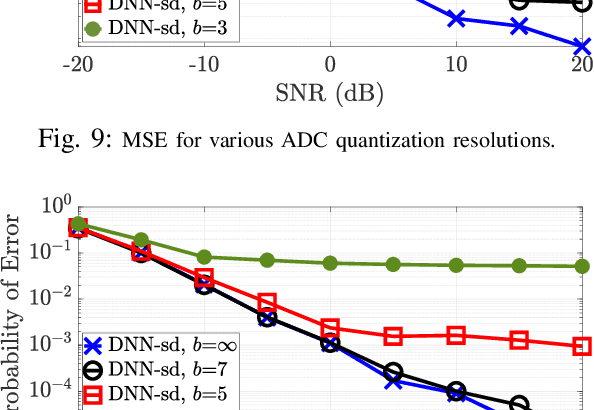
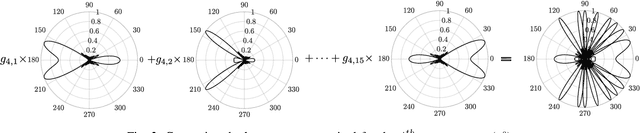
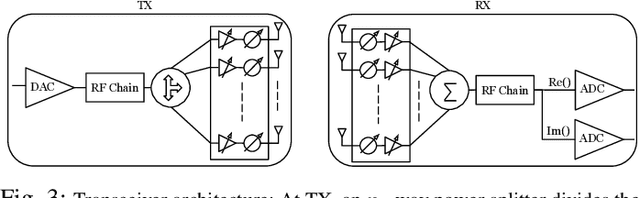
Abstract:mmWave technology is set to become a main feature of next generation wireless networks, e.g., 5G mobile and WiFi 802.11ad/ay. Among the basic and most fundamental challenges facing mmWave is the ability to overcome its unfavorable propagation characteristics using energy efficient solutions. This has been addressed using innovative transceiver architectures. However, these architectures have their own limitations when it comes to channel estimation. This paper focuses on channel estimation and poses it as a source compression problem, where channel measurements are designed to mimic an encoded (compressed) version of the channel. We show that linear source codes can significantly reduce the number of channel measurements required to discover all channel paths. We also propose a deep-learning-based approach for decoding the obtained measurements, which enables high-speed and efficient channel discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge