Brian Litt
University of Pennsylvania
Modeling the Complex Dynamics and Changing Correlations of Epileptic Events
Jul 14, 2014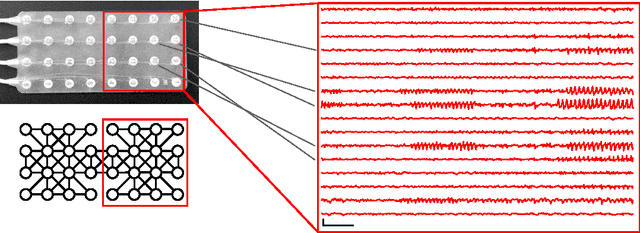
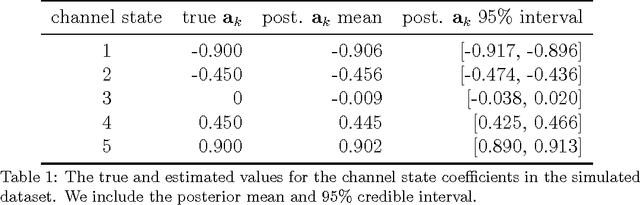
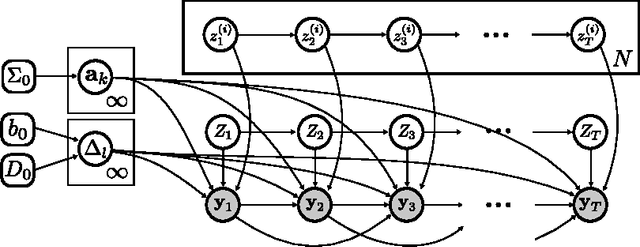
Abstract:Patients with epilepsy can manifest short, sub-clinical epileptic "bursts" in addition to full-blown clinical seizures. We believe the relationship between these two classes of events---something not previously studied quantitatively---could yield important insights into the nature and intrinsic dynamics of seizures. A goal of our work is to parse these complex epileptic events into distinct dynamic regimes. A challenge posed by the intracranial EEG (iEEG) data we study is the fact that the number and placement of electrodes can vary between patients. We develop a Bayesian nonparametric Markov switching process that allows for (i) shared dynamic regimes between a variable number of channels, (ii) asynchronous regime-switching, and (iii) an unknown dictionary of dynamic regimes. We encode a sparse and changing set of dependencies between the channels using a Markov-switching Gaussian graphical model for the innovations process driving the channel dynamics and demonstrate the importance of this model in parsing and out-of-sample predictions of iEEG data. We show that our model produces intuitive state assignments that can help automate clinical analysis of seizures and enable the comparison of sub-clinical bursts and full clinical seizures.
A Hierarchical Dirichlet Process Model with Multiple Levels of Clustering for Human EEG Seizure Modeling
Jun 18, 2012



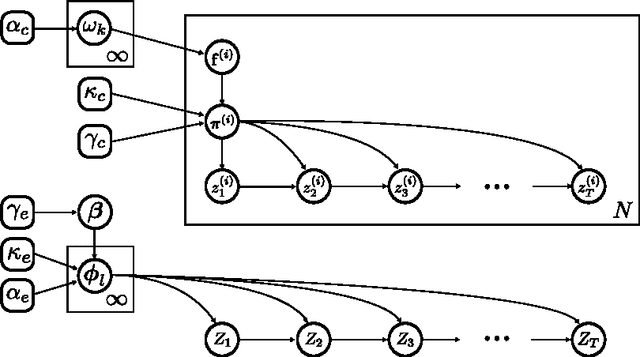
Abstract:Driven by the multi-level structure of human intracranial electroencephalogram (iEEG) recordings of epileptic seizures, we introduce a new variant of a hierarchical Dirichlet Process---the multi-level clustering hierarchical Dirichlet Process (MLC-HDP)---that simultaneously clusters datasets on multiple levels. Our seizure dataset contains brain activity recorded in typically more than a hundred individual channels for each seizure of each patient. The MLC-HDP model clusters over channels-types, seizure-types, and patient-types simultaneously. We describe this model and its implementation in detail. We also present the results of a simulation study comparing the MLC-HDP to a similar model, the Nested Dirichlet Process and finally demonstrate the MLC-HDP's use in modeling seizures across multiple patients. We find the MLC-HDP's clustering to be comparable to independent human physician clusterings. To our knowledge, the MLC-HDP model is the first in the epilepsy literature capable of clustering seizures within and between patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge