Brian Kunzer
The Digital Twin Landscape at the Crossroads of Predictive Maintenance, Machine Learning and Physics Based Modeling
Jun 23, 2022


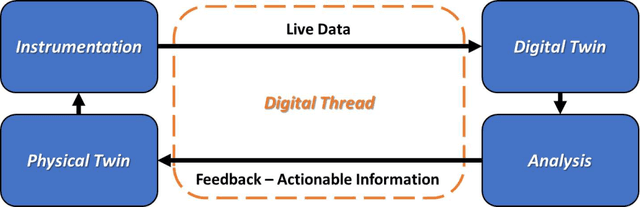
Abstract:The concept of a digital twin has exploded in popularity over the past decade, yet confusion around its plurality of definitions, its novelty as a new technology, and its practical applicability still exists, all despite numerous reviews, surveys, and press releases. The history of the term digital twin is explored, as well as its initial context in the fields of product life cycle management, asset maintenance, and equipment fleet management, operations, and planning. A definition for a minimally viable framework to utilize a digital twin is also provided based on seven essential elements. A brief tour through DT applications and industries where DT methods are employed is also outlined. The application of a digital twin framework is highlighted in the field of predictive maintenance, and its extensions utilizing machine learning and physics based modeling. Employing the combination of machine learning and physics based modeling to form hybrid digital twin frameworks, may synergistically alleviate the shortcomings of each method when used in isolation. Key challenges of implementing digital twin models in practice are additionally discussed. As digital twin technology experiences rapid growth and as it matures, its great promise to substantially enhance tools and solutions for intelligent upkeep of complex equipment, are expected to materialize.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge