Blair Rossetti
Clumped Nuclei Segmentation with Adjacent Point Match and Local Shape based Intensity Analysis for Overlapped Nuclei in Fluorescence In-Situ Hybridization Images
Aug 14, 2018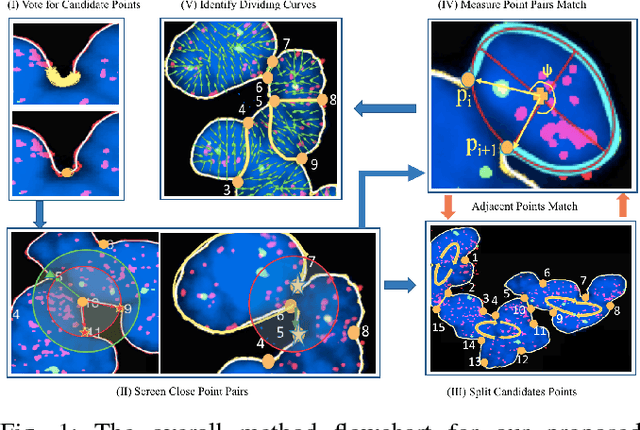
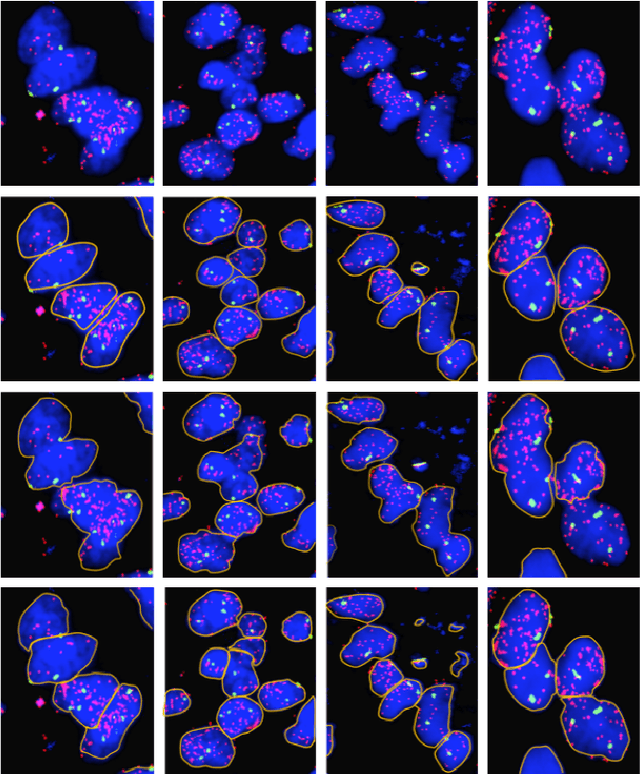
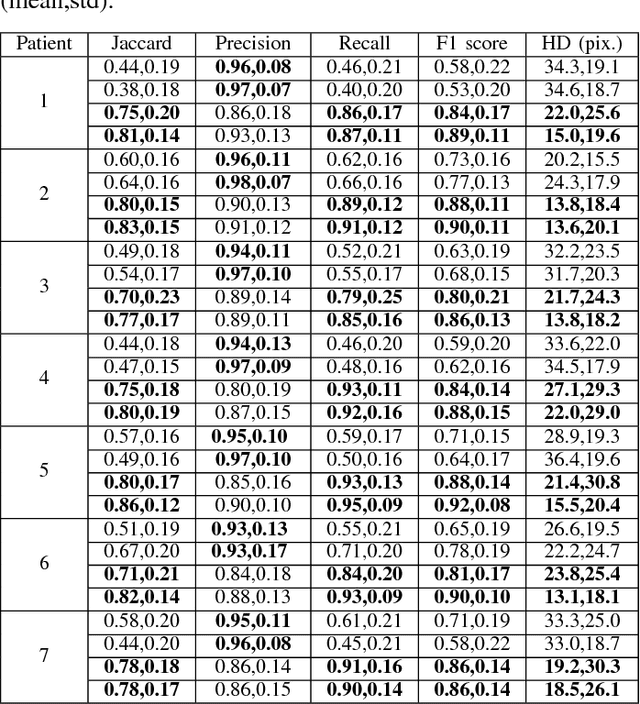
Abstract:Highly clumped nuclei clusters captured in fluorescence in situ hybridization microscopy images are common histology entities under investigations in a wide spectrum of tissue-related biomedical investigations. Due to their large scale in presence, computer based image analysis is used to facilitate such analysis with improved analysis efficiency and reproducibility. To ensure the quality of downstream biomedical analyses, it is essential to segment clustered nuclei with high quality. However, this presents a technical challenge commonly encountered in a large number of biomedical research, as nuclei are often overlapped due to a high cell density. In this paper, we propose an segmentation algorithm that identifies point pair connection candidates and evaluates adjacent point connections with a formulated ellipse fitting quality indicator. After connection relationships are determined, we recover the resulting dividing paths by following points with specific eigenvalues from Hessian in a constrained searching space. We validate our algorithm with 560 image patches from two classes of tumor regions of seven brain tumor patients. Both qualitative and quantitative experimental results suggest that our algorithm is promising for dividing overlapped nuclei in fluorescence in situ hybridization microscopy images widely used in various biomedical research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge