Bita Shams
GEMRank: Global Entity Embedding For Collaborative Filtering
Nov 05, 2018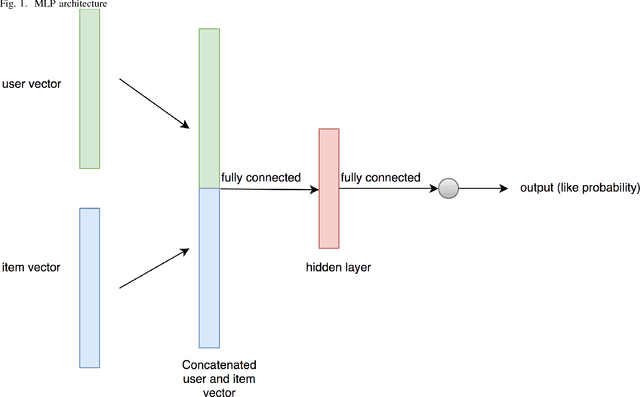
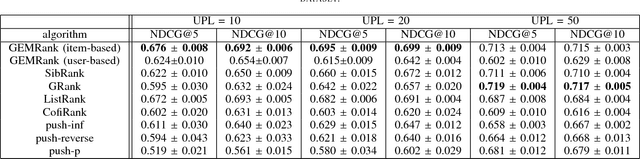
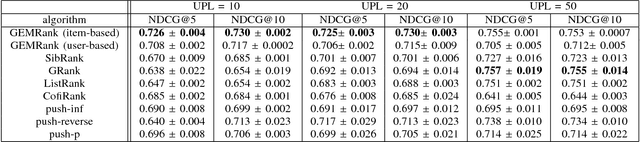
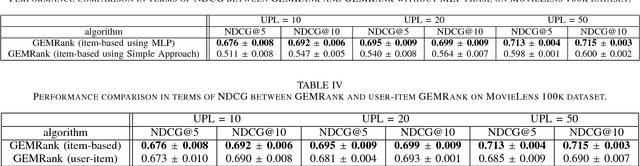
Abstract:Recently, word embedding algorithms have been applied to map the entities of recommender systems, such as users and items, to new feature spaces using textual element-context relations among them. Unlike many other domains, this approach has not achieved a desired performance in collaborative filtering problems, probably due to unavailability of appropriate textual data. In this paper we propose a new recommendation framework, called GEMRank that can be applied when the user-item matrix is the sole available souce of information. It uses the concept of profile co-occurrence for defining relations among entities and applies a factorization method for embedding the users and items. GEMRank then feeds the extracted representations to a neural network model to predict user-item like/dislike relations which the final recommendations are made based on. We evaluated GEMRank in an extensive set of experiments against state of the art recommendation methods. The results show that GEMRank significantly outperforms the baseline algorithms in a variety of data sets with different degrees of density.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge