Biswadip Mandal
HistoryBankQA: Multilingual Temporal Question Answering on Historical Events
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Temporal reasoning about historical events is a critical skill for NLP tasks like event extraction, historical entity linking, temporal question answering, timeline summarization, temporal event clustering and temporal natural language inference. Yet efforts on benchmarking temporal reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) are rather limited. Existing temporal reasoning datasets are limited in scale, lack multilingual coverage and focus more on contemporary events. To address these limitations, we present HistoryBank, a multilingual database of 10M+ historical events extracted from Wikipedia timeline pages and article infoboxes. Our database provides unprecedented coverage in both historical depth and linguistic breadth with 10 languages. Additionally, we construct a comprehensive question answering benchmark for temporal reasoning across all languages. This benchmark covers a diverse set of 6 temporal QA reasoning tasks, and we evaluate a suite of popular language models (LLaMA-3-8B, Mistral-7B, Gemma-2-9b, Qwen3-8B, GPT4o) to assess their performance on these tasks. As expected GPT4o performs best across all answer types and languages; Gemma-2 outperforms the other small language models. Our work aims to provide a comprehensive resource for advancing multilingual and temporally-aware natural language understanding of historical events. To facilitate further research, we will make our code and datasets publicly available upon acceptance of this paper.
Improving Citation Text Generation: Overcoming Limitations in Length Control
Jul 20, 2024Abstract:A key challenge in citation text generation is that the length of generated text often differs from the length of the target, lowering the quality of the generation. While prior works have investigated length-controlled generation, their effectiveness depends on knowing the appropriate generation length. In this work, we present an in-depth study of the limitations of predicting scientific citation text length and explore the use of heuristic estimates of desired length.
Contextualizing Generated Citation Texts
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:Abstractive citation text generation is usually framed as an infilling task, where a sequence-to-sequence model is trained to generate a citation given a reference paper and the context window around the target; the generated citation should be a brief discussion of the reference paper as it relates to the citing context. However, examining a recent LED-based citation generation system, we find that many of the generated citations are generic summaries of the reference papers main contribution, ignoring the citation contexts focus on a different topic. To address this problem, we propose a simple modification to the citation text generation task: the generation target is not only the citation itself, but the entire context window, including the target citation. This approach can be easily applied to any abstractive citation generation system, and our experimental results show that training in this way is preferred by human readers and allows the generation model to make use of contextual clues about what topic to discuss and what stance to take.
CORWA: A Citation-Oriented Related Work Annotation Dataset
May 07, 2022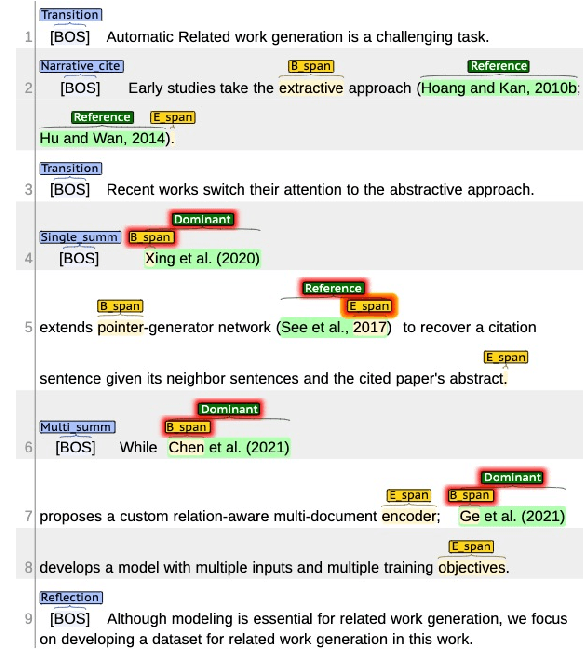
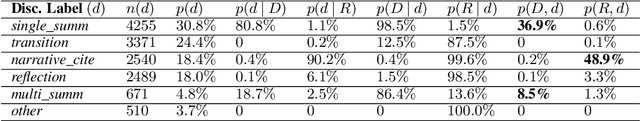
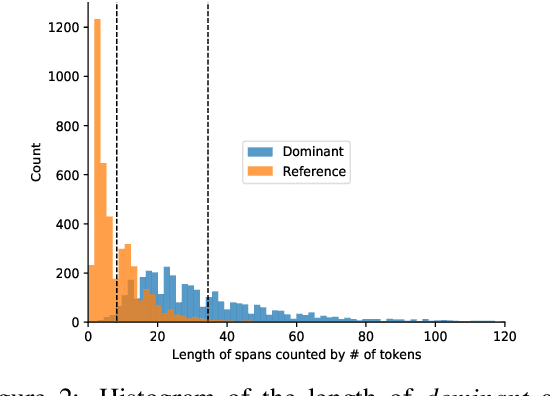
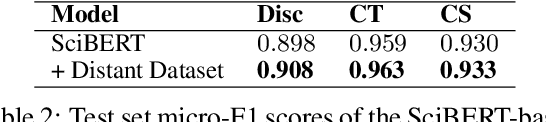
Abstract:Academic research is an exploratory activity to discover new solutions to problems. By this nature, academic research works perform literature reviews to distinguish their novelties from prior work. In natural language processing, this literature review is usually conducted under the "Related Work" section. The task of related work generation aims to automatically generate the related work section given the rest of the research paper and a list of papers to cite. Prior work on this task has focused on the sentence as the basic unit of generation, neglecting the fact that related work sections consist of variable length text fragments derived from different information sources. As a first step toward a linguistically-motivated related work generation framework, we present a Citation Oriented Related Work Annotation (CORWA) dataset that labels different types of citation text fragments from different information sources. We train a strong baseline model that automatically tags the CORWA labels on massive unlabeled related work section texts. We further suggest a novel framework for human-in-the-loop, iterative, abstractive related work generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge