Bipasha Banerjee
When LLMs Disagree: Diagnosing Relevance Filtering Bias and Retrieval Divergence in SDG Search
Jul 02, 2025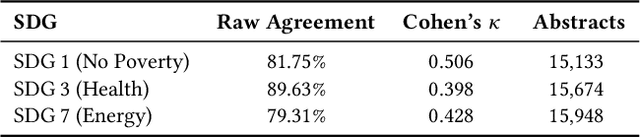
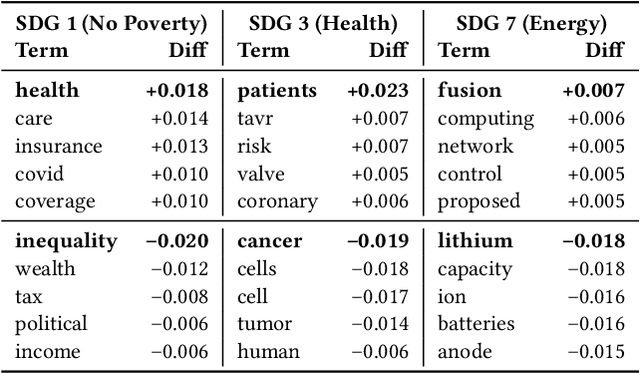
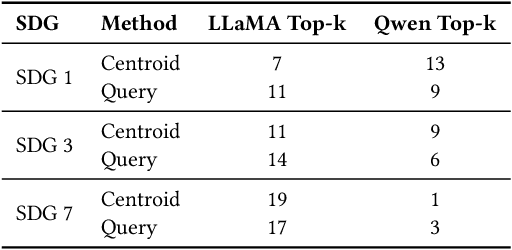
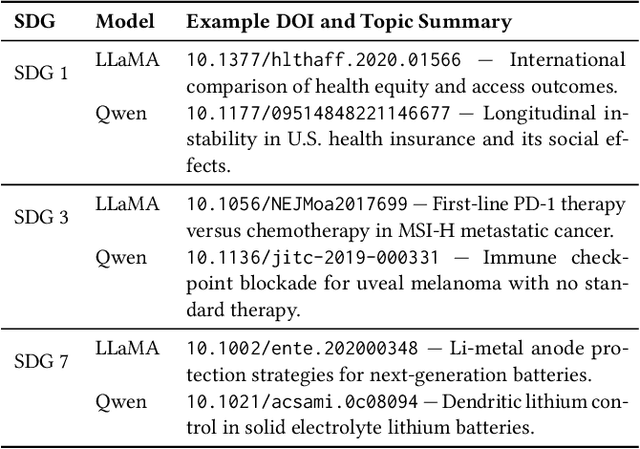
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used to assign document relevance labels in information retrieval pipelines, especially in domains lacking human-labeled data. However, different models often disagree on borderline cases, raising concerns about how such disagreement affects downstream retrieval. This study examines labeling disagreement between two open-weight LLMs, LLaMA and Qwen, on a corpus of scholarly abstracts related to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 1, 3, and 7. We isolate disagreement subsets and examine their lexical properties, rank-order behavior, and classification predictability. Our results show that model disagreement is systematic, not random: disagreement cases exhibit consistent lexical patterns, produce divergent top-ranked outputs under shared scoring functions, and are distinguishable with AUCs above 0.74 using simple classifiers. These findings suggest that LLM-based filtering introduces structured variability in document retrieval, even under controlled prompting and shared ranking logic. We propose using classification disagreement as an object of analysis in retrieval evaluation, particularly in policy-relevant or thematic search tasks.
Making History Readable
Nov 26, 2024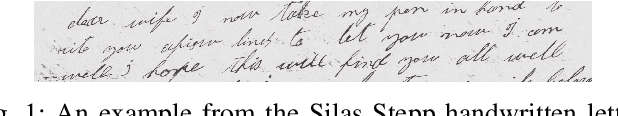

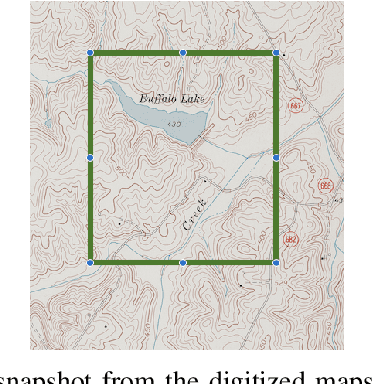
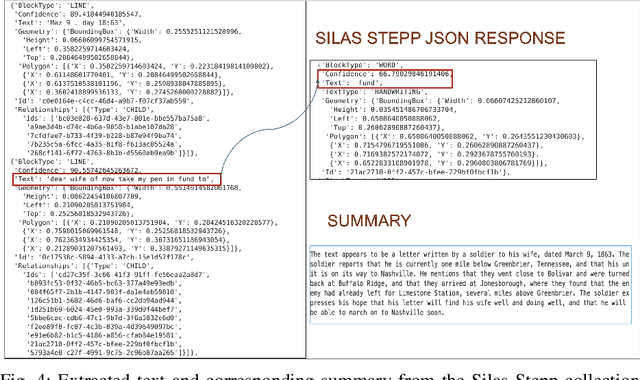
Abstract:The Virginia Tech University Libraries (VTUL) Digital Library Platform (DLP) hosts digital collections that offer our users access to a wide variety of documents of historical and cultural importance. These collections are not only of academic importance but also provide our users with a glance at local historical events. Our DLP contains collections comprising digital objects featuring complex layouts, faded imagery, and hard-to-read handwritten text, which makes providing online access to these materials challenging. To address these issues, we integrate AI into our DLP workflow and convert the text in the digital objects into a machine-readable format. To enhance the user experience with our historical collections, we use custom AI agents for handwriting recognition, text extraction, and large language models (LLMs) for summarization. This poster highlights three collections focusing on handwritten letters, newspapers, and digitized topographic maps. We discuss the challenges with each collection and detail our approaches to address them. Our proposed methods aim to enhance the user experience by making the contents in these collections easier to search and navigate.
Automating Chapter-Level Classification for Electronic Theses and Dissertations
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Traditional archival practices for describing electronic theses and dissertations (ETDs) rely on broad, high-level metadata schemes that fail to capture the depth, complexity, and interdisciplinary nature of these long scholarly works. The lack of detailed, chapter-level content descriptions impedes researchers' ability to locate specific sections or themes, thereby reducing discoverability and overall accessibility. By providing chapter-level metadata information, we improve the effectiveness of ETDs as research resources. This makes it easier for scholars to navigate them efficiently and extract valuable insights. The absence of such metadata further obstructs interdisciplinary research by obscuring connections across fields, hindering new academic discoveries and collaboration. In this paper, we propose a machine learning and AI-driven solution to automatically categorize ETD chapters. This solution is intended to improve discoverability and promote understanding of chapters. Our approach enriches traditional archival practices by providing context-rich descriptions that facilitate targeted navigation and improved access. We aim to support interdisciplinary research and make ETDs more accessible. By providing chapter-level classification labels and using them to index in our developed prototype system, we make content in ETD chapters more discoverable and usable for a diverse range of scholarly needs. Implementing this AI-enhanced approach allows archives to serve researchers better, enabling efficient access to relevant information and supporting deeper engagement with ETDs. This will increase the impact of ETDs as research tools, foster interdisciplinary exploration, and reinforce the role of archives in scholarly communication within the data-intensive academic landscape.
Agentic AI for Improving Precision in Identifying Contributions to Sustainable Development Goals
Nov 26, 2024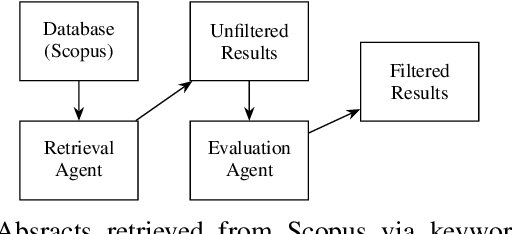
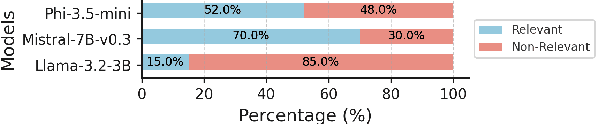
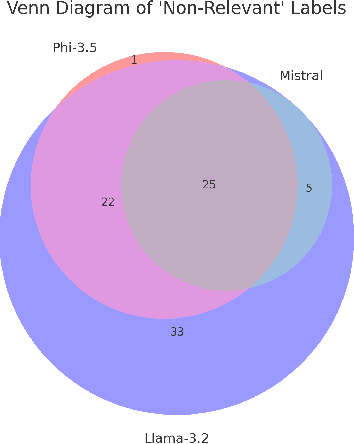
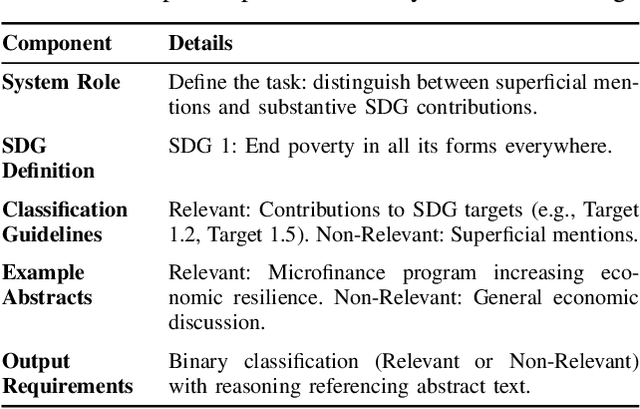
Abstract:As research institutions increasingly commit to supporting the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), there is a pressing need to accurately assess their research output against these goals. Current approaches, primarily reliant on keyword-based Boolean search queries, conflate incidental keyword matches with genuine contributions, reducing retrieval precision and complicating benchmarking efforts. This study investigates the application of autoregressive Large Language Models (LLMs) as evaluation agents to identify relevant scholarly contributions to SDG targets in scholarly publications. Using a dataset of academic abstracts retrieved via SDG-specific keyword queries, we demonstrate that small, locally-hosted LLMs can differentiate semantically relevant contributions to SDG targets from documents retrieved due to incidental keyword matches, addressing the limitations of traditional methods. By leveraging the contextual understanding of LLMs, this approach provides a scalable framework for improving SDG-related research metrics and informing institutional reporting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge